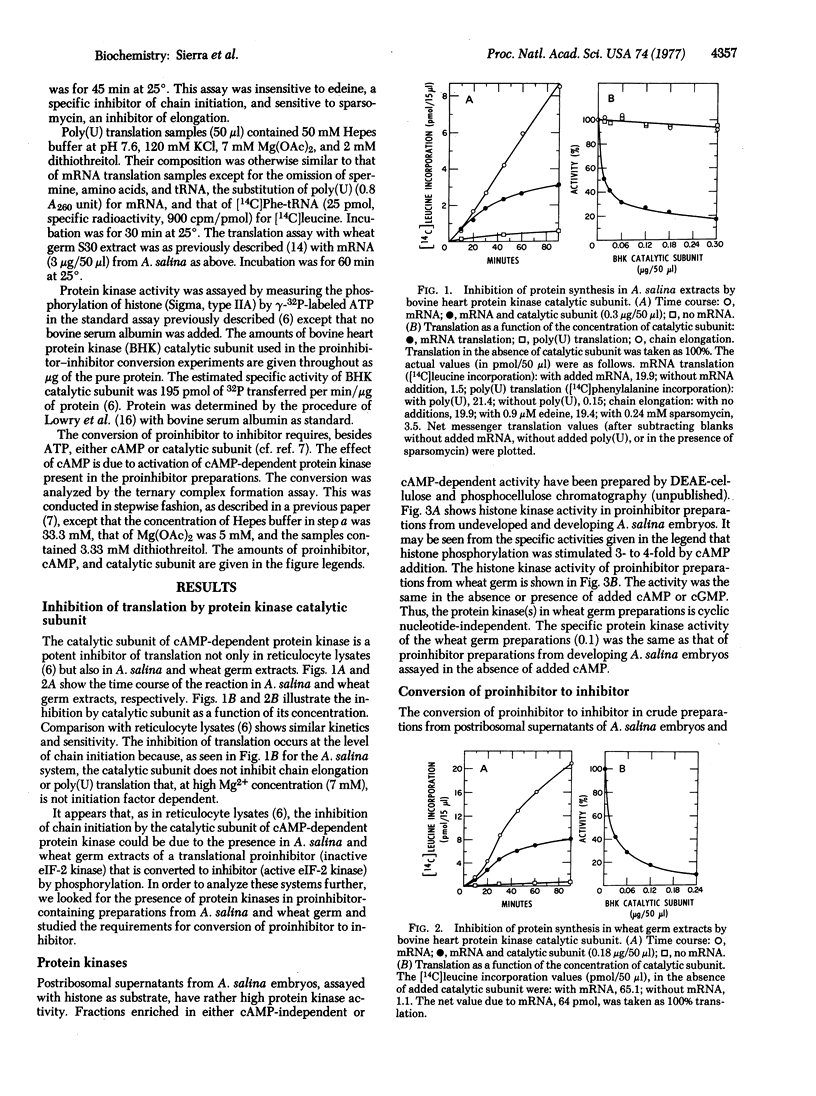
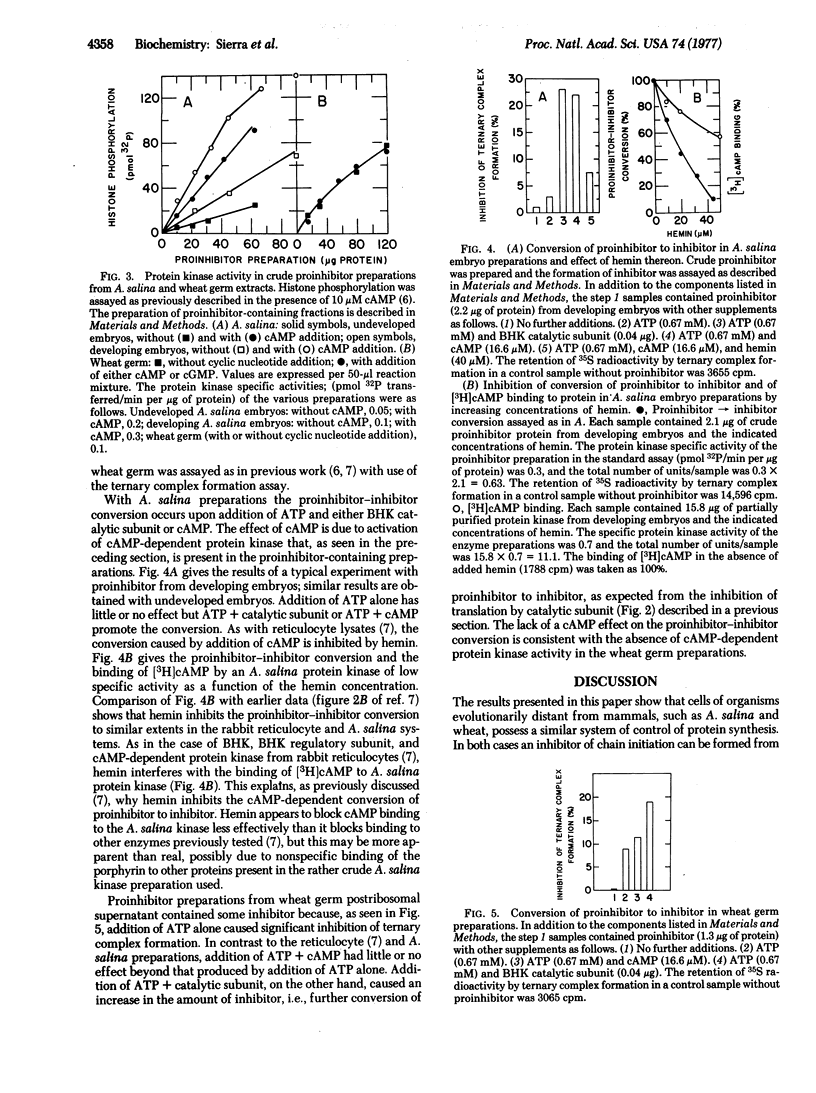
Abstract
The catalytic subunit of cyclic 3':5'-AMP-dependent protein kinase (ATP:protein phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.37) inhibits translation in Artemia salina and wheat germ extracts. It acts, as in reticulocyte lysates [Datta, A., de Haro, C., Sierra, J. M. & Ochoa, S. (1977) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 1463-1467] by catalyzing the conversion of a proinhibitor to an inhibitor of polypeptide chain initiation. Addition of ATP and either cyclic AMP or catalytic subunit promotes the proinhibitor-inhibitor conversion in crude proinhibitor preparations from A. salina embryos. The effect of cyclic AMP is due to stimulation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, present in such preparations, and is inhibited by hemin. In similar preparations from wheat germ, addition of ATP and catalytic subunit promoted proinhibitor-inhibitor conversion, but addition of ATP and cyclic AMP has little or no effect. As assayed with histone as substrate, wheat germ preparations exhibit a protein kinase activity that is not stimulated by the addition of cyclic AMP or cyclic GMP. Our results suggest that a translational control system, similar to that existing in rabbit reticulocytes and other mammalian cells, is present in organisms evolutionarily far removed from mammals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clemens M. J., Pain V. M., Henshaw E. C., London I. M. Characterization of a macromolecular inhibitor of polypeptide chain initiation from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):768–775. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A., de Haro C., Sierra J. M., Ochoa S. Mechanism of translational control by hemin in reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3326–3329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A., de Haro C., Sierra J. M., Ochoa S. Role of 3':5'-cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase in regulation of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1463–1467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaunay J., Ranu R. S., Levin D. H., Ernst V., London I. M. Characterization of a rat liver factor that inhibits initiation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2264–2268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Mendelewski J. Additional evidence that the hemin-controlled translational repressor from rabbit reticulocytes is a protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90340-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Rabinovitz M. Control of globin synthesis by hemin: factors influencing formation of an inhibitor of globin chain initiation in reticulocyte lysates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa T., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. Studies of the subunit structure of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):574–580. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer G., Cimadevilla J. M., Hardesty B. Specificity of the protein kinase activity associated with the hemin-controlled repressor of rabbit reticulocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3078–3082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., Ranu R. S., Ernst V., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates: phosphorylation of methionyl-tRNAf binding factor by protein kinase activity of translational inhibitor isolated from hemedeficient lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3112–3116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moens L., Kondo M. The structure of Artemia salina haemoglobins. A comparative characterisation of four naupliar and adult heamoglobins. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 16;67(2):397–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinphanichakarn P., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Partial purification and characterization of a translational inhibitor from Friend leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2106–2112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra J. M., Filipowicz W., Ochoa S. Messenger RNA in undeveloped and developing Artemia salina embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra J. M., Meier D., Ochoa S. Effect of development on the translation of messenger RNA in Artemia salina embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2693–2697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauch J. A., Mumby M., Traut R. R. Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins by substrate-specific protein kinases from rabbit reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):373–376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



