The gene name Nfkbiz−/− appears incorrectly in the figure legends. The correct gene name should be Nfkbid−/−.
The authors have provided the corrected figure legends below.
Fig 1. Characteristics of immune homeostasis in Nfkbid −/− mice.
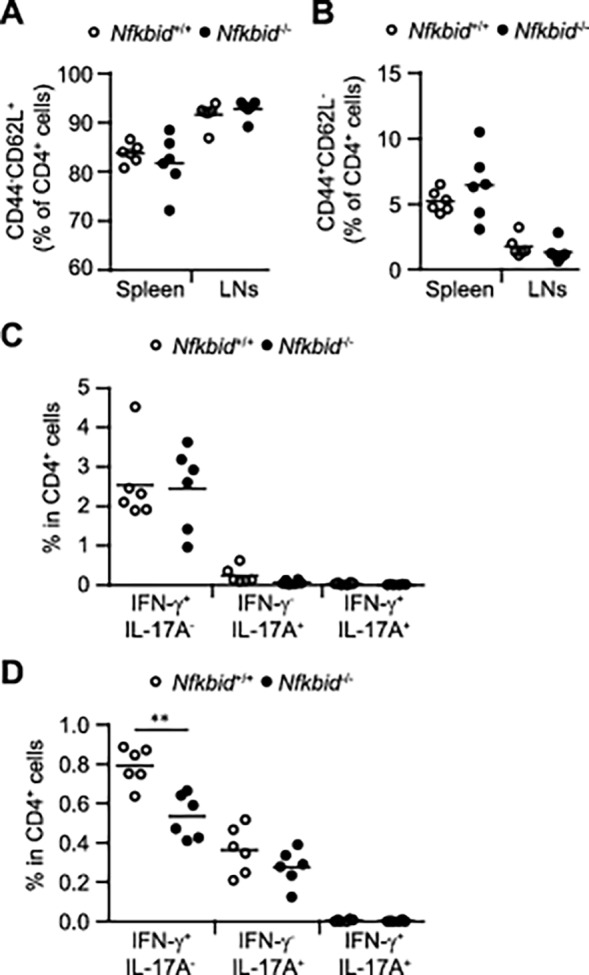
(A, B) Naive CD4+ cells in the spleen and lymph nodes (LNs) of 8–12 week old Nfkbid +/+ and Nfkbid −/− mice. (C, D) Flow cytometric analysis of IFN-γ- and IL-17-producing CD4+ cells isolated from the spleen (C) and LNs (D) of Nfkbid +/+ and Nfkbid −/− mice at 8–12 weeks of age. Paired data were evaluated using the Student’s t test. **p<0.01.
Fig 2. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model in Nfkbid −/− mice.
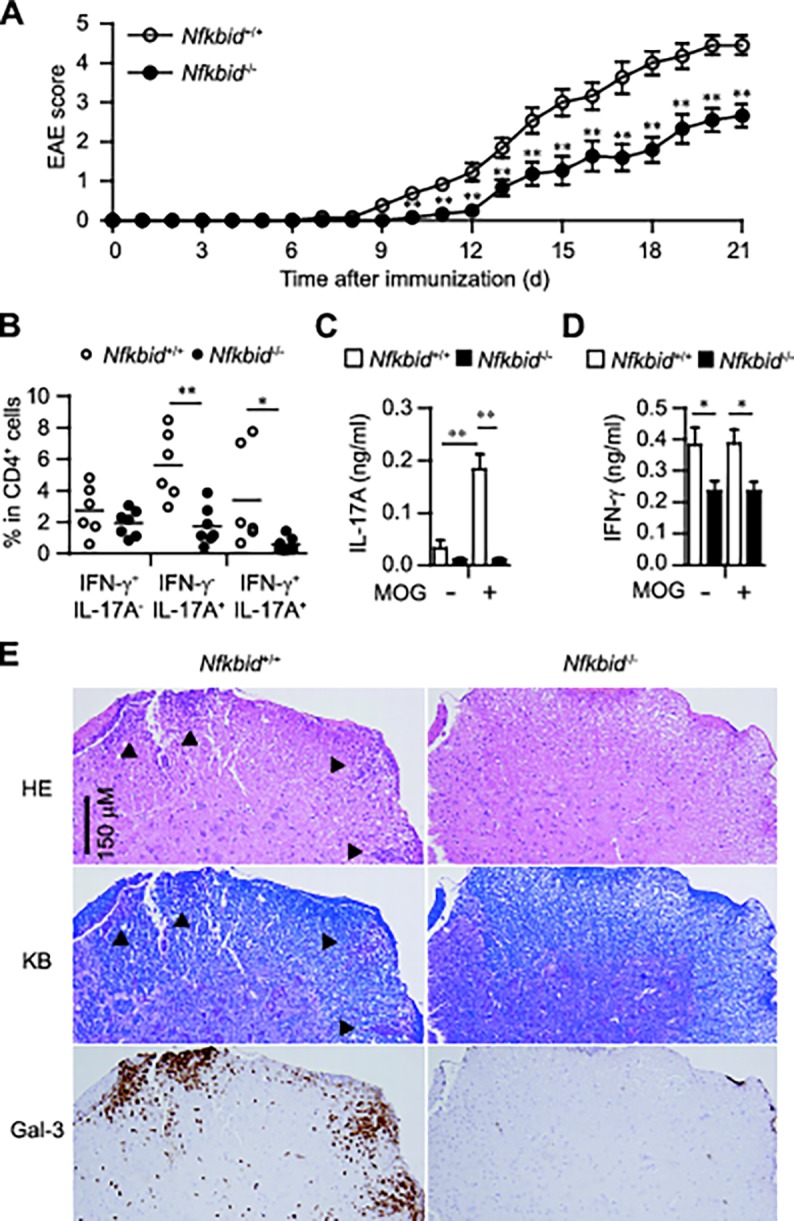
(A) Disease progression of EAE in Nfkbid +/+ (n = 11–13) and Nfkbid −/− mice (n = 9–11). (B-D) Analysis of mice 12 days after immunization. (B) Cytokine profile of CD4+ cells in draining LNs. (C, D) Measurement of IL-17A (C) and IFN-γ (D) supernatant