Abstract
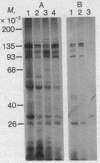
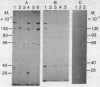
Proteins that are located adjacent to the 5' end of mRNA in initiation complexes have been detected by chemical crosslinking. Reovirus mRNA containing radioactivity exclusively in the [3H]methyl-labeled "cap," m7G(5')ppp(5')-Gm, was oxidized with sodium periodate to convert the 2',3'-cis-diol of the 5'-terminal m7G to a reactive dialdehyde. Oxidized mRNA was incubated in cell-free protein-synthesizing systems derived from wheat germ or mammalian cells, and the resulting mRNA-ribosome initiation complexes were reduced with NaBH3CN. By this chemical procedure, putative Schiff bases between mRNA 5'termini and amino groups of neighboring proteins were stabilized by reduction, yielding covalently linked protein-RNA conjugates. Under conditions of ribosome binding, a limited number of polypeptides associated with the mRNA-ribosome complexes were crosslinked, suggesting that these proteins are positioned near and may interact with the 5' end of mRNA during initiation. This method should also be useful for studying the spatial relationships between molecules in other similar nucleoprotein complexes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benne R., Hershey J. W. Purification and characterization of initiation factor IF-E3 from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Methylation-dependent translation of viral messenger RNAs in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1189–1193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Furuichi Y., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Effect of 5'-terminal structure and base composition on polyribonucleotide binding to ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):637–658. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90126-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Furuichi Y., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J. Ribosome binding to reovirus mRNA in protein synthesis requires 5' terminal 7-methylguanosine. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani D., Revel M., Groner Y. Translational discrimination of 'capped' and 'non-capped' mRNAS: inhibition of a series of chemical analogs of m7GpppX. FEBS Lett. 1976 May 1;64(2):326–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Elson N. A., Anderson W. F. Initiation of globin synthesis: assays. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:101–127. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Kurland C. G., Stöffler G. 30S ribosomal proteins associated with the 3'-terminus of 16S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):281–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggen K. L., Shatkin A. J. In vitro translation of cardiovirus ribonucleic acid by mammalian cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):636–645. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.636-645.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipowicz W., Furuichi Y., Sierra J. M., Muthukrishnan S., Shatkin A. J., Ochoa S. A protein binding the methylated 5'-terminal sequence, m7GpppN, of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1559–1563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal structure and mRNA stability. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):235–239. doi: 10.1038/266235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. 5'-termini of reovirus mRNA: ability of viral cores to form caps post-transcriptionally. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):566–578. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. Differential synthesis of blocked and unblocked 5'-termini in reovirus mRNA: effect of pyrophosphate and pyrophosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey E. D., Weber L. A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis by 7-methylguanosine-5'-monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):19–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. A., Traugh J. A., Croser E. A., Traut R. R. Ribosomal proteins from rabbit reticulocytes: number and molecular weights of proteins from ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 15;93(3):391–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenner R. A. A protein-nucleic acid crosslink in 30S ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):932–938. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Characterization of ribosome-protected fragments from reovirus messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4259–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Favre M. Maturation of the head of bacteriophage T4. I. DNA packaging events. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 15;80(4):575–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Brayley A., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. The effect of cyclic AMP and related compounds on the control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. Tobacco mosaic virus ribonucleic acid-dependent amino acid incorporation in a wheat embryo system in vitro. Analysis of the rate-limiting reaction. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):955–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Both G. W., Furuichi Y., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal 7-methylguanosine in eukaryotic mRNA is required for translation. Nature. 1975 May 1;255(5503):33–37. doi: 10.1038/255033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthukrishnan S., Morgan M., Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Influence of 5'-terminal m7G and 2'--O-methylated residues on messenger ribonucleic acid binding to ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5761–5768. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman R., Brooker J. D., Seal S. N., Marcus A. Inhibition of the transition of a 40 S ribosome-Met-tRNA-i-Met complex to an 80 S ribosome-Met-tRNA-i-Met- complex by 7-Methylguanosine-5'-phosphate. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):359–360. doi: 10.1038/260359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Lodish H. F. Translation in vitro of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA lacking 5'-terminal 7-methylguanosine. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):32–37. doi: 10.1038/262032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Adams S. L., Kemper W. M., Berry K. W., Lloyd M., Merrick W. C. Purification and characterization of two initiation factors required for maximal activity of a highly fractionated globin mRNA translation system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2584–2588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Weinstein J. A., Safer B., Merrick W. C., Weber L. A., Hickey E. D., Baglioni C. Evidence for role of m7G5'-phosphate group in recognition of eukaryotic mRNA by initiation factor IF-M3. Nature. 1976 May 27;261(5558):291–294. doi: 10.1038/261291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundkvist I. C., Staehelin T. Structure and function of free 40 S ribosome subunits: Characterization of initiation factors. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):401–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Duin J., Kurland C. G., Dondon J., Grunberg-Mangago M., Branlant C., Ebel J. P. New aspects of the IF3-ribosome interaction. FEBS Lett. 1976 Feb 15;62(2):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zan-Kowalczewska M., Bretner M., Sierakowska H., Szczesna E., Filipowicz W., Shatkin A. J. Removal of 5'-terminal m7G from eukaryotic mRNAs by potato nucleotide pyrophosphatase and its effect on translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3065–3081. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]