Abstract
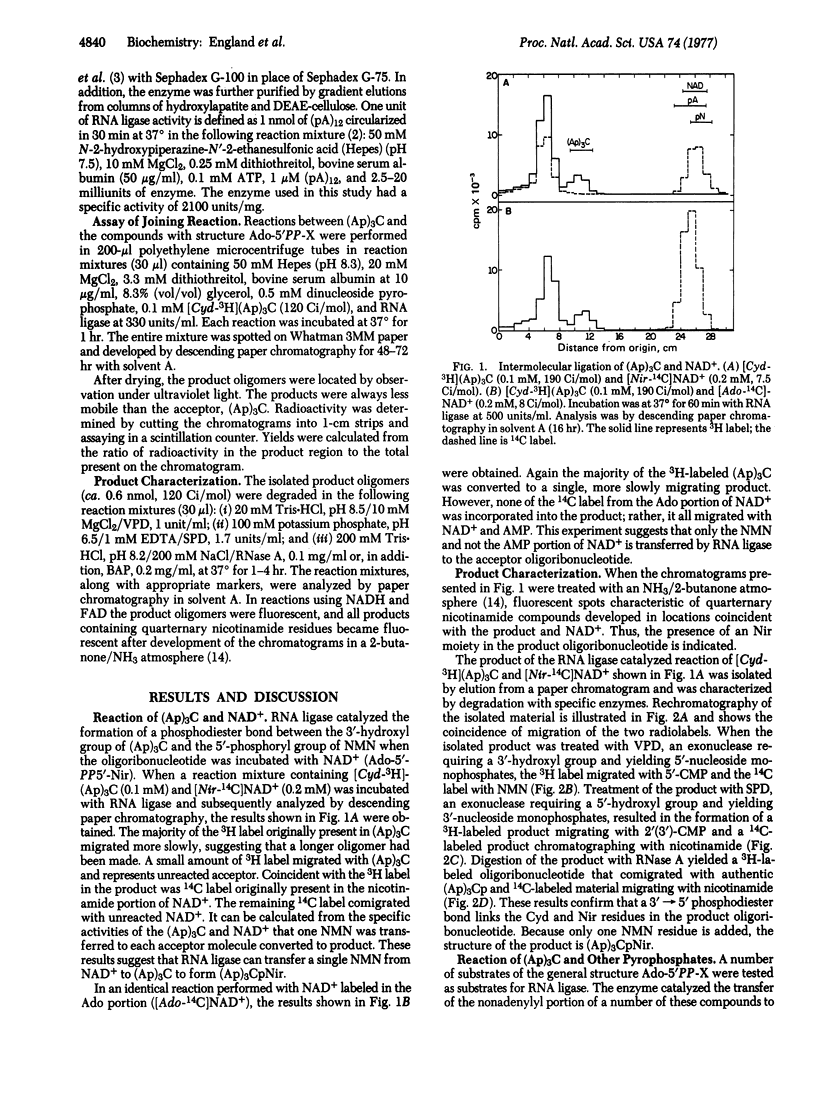
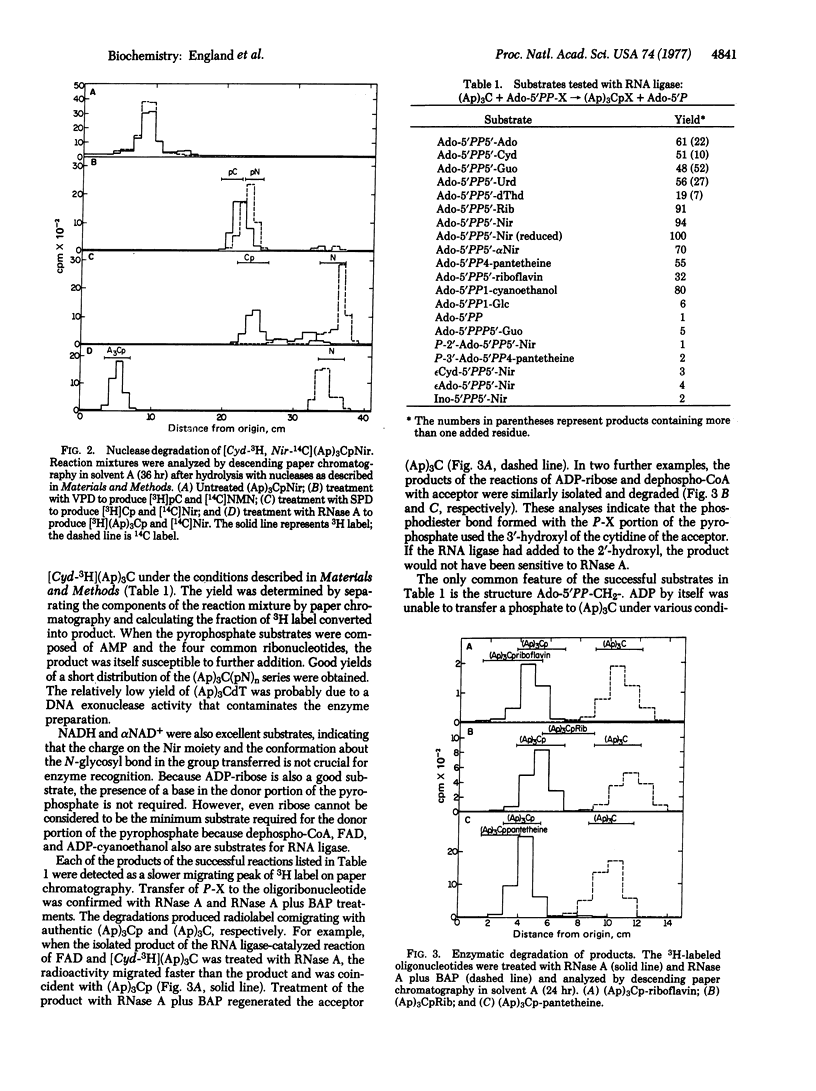
RNA ligase isolated from bacteriophage T4-infected Escherichia coli will utilize a number of different compounds with the general structure Ado-5'PP-X as substrates in an ATP-independent reaction. The P-X portions of these molecules are transferred to the 3'-hydroxyl of an oligoribonucleotide to form a phosphodiester bond, and the Ado-5'P (AMP) portion is released. AMP, CMP, GMP, UMP, dTMP, NMN, alphaNMN, reduced NMN, FMN, Rib-5P, phosphopantetheine, and cyanoethylphosphate all have been added to [Cyd-3H](Ap)3C from their corresponding AMP adducts. Contrary to the relative lack of specificity of RNA ligase for the P-X -group added, the failure of NADP+, deamino-NAD+, epsilonNCD+, epsilon NAD and CoA to react indicates that the enzyme shows a high degree of selectivity for the AMP portion of the substrate. The diversity of chemical groups that can be efficiently added suggests that this reaction of RNA ligase will prove useful for the modification of the 3' ends of RNA molecules.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cranston J. W., Silber R., Malathi V. G., Hurwitz J. Studies on ribonucleic acid ligase. Characterization of an adenosine triphosphate-inorganic pyrophosphate exchange reaction and demonstration of an enzyme-adenylate complex with T4 bacteriophage-induced enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7447–7456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield J. C., Leonard N. J., Gumport R. I. Nicotinamide 3,N4-ethenocytosine dinucleotide, an analog of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Synthesis and enzyme studies. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):698–706. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W., Lehman I. R. Enzymatic joining of polynucleotides. VI. Activity of a synthetic adenylylated polydeoxynucleotide in the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):43–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KODKICEK E., REDDI K. K. Paper chromatography of nicotinic acid derivatives. Nature. 