Abstract
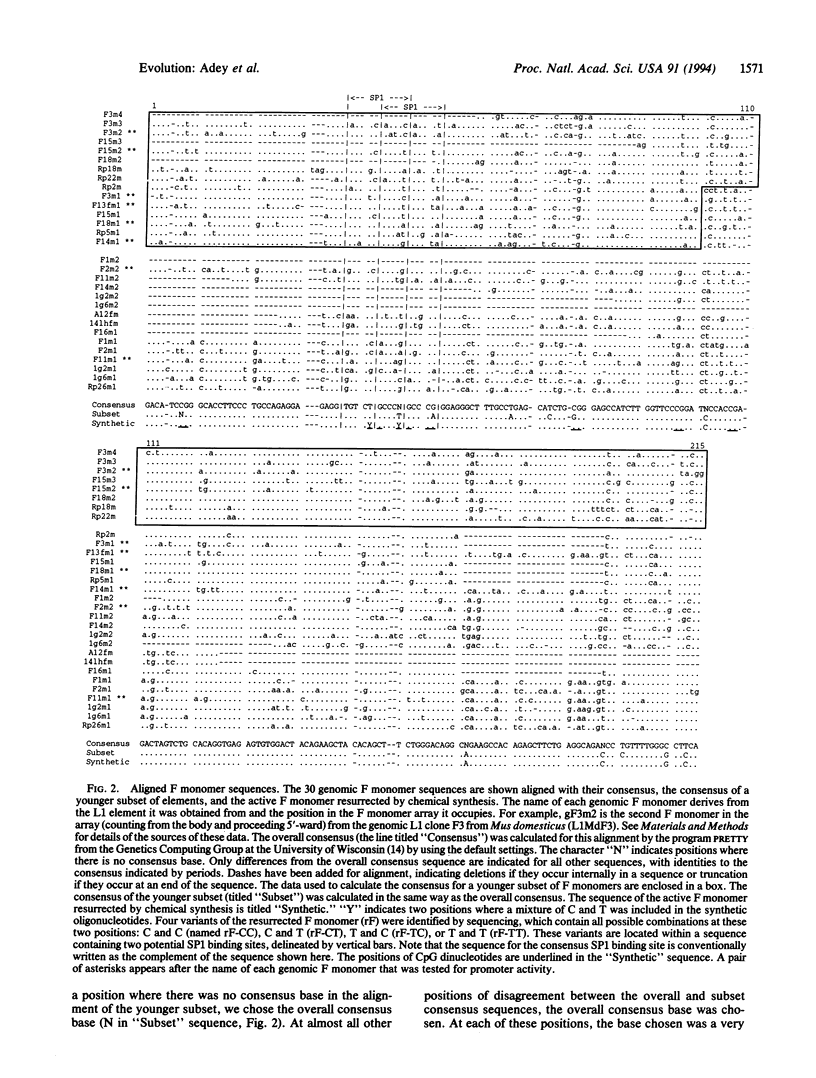
The F-type subfamily of LINE-1 or L1 retroposons [for long interspersed (repetitive) element 1] was dispersed in the mouse genome several million years ago. This subfamily appears to be both transcriptionally and transpositionally inactive today and therefore may be considered evolutionarily extinct. We hypothesized that these F-type L1s are inactive because of the accumulation of mutations. To test this idea we used phylogenetic analysis to deduce the sequence of a transpositionally active ancestral F-type promoter, resurrected it by chemical synthesis, and showed that it has promoter activity. In contrast, F-type sequences isolated from the modern genome are inactive. This approach, in which the automated DNA synthesizer is used as a "time machine," should have broad application in testing models derived from evolutionary studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adey N. B., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Nucleotide sequence of a mouse full-length F-type L1 element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2497–2497. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adey N. B., Schichman S. A., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Composite of A and F-type 5' terminal sequences defines a subfamily of mouse LINE-1 elements. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 20;221(2):367–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begg C. E., Delius H., Leader D. P. Duplicated region of the mouse genome containing a cytoplasmic gamma-actin processed pseudogene associated with long interspersed repetitive elements. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):677–687. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherfas J. Ancient DNA: still busy after death. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1354–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.1910205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm B. A., Wilson K. P., Matthews B. W., Kirsch J. F., Wilson A. C. Ancestral lysozymes reconstructed, neutrality tested, and thermostability linked to hydrocarbon packing. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):86–89. doi: 10.1038/345086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S. L., Scott A. F., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boeke J. D., Gabriel A. Reverse transcriptase encoded by a human transposable element. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1808–1810. doi: 10.1126/science.1722352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nur I., Pascale E., Furano A. V. The left end of rat L1 (L1Rn, long interspersed repeated) DNA which is a CpG island can function as a promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9233–9251. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. W., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. The F-type 5' motif of mouse L1 elements: a major class of L1 termini similar to the A-type in organization but unrelated in sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):739–749. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schichman S. A., Adey N. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd L1 A-monomer tandem arrays have expanded during the course of mouse L1 evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1993 May;10(3):552–570. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schichman S. A., Severynse D. M., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Strand-specific LINE-1 transcription in mouse F9 cells originates from the youngest phylogenetic subgroup of LINE-1 elements. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 5;224(3):559–574. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90544-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severynse D. M., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Identification of transcriptional regulatory activity within the 5' A-type monomer sequence of the mouse LINE-1 retroposon. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(1):41–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00570439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swergold G. D. Identification, characterization, and cell specificity of a human LINE-1 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6718–6729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wincker P., Jubier-Maurin V., Roizès G. Unrelated sequences at the 5' end of mouse LINE-1 repeated elements define two distinct subfamilies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8593–8606. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]