Abstract
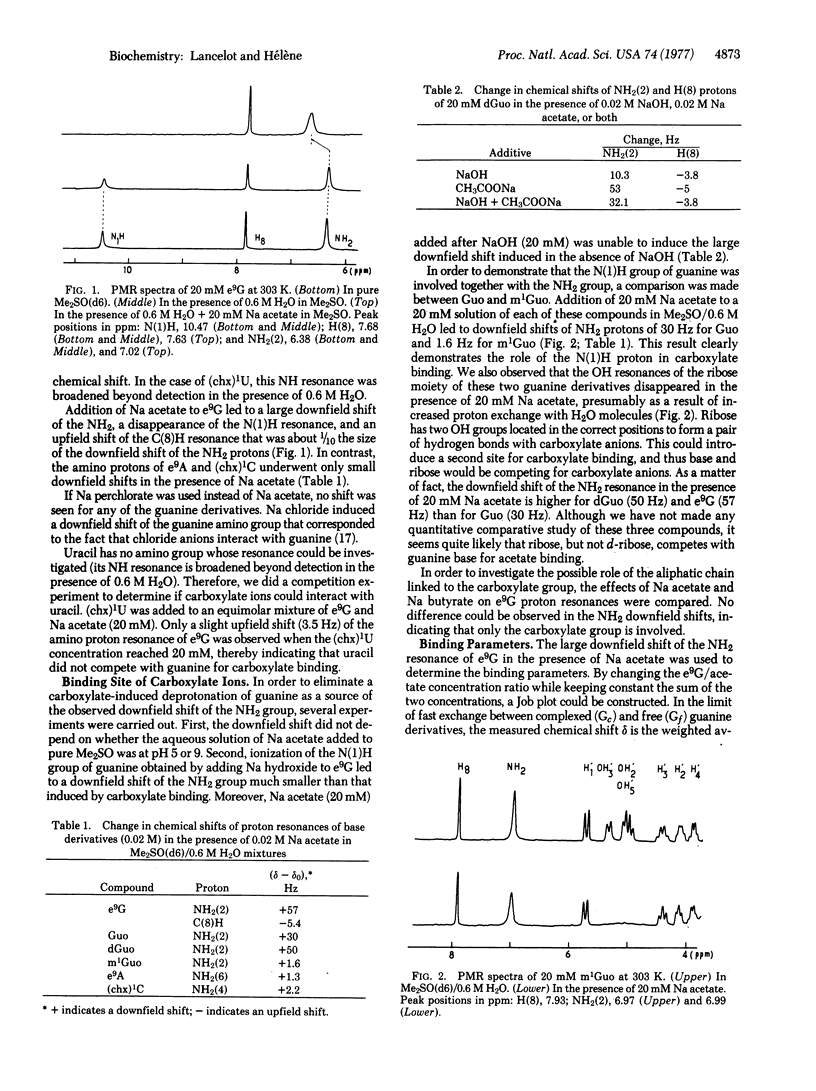
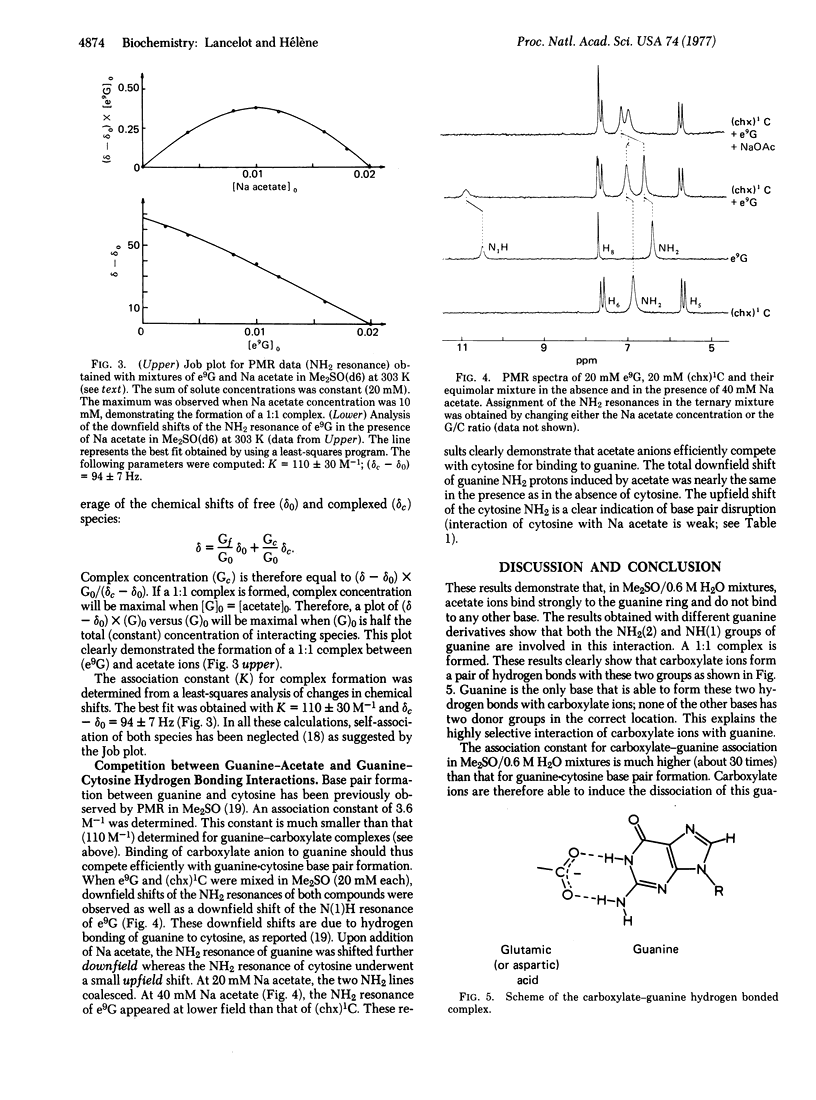
The interaction of carboxylate ions (acetate, butyrate) with nucleic aicd bases and nucleosides has been investigated by proton magnetic resonance in dimethyl sulfoxide (d6)/H2O mixtures. Carboxylate ions interacted only with guanine derivatives and led to a large downfield shift of the NH2 resonance. A 1:1 stoichiometry was deduced from a study of the concentration dependence of chemical shifts. A study of substituted guanine showed that hydrogen bonding involved N(1)H and NH2(2). An association constant of 110 M-1 was determined. This value is about 30 times higher than the association constant for guanine-cytosine base pair formation under the same experimental conditions. As a matter of fact, carboxylate ions induced a dissociation of guanine-cytosine base pairs. This guanine-carboxylate association is experimental evidence for a highly specific interaction that could play an important role in protein/nucleic acid recognition.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brun F., Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. Interactions of aromatic residues of proteins with nucleic acids. Fluorescence studies of the binding of oligopeptides containing tryptophan and tyrosine residues to polynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):558–563. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruskov V. I. Ob uznavanii osnovanii nukleinovykh kislot aminokislotami i peptidami s pomoshch'iu vodorodnykh sviazei. Mol Biol (Mosk) 1975 Mar-Apr;9(2):304–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Marzilli L. G. Letter: Nucleoside complexing. A charge reversed chelate compound between guanosine and chloride ion. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 May 29;96(11):3656–3657. doi: 10.1021/ja00818a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimicoli J. L., Hélène C. Interactions of aromatic residues of proteins with nucleic acid. II. Proton magnetic resonance studies of the binding of tyramine and tyrosine-containing peptides to poly(adenylic acid) and deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):724–730. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimicoli J. L., Hélène C. Interactions of aromatic residues of proteins with nucleic acids. I. Proton magnetic resonance studies of the binding of tryptophan-containing peptides to poly(adenylic acid) and deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):714–723. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann B., Reinbolt J., Ebel J. P. Studies of the binding of E. coli ribosomal protein S4 to 16S rRNA after UV irradiation of the S4--16S rRNA complex. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):106–111. