Abstract
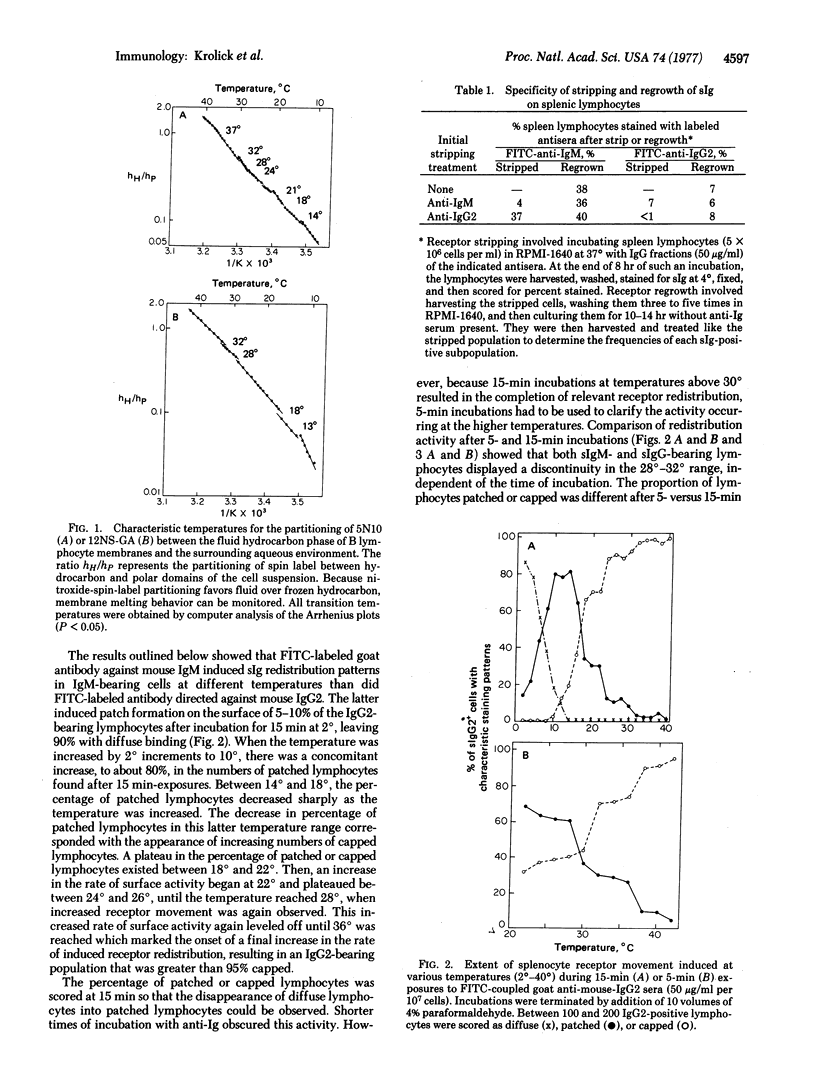
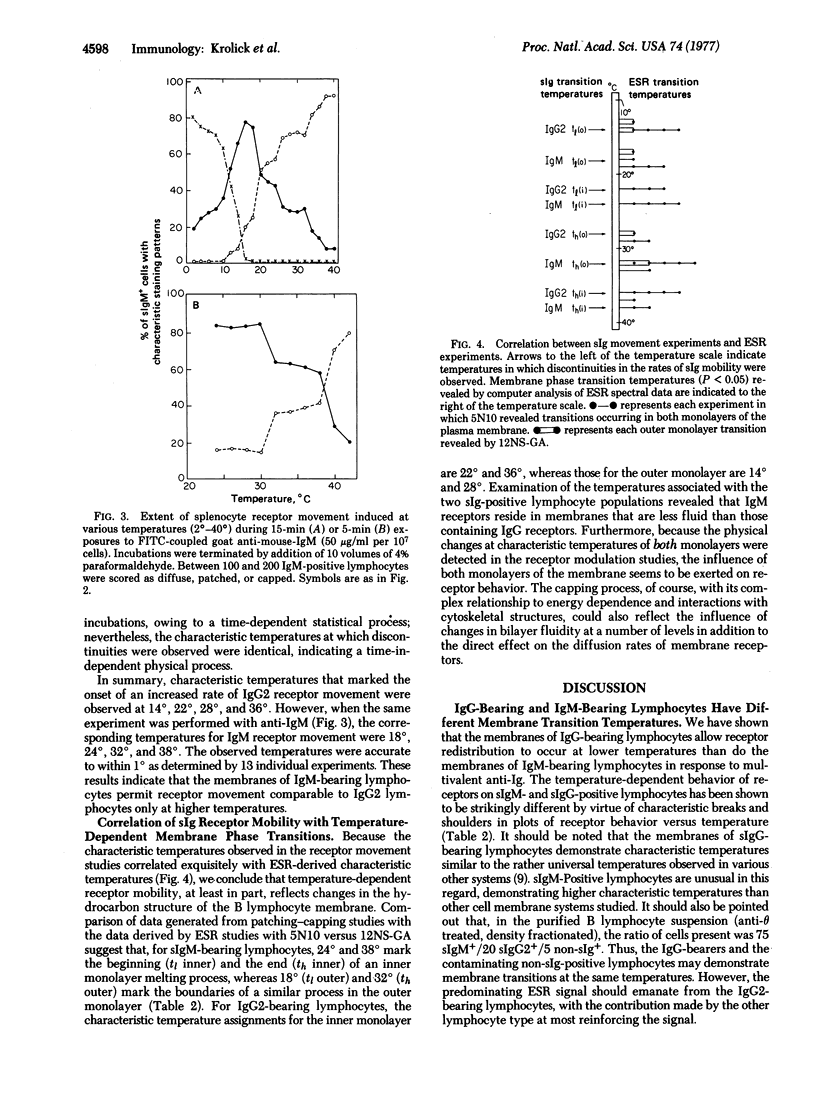
Anti-Ig induced redistribution of different Ig subclasses was studied as a function of temperature and correlated with membrane phase transitions as revealed by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Fluorescein isothiocyanate-coupled anti-IgG2 and anti-IgM antibodies induced patching and capping that proceeded with increasing rates from 2° to 40° (measured at 2° intervals). Characteristic temperatures marked the onset of discontinuities in such rate changes. IgG2-bearing lymphocytes displayed discontinuities at 14°, 22°, 28°, and 36°, whereas IgM-bearing lymphocytes displayed discontinuities at 18°, 24°, 32°, and 38°. Electron spin resonance spectroscopy studies using the spin label 2,2-dimethyl-4-butyl-4-penty-N-oxyloxazolidine, a nitroxide-substituted decane, indicated that these temperatures are a function of hydrocarbon phase separations in the B lymphocyte membrane. With a glucosamine-derivative [2-(10-carboxydecyl)-2-hexyl-4,4-dimethyl-3-oxazolidinyloxyl glucosamide] as a probe restricted to the outer monolayer of the plasma membrane, the temperatures 14° and 28° denoted the onset and end, respectively, of a fluidizing process in the outer monolayers of IgG2-bearing lymphocytes. Temperatures of 18° and 32° denoted these boundaries in IgM-bearing lymphocytes. Inner monolayer transitions are associated with the remaining temperatures. We conclude that membranes of IgM-bearing lymphocytes are less fluid than those of IgG2-bearing lymphocytes.
Keywords: membrane fluidity, electron spin resonance spectroscopy
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ault K. A., Unanue E. R. Events after the binding of antigen to lymphocytes: removal and regeneration of the antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1110–1124. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S. Membrane structure: some general principles. Science. 1973 Aug 17;181(4100):622–629. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4100.622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Kearney J. F., Lawton A. R., Abney E. R., Parkhouse R. M., Preud'homme J. L., Seligmann M. Generation of immunoglobulin class diversity in b cells: a discussion with emphasis on idg development. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Jun-Jul;127(3-4):573–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinna L. S. Multiple thermal discontinuities in glucose-6-phosphatase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 22;403(2):388–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J., Unanue E. R. Mapping and migration of lymphocyte surface macromolecules. Fed Proc. 1973 Jan;32(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. J., Raff M. C. Studies on the differentiation of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Dec 1;132(6):1216–1232. