Abstract
Certain strains of Lactobacillus casei can grow at the expense of one or more pentitols. These microorganisms possess a pentitol phosphate pathway that appears to be analogous to the hexitol phosphate pathway found in many facultatively anaerobic bacteria. Pentitol is transported into the cell by a phospho enolpyruvate phosphotransferase system that converts it to pentitol phosphate, whereupon a specific dehydrogenase oxidizes the intermediate product to ketopentose phosphate. The ketopentose phosphate is subsequently converted to xylulose-5-P and enters one of the pathways of central metabolism.
Keywords: pentitol phosphate, lactobacilli
Full text
PDF
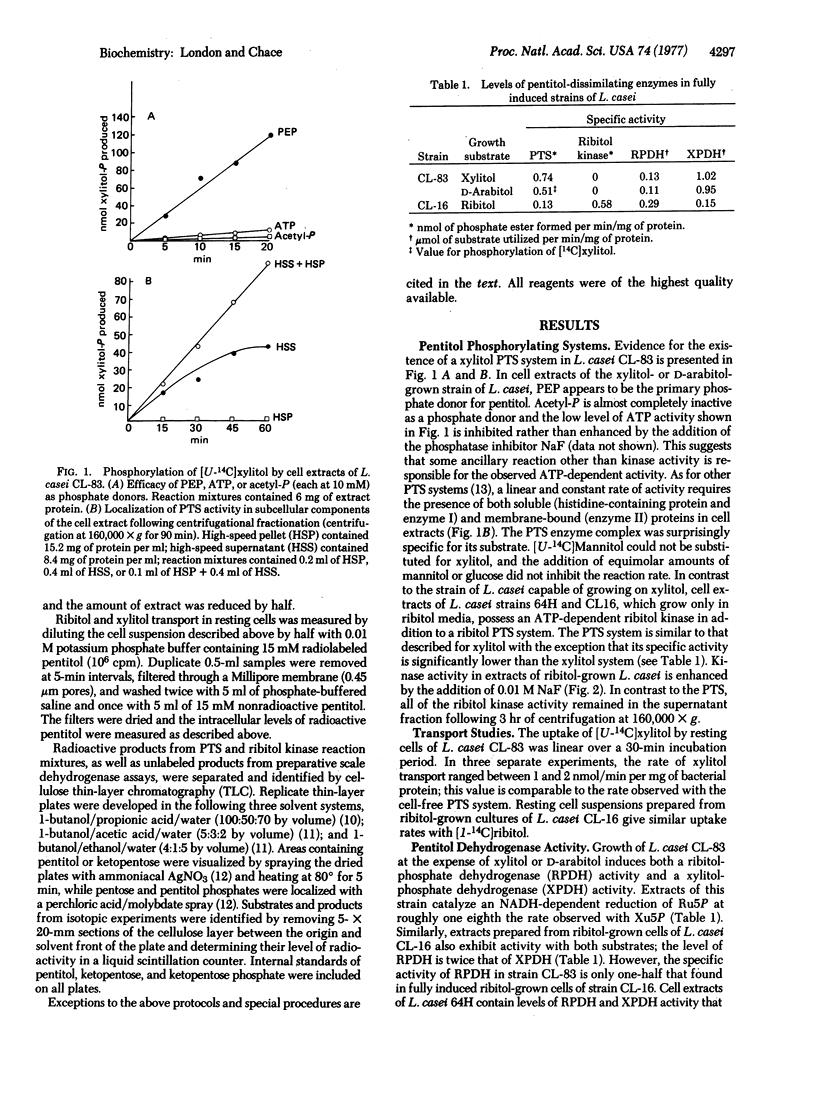
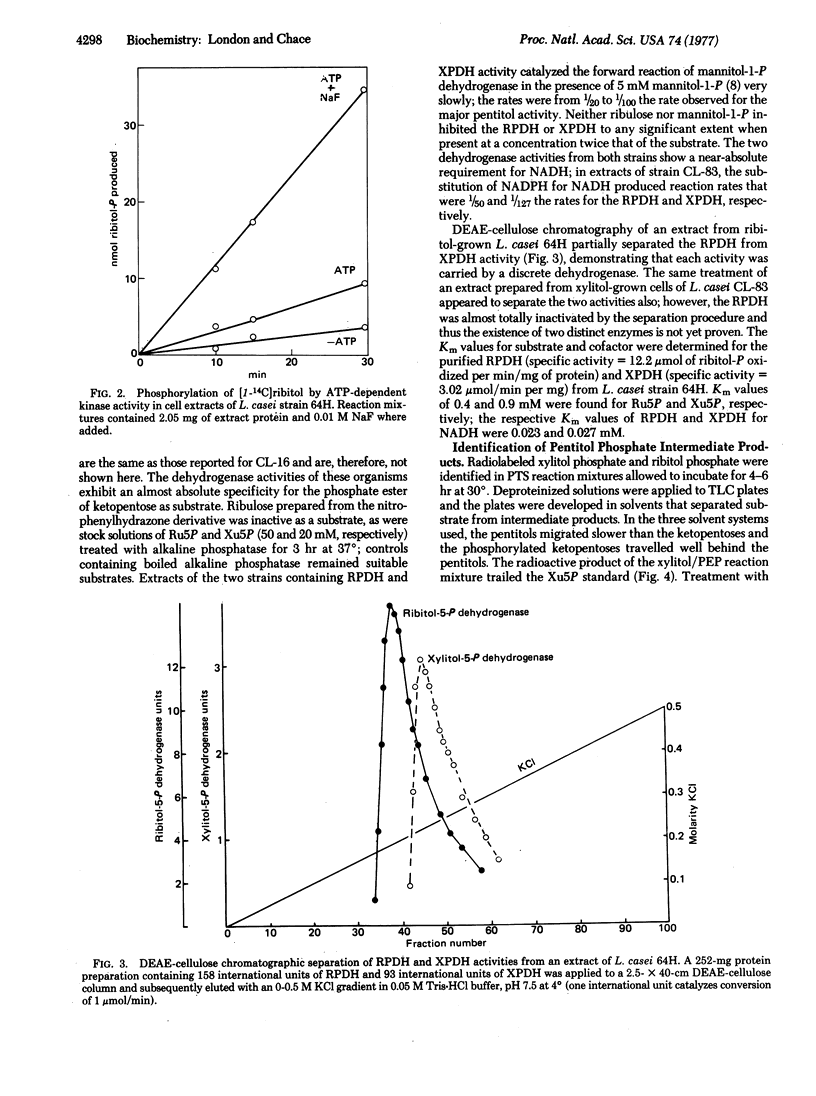
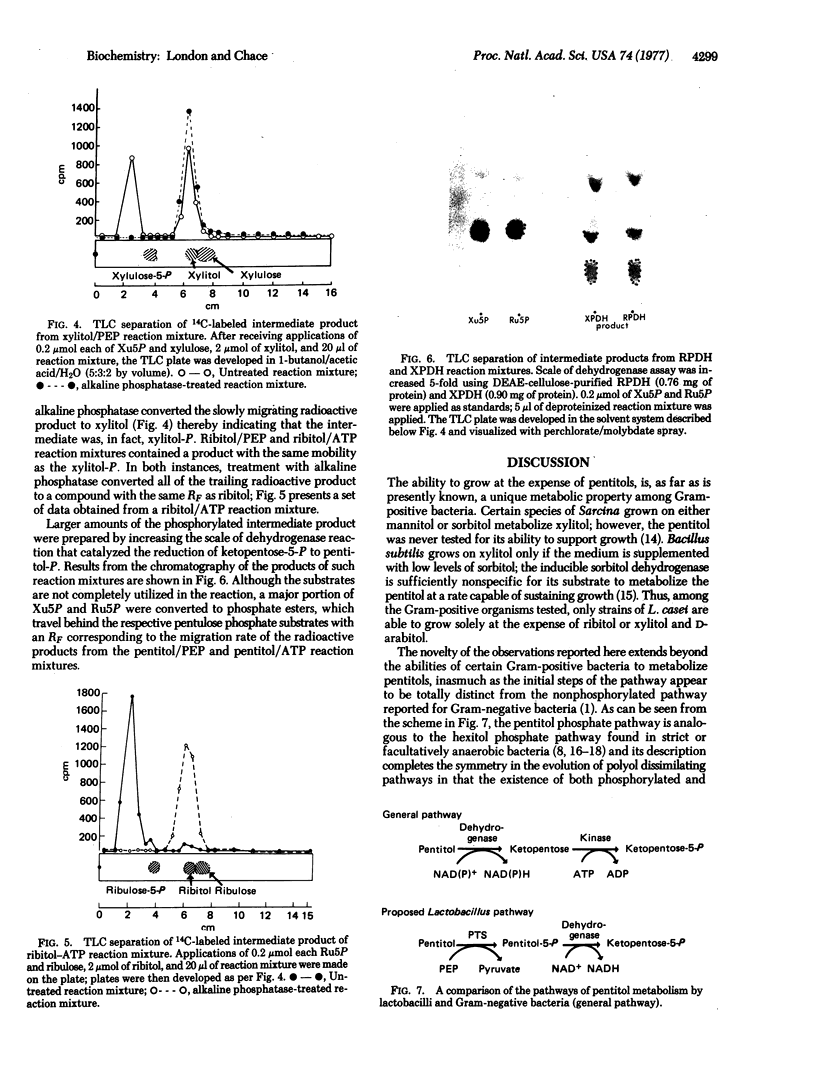

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews K. J., Lin E. C. Selective advantages of various bacterial carbohydrate transport mechanisms. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2185–2189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz D. D-Mannitol utilization in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):232–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.232-240.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORWITZ S. B., KAPLAN N. O. HEXITOL DEHYDROGENASES OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:830–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin E. C. The genetics of bacterial transport systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:225–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. I. DEMONSTRATION OF PENTOSE ISOMERASE, PENTULOKINASE, AND PENTITOL DEHYDROGENASE ENZYME FAMILIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.838-844.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryanski J. H., Wittenberger C. L. Mannitol transport in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1475–1481. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1475-1481.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patni N. J., Alexander J. K. Catabolism of fructose and mannitol in Clostridium thermocellum: presence of phosphoenolpyruvate: fructose phosphotransferase, fructose 1-phosphate kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate: mannitol phosphotransferase, and mannitol 1-phosphate dehydrogenase in cell extracts. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):226–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.226-231.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Lerner S. A., Lin E. C. Replacement of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase by a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-linked dehydrogenase for the utilization of mannitol. J Bacteriol. 1967 Feb;93(2):642–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.2.642-648.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka K., Sakai S. Production of polyol dehydrogenases in bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):391–396. doi: 10.1139/m68-062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]