Abstract
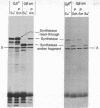
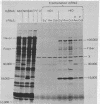
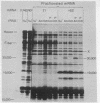
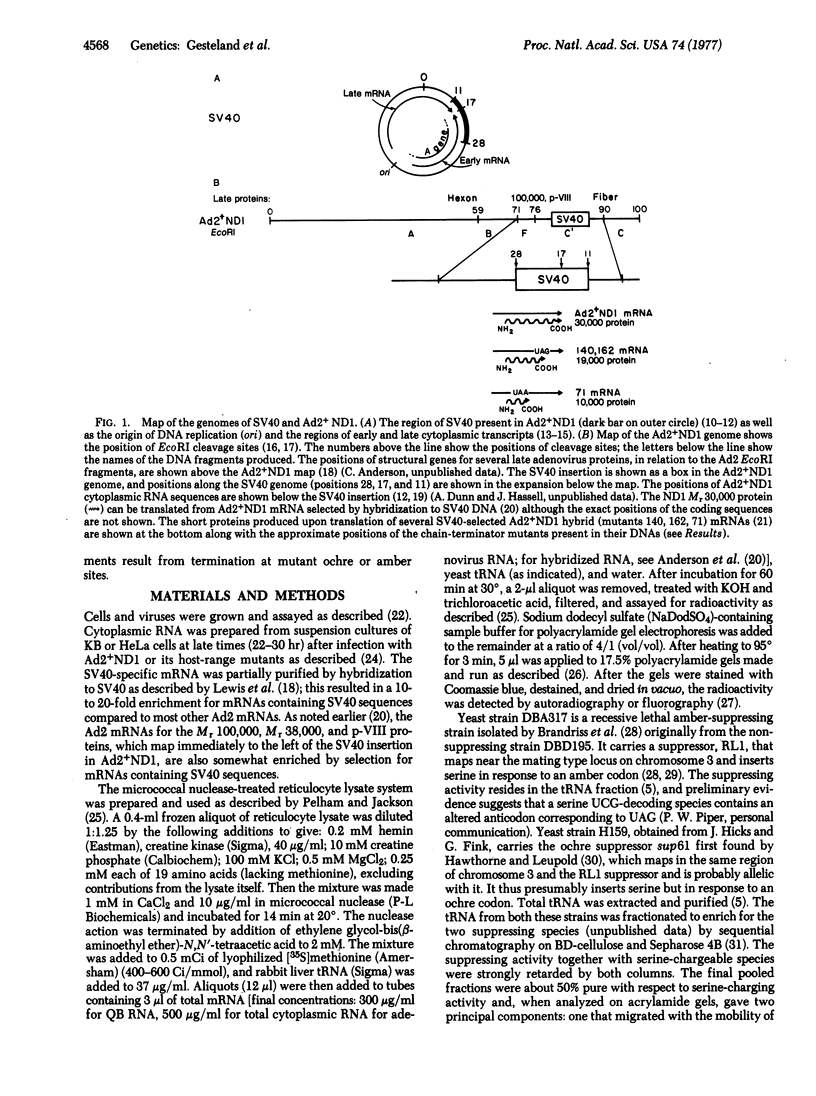
Although human adenoviruses grow poorly in monkey cells, this defect can be overcome either by coinfection of cells with simian virus 40 (SV40) or by insertion of the relevant portion of the SV40 genome into the adenovirus genome to form an adenovirus-SV40 hybrid virus. The nondefective adenovirus-2-SV40 hybrid virus, Ad2+ND1, contains an insertion of 17% of the SV40 genome, which codes for at least part of a 30,000 dalton protein. A set of Ad2+ND1 host-range mutants that have lost the ability to grow in monkey cells and behave as point mutants fail to synthesize the 30,000 dalton ND1 protein. Translation in vitro of SV40-specific mRNA from mutant-infected cells produces unique short polypeptides instead of the 30,000 dalton protein. Here we show that this set of host-range mutants includes both ochre and amber nonsense mutations. When the SV40-specific mRNA from the host-range mutants is translated in vitro to produce the polypeptide fragments, yeast suppressor tRNA can partially restore synthesis of wild-type-size 30,000 dalton protein. By this assay, one mutant is ochre and two are amber.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Cell-free synthesis of adenovirus 2 proteins programmed by fractionated messenger RNA: a comparison of polypeptide products and messenger RNA lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2756–2760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Lewis J. B., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Simian virus 40-specific polypeptides in AD2+ ND1- and Ad2+ ND4-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):685–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.685-692.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins J. F., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W., Gesteland R. F. Enhanced differential synthesis of proteins in a mammalian cell-free system by addition of polyamines. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5688–5695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Boime I., Loyd B., Leder P. Translation of bacteriophage Q messenger RNA in a murine Krebs 2 ascites tumor cell-free system. Science. 1972 Dec 22;178(4067):1293–1295. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4067.1293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Soll L., Botstein D. Recessive lethal amber suppressors in yeast. Genetics. 1975 Apr;79(4):551–560. doi: 10.1093/genetics/79.4.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Stewart J. W., Sherman F., Botstein D. Substitution of serine caused by a recessive lethal suppressor in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):467–476. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R., Hughes S. H., Wahl G. M. Yeast super-suppressors are altered tRNAs capable of translating a nonsense codon in vitro. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Contopolou-Griva I., Caroutsos K., Poungouras P., Tsevrenis H. Haemoglobin Icaria, a new chain-termination mutant with causes alpha thalassaemia. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):245–247. doi: 10.1038/251245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar R., Weissman S. M., Zain B. S., Pan J., Lewis A. M., Jr The nucleotide sequence preceding an RNA polymerase initiation site on SV40 DNA. Part 2. The sequence of the early strand transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Apr;1(4):595–611. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.4.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Wewerka-Lutz Y., Levine A. S., Sambrook J., Sharp P. A. Adenovirus transcription. II. RNA sequences complementary to simian virus 40 and adenovirus 2DNA in AD2+ND1- and AD2+ND3-infected cells. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):662–673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.662-673.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget B. G., Marotta C. A., Weissman S. M., Cohen-Solal M. Nucleotide sequences of the 3'-terminal untranslated region of messenger RNA for human beta globin chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3614–3618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F., Wolfner M., Grisafi P., Fink G., Botstein D., Roth J. R. Yeast suppressors of UAA and UAG nonsense codons work efficiently in vitro via tRNA. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorini L. Informational suppression. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:107–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Anderson C., Sharp P. A., Sambrook J. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. I. Host range mutants of Ad2+ND1. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1237–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1237-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. II. Ad2+ND1 host-range mutants that synthesize fragments of the Ad2+ND1 30K protein. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):559–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.559-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Davoli D., Thomas C. A., Jr, Fareed G. C. Simian virus 40 carrying an Escherichia coli suppressor gene. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 15;112(2):155–182. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P. H., Schnipper L. E., Samaha R. J., Crumpacker C. S., Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S. Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. VI. Characterization of the DNA from five nondefective hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):665–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.665-671.