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.6.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit V. A., Edidin M. Lateral phase separation of lipids in plasma membranes: effect of temperature on the mobility of membrane antigens. Science. 1974 Jun 14;184(4142):1183–1185. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4142.1183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Dawidowicz E. A. Asymmetric exchange of vesicle phospholipids catalyzed by the phosphatidylcholine exhange protein. Measurement of inside--outside transitions. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2809–2816. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimshick E. J., McConnell H. M. Lateral phase separation in phospholipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2351–2360. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda M. J., Ito T., Okada T. S., Ohnishi S. I. A correlation between membrane fluidity and the critical temperature for cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):670–674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Karnovsky M. J., Engers H. D. Ligand-induced movement of lymphocyte membrane macromolecules. 3. Relationship between the formation and fate of anti-Ig-surface Ig complexes and cell metabolism. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):675–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Immunoglobulin-receptors revisited. Science. 1975 Sep 19;189(4207):964–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1083069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Huang Y. O., Fox C. F. Physical properties of the lipid phase of membranes from cultured animal cells. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(5-6):593–608. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Iwata K. K. Electron spin resonance evidence for vertical asymmetry in animal cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1321–1326. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski B. J., Parkes J. G., Huang Y. O., Fox C. F. Physical and physiological evidence for two phase transitions in cytoplasmic membranes of animal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Petris S., Raff M. C. Normal distribution, patching and capping of lymphocyte surface immunoglobulin studied by electron microscopy. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):257–259. doi: 10.1038/newbio241257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


