Abstract
A new procedure is described for purification of rat liver albumin mRNA. First a population of RNA molecules is enriched for albumin mRNA by immunoprecipitation of polysomes containing albumin nascent chains. Polyadenylylated RNA is prepared from immunoprecipitates, transcribed into complementary DNA, and shown to be enriched severalfold for a particular RNA frequency component. This enriched RNA component is then purified by molecular hybridization to a limited R0t value (product of RNA concentration and incubation time), under conditions in which only the most abundant sequence component is annealed. Potentially, this procedure can be employed for the purification of a wide variety of mRNAs present in lesser amounts in the cell.
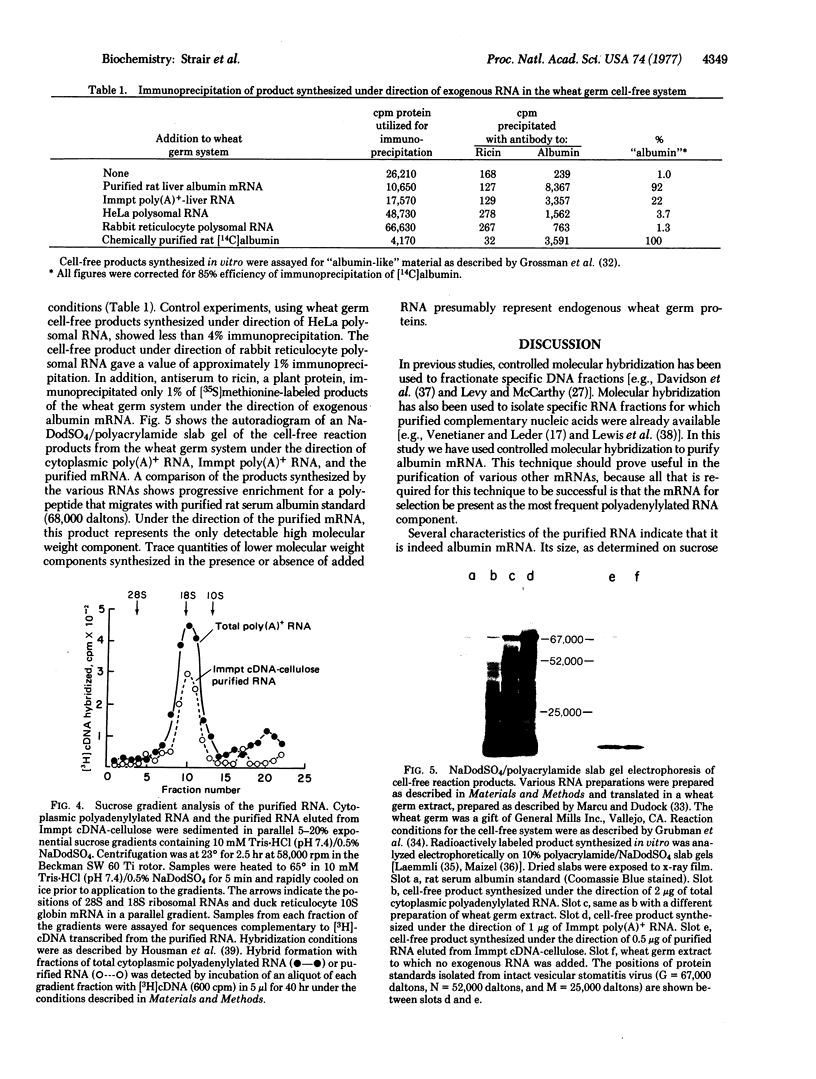
The isolated RNA appears to be a single frequency component by hybridization to complementary DNA transcribed from itself. This RNA is a 17S species and represents 5-8% of total cytoplasmic polyadenylylated RNA. In vitro translation of the purified RNA has shown that it codes for a single polypeptide that can be identified immunologically as albumin and migrates with rat serum albumin on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels. This albumin mRNA was determined to be essentially pure by comparing its kinetics of hybridization to those obtained with rabbit α + β globin mRNA and its DNA complement. The sequence complexity of purified rat albumin mRNA corresponds to 5.9 × 105 daltons.