1951 Sep 15;168(4272):475–477. doi: 10.1038/168475b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Kallenbach N. R. Determination of recognition sites of T4 RNA ligase on the 3'-OH and 5' -P termini of polyribonucleotide chains. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):452–454. doi: 10.1038/254452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka E., Nishikawa S., Sugiura M., Ikehara M. Joining of ribooligonucleotides with T4 RNA ligase and identification of the oligonucleotide-adenylate intermediate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jun;3(6):1613–1623. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.6.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silber R., Malathi V. G., Hurwitz J. Purification and properties of bacteriophage T4-induced RNA ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky J. J., Last J. A., Gilham P. T. The use of terminal blocking groups for the specific joining of oligonucleotides in RNA ligase reactions containing equimolar concentrations of acceptor and donor molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3157–3166. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Snoper T. J., Cozzarelli N. R. Bacteriophage T4 RNA ligase. Reaction intermediates and interaction of substrates. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 10;252(5):1732–1738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Practical methods for the routine chemical synthesis of 32P-labelled nucleoside di- and triphosphates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;209(2):296–305. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90728-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C., Baller J., Doty P. Complementary oligonucleotide binding to the anticodon loop of fMet-transfer RNA. Nature. 1970 Feb 7;225(5232):508–510. doi: 10.1038/225508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlenbeck O. C., Cameron V. Equimolar addition of oligoribonucleotides with T4 RNA ligase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):85–98. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C., Uhlenbeck O. C., Bedows E., Gumport R. I. T4-induced RNA ligase joins single-stranded oligoribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