concentrations by ELISAs (Nfkbid +/+: n = 5; Nfkbid −/−: n = 6), using cultured draining LNs incubated in the presence or absence of MOG peptide (10 ng/ml) for 72 h. Data shown represent mean ± S.E. Paired data were evaluated using the Student’s t test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. (E) Histology of spinal cord specimens in EAE models. Twelve days after MOG immunization, Nfkbid +/+ and Nfkbid −/− mice were sacrificed and their lumber section of spinal codes were collected. Three-micrometer-thick sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE), Klüver-Barrera staining (KB) or galectin-3 (Gal-3) immunohistochemistry. Serial sections were used for HE staining, KB staining and Gal-3 immunohistochemistry. Arrowheads in HE staining and KB staining indicate the demyelinated lesions. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments.
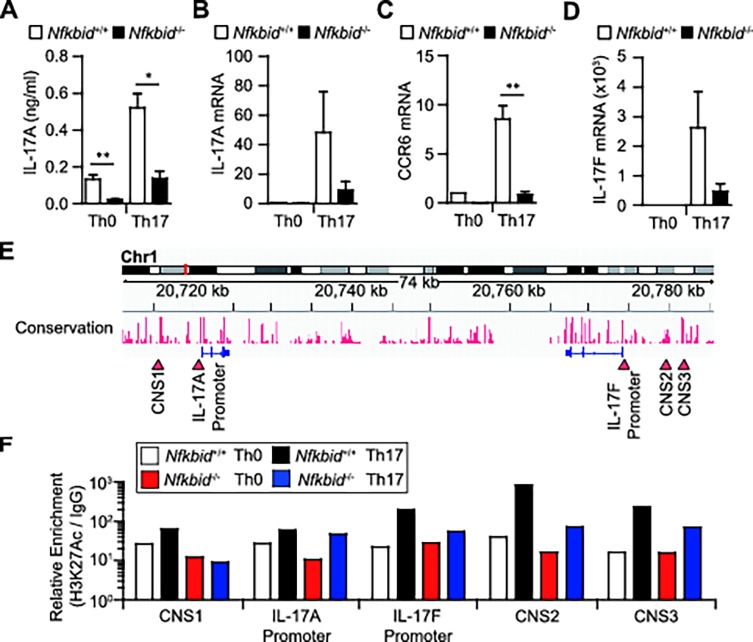
Fig 3. Nfkbid −/− mouse T cells fail to generate Th17 cells in vitro.