Keywords: immunoprecipitation of polysomes, complementary DNA-cellulose, cell-free protein synthesis
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adesnik M., Salditt M., Thomas W., Darnell J. E. Evidence that all messenger RNA molecules (except histone messenger RNA) contain Poly (A) sequences and that the Poly(A) has a nuclear function. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 28;71(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axel R., Feigelson P., Schutz G. Analysis of the complexity and diversity of mRNA from chicken liver and oviduct. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Morton J. G., Rosbash M., Richardson M. Three abundance classes in HeLa cell messenger RNA. Nature. 1974 Jul 19;250(463):199–204. doi: 10.1038/250199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Hough B. R., Klein W. H., Britten R. J. Structural genes adjacent to interspersed repetitive DNA sequences. Cell. 1975 Mar;4(3):217–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delovitch T. L., Baglioni C. Estimation of light-chain gene reiteration of mouse immunoglobulin by DNA-RNA hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):173–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getz M. J., Birnie G. D., Young B. D., MacPhail E., Paul J. A kinetic estimation of base sequence complexity of nuclear poly(A)-containing RNA in mouse Friend cells. Cell. 1975 Feb;4(2):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Getz M. J., Elder P. K., Benz E. W., Jr, Stephens R. E., Moses H. L. Effect of cell proliferation on levels and diversity of poly(A)-containing mRNA. Cell. 1976 Feb;7(2):255–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R., Perry R. P. Relative occurrence of polyadenylic acid sequences in messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA of L cells as determined by poly (U)-hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 14;72(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. B., Yap S. H., Shafritz D. A. Influence of chronic renal failure on protein synthesis and albumin metabolism in rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):869–878. doi: 10.1172/JCI108709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Weinstein J. A., Shafritz D. A. Studies on the mechanism for entry of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein G mRNA into membrane-bound polyribosome complexes. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):43–57. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Levy S., Schedl P., Kedes L. Messenger RNAs for individual histone proteins: fingerprint analysis and in vitro translation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:717–724. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Packman S., Swan D., Nau M., Leder P. Organization of immunoglobulin genes: reiteration frequency of the mouse kappa chain constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3659–3663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housman D., Skoultchi A., Forget B. G., Benz E. J., Jr Use of globin cDNA as a hybridization probe for globin mRNA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Nov 29;241(0):280–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb21887.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Lorena M., Baglioni C., Borun T. W. Translation of messenger RNA for histones from HeLa cells by a cell-free extract from mouse ascites tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2095–2099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G. H., Taylor J. M. Effect of hypophysectomy on the synthesis of rat liver albumin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3768–3773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy B., McCarthy B. J. Relationship between nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA in Drosophilia cells. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2415–2419. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S., Aviv H. Quantitation of labeled globin messenger RNA by hybridization with excess complementary DNA covalently bound to cellulose. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):1844–1847. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Mapping of late adenovirus genes by cell-free translation of RNA selected by hybridization to specific DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1344–1348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Lingrel J. B. The synthesis of mouse hemoglobin beta-chains in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system programmed with mouse reticulocyte 9S RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 8;37(2):204–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90720-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milcarek C., Price R., Penman S. The metabolism of a poly(A) minus mRNA fraction in HeLa cells. Cell. 1974 Sep;3(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Dubroff L. M., Graham M. Properties of sea urchin embryo messenger RNA containing and lacking poly(A). Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Palmiter R. D., Schimke R. T. Identification and isolation of ovalbumin-synthesizing polysomes. I. Specific binding of 125 I-anti-ovalbumin to polysomes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2316–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Sullivan D., Summers N. M., Kiely M. L., Schimke R. T. Purification of ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid by specific immunoadsorption of ovalbumin-synthesizing polysomes and millipore partition of ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):540–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H., Milstein C. Mouse immunoglobulin genes: studies on the reiteration frequency of light-chain genes by hybridisation procedures. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Mar 3;52(1):125–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03980.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Use of antibodies for the isolation of biologically pure messenger ribonucleic acid from fully functional eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1875–1885. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Perry R. P. Characterization of the messenger RNA released from L cell polyribosomes as a result of temperature shock. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):577–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Schimke R. T. Immunochemical isolation and characterization of ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1759–1764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss A. W., Donohue A. M., Bennett C. D., Rodkey J. A., Alberts A. W. Rat liver preproalbumin: in vitro synthesis and partial amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1358–1362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Brown D. D. Isolation and identification of the messenger RNA for silk fibroin from Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):409–429. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Schimke R. T. Synthesis of rat liver albumin in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free protein-synthesizing system. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7661–7668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Tse T. P. Isolation of rat liver albumin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 10;251(23):7461–7467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Bernardini A., Weimann B. J., Steinberg C. Reiteration frequency of antibody genes. Studies with k-chain mRNA. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80901-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse T. P., Taylor J. M. Translation of albumin messenger RNA in a cell-free protein-synthesizing system derived from wheat germ. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1272–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venetianer P., Leder P. Enzymatic synthesis of solid phase-bound DNA sequences corresponding to specific mammalian genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3892–3895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Penman S. The messenger RNA sequences in growing and resting mouse fibroblasts. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo S. L., Rosen J. M., Liarakos C. D., Choi Y. C., Busch H., Means A. R., O'Malley Physical and chemical characterization of purified ovalbumin messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):7027–7039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]