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes W. M., Hurd R. E., Reid B. R., Rimerman R. A., Hatfield G. W. Separation of transfer ribonucleic acid by sepharose chromatography using reverse salt gradients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1068–1071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr Use of nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrids for mapping the simian virus 40 genome. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):643–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.643-652.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Howley P., Nathans D., Martin M. Posttranscriptional selection of simian virus 40-specific RNA. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):433–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.433-437.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Lewis A. M., Jr, Oxman M. N., Levine A. S. Strand orientation of SV40 transcription in cells infected by non-defective adenovirus 2-SV40 hybrid viruses. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 19;246(155):202–205. doi: 10.1038/newbio246202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Levine A. S., Crumpacker C. S., Levin M. J., Samaha R. J., Henry P. H. Studies of nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. V. Isolation of additional hybrids which differ in their simian virus 40-specific biological properties. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):655–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.655-664.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Mapping of late adenovirus genes by cell-free translation of RNA selected by hybridization to specific DNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1344–1348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman S. W., Stewart J. W., Sherman F. Serine substitutions caused by an ochre suppressor in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 5;94(4):595–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Revilla R., Walter G. Polypeptide specific for cells with adenovirus 2-SV40 hybrid Ad2+ND1. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 8;244(136):165–167. doi: 10.1038/newbio244165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Maizel J. V., Salzman N. P. Mapping of transcription sites of simian virus 40-specific late 16S and 19S mRNA by electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):496–500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Lodish H. F. Translation of bacteriophage Q RNA by cytoplasmic extracts of mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):315–319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. F., Berg P., Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr Mapping of simian virus 40 early functions on the viral chromosome. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):653–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.653-658.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder C., Arrand J. R., Delius H., Keller W., Pettersson U., Roberts R. J., Sharp P. A. Cleavage maps of DNA from adenovirus types 2 and 5 by restriction endonucleases EcoRI and HpaI. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):397–400. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Complete 3' noncoding region sequences of rabbit and human beta-globin messenger RNAs. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):559–570. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Longley J. I. The 3' terminal sequences of human alpha and beta globin messenger RNAs: comparison with rabbit globin messenger RNA. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. Sequence analysis of the 3' non-coding regions of rabbit alpha- and beta-globin messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 15;107(4):491–525. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABSON A. S., O'CONOR G. T., BEREZESKY I. K., PAUL F. J. ENHANCEMENT OF ADENOVIRUS GROWTH IN AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY KIDNEY CELL CULTURES BY SV40. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 May;116:187–190. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Williams J., Sharp P. A., Grodzicker T. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of adenoviruses. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 25;97(3):369–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T., Gesteland R. F., Spahr P. F. Translation of bacteriophage R17 and Qbeta RNA in a mammalian cell-free system. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 15;75(3):575–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of mammalian protein synthesis: the importance of ribosome and initiation factor quality for the efficiency of in vitro systems. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):329–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. D., Capecchi N. E., Capecchi M. R. Altered enzymes in drug-resistant variants of mammalian tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3145–3149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. W., Sherman F. Demonstration of UAG as a nonsense codon in bakers' yeast by amino-acid replacements in iso-1-cytochrome c. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):429–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. W., Sherman F., Jackson M., Thomas F. L., Shipman N. Demonstration of the UAA ochre codon in bakers yeast by amino-acid replacements in iso-1-cytochrome c. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 14;68(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90264-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Wagner M., Summers W. C. Possible peptide chain termination mutants in thymide kinase gene of a mammalian virus, herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4081–4084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]