(A–D) Expression of IL-17A protein or Il-17a mRNA (A, B) and of the Th17-related mRNAs Ccr6 and Il-17f (C, D) in CD4+ T cells from Nfkbid +/+ and Nfkbid −/− mice, cultured for 48 h under Th0 or Th17 conditions. (E) Diagram of Il-17a and Il-17f gene conservation. Red-arrows indicate the Il-17a promoter, the Il-17f promoter, and the CNS 1, CNS 2, and CNS 3 regions. (F) ChIP analysis of H3K27Ac. Cells were cultured under Th0 or Th17 conditions for 48 h. Data shown are from one experiment that was representative at three independent experiments. (A-D) Data shown represent mean ± S.E. (n = 3). Paired data were evaluated using the Student’s t test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01.
Fig 5. Nfkbid −/− T cells show decreased RORγt expression.
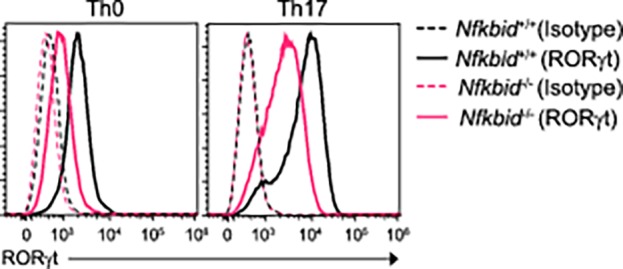
RORγt expression in CD4+ T cells from Nfkbiz +/+ and Nfkbid −/− mice, cultured for 72 h under Th0 or Th17 conditions. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
Supporting Information
Collected draining LNs from the Nfkbid +/+ and Nfkbid −/− mice at day 12 after MOG immunizations. LN cells were re-stimulated by MOG (10 ng/ml) after 3 days in culture, and CD4+ T cells were isolated using the CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi Biotec). Nfkbid +/+ mice (n = 3–4/group) were intravenously injected (5 × 105 CD4+ T cells/mouse) and EAE symptoms were scored for up to 12 days. In addition, these mice received 500 ng pertussis toxin (Sigma) by i.p. injection to boost their immunological responses on Days 0 and 2. Data shown represent mean + S.E. Paired data were evaluated using the Student’s t test. *p <0.05.
(TIF)
Reference
- 1. Kobayashi S, Hara A, Isagawa T, Manabe I, Takeda K, et al. (2014) The Nuclear IκB Family Protein IκBNS Influences the Susceptibility to Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in a Murine Model. PLoS ONE 9(10): e110838 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0110838 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Collected draining LNs from the Nfkbid +/+ and Nfkbid −/− mice at day 12 after MOG immunizations. LN cells were re-stimulated by MOG (10 ng/ml) after 3 days in culture, and CD4+ T cells were isolated using the CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T cell Isolation Kit (Miltenyi Biotec). Nfkbid +/+ mice (n = 3–4/group) were intravenously injected (5 × 105 CD4+ T cells/mouse) and EAE symptoms were scored for up to 12 days. In addition, these mice received 500 ng pertussis toxin (Sigma) by i.p. injection to boost their immunological responses on Days 0 and 2. Data shown represent mean + S.E. Paired data were evaluated using the Student’s t test. *p <0.05.
(TIF)