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helene C. Metal ion-mediated specific interactions between nucleic acid bases of polynucleotides and amino acid side chains of polypeptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Jun;2(6):961–969. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helene C. Specific recognition of guanine bases in protein-nucleic acid complexes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 15;74(1):10–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80740-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancelot G. Hydrogen bonding of adenine derivatives to tyrosine side chain. Biophys J. 1977 Mar;17(3):243–254. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85653-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancelot G. Hydrogen bonding of amino acid side chains to nucleic acid bases. Biochimie. 1977;59(7):587–596. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(77)80168-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmark R. A., Cantor C. R. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the interactions of guanosine and cytidine in dimethyl sulfoxide. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Aug 28;90(18):5010–5017. doi: 10.1021/ja01020a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaush A. C., Sharp R. R. Ion binding to nucleosides. A 35C1 and 7Li NMR study. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Dec 8;98(25):7973–7980. doi: 10.1021/ja00441a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellini H., Maurizot J. C., Dimicoli J. L., Helene C. Hydrogen bonding of amino acid side chains to nucleic acid bases. FEBS Lett. 1973 Mar 1;30(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80655-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Stein W. H., Moore S. The identification of a glutamic acid residue as part of the active site of ribonuclease T-1. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 25;242(20):4682–4690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toulmé J. J., Charlier M., Héléne C. Specific recognition of single-stranded regions in ultraviolet-irradiated and heat-denatured DNA by tryptophan-containing peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3185–3188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. Specific recognition of single-stranded nucleic acids. Interaction of tryptophan-containing peptides with native, denatured, and ultraviolet-irradiated DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):244–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. M., Li N. C. Proton magnetic resonance studies of self-association and metal complexation of nucleosides in dimethyl sulfoxide. J Am Chem Soc. 1968 Sep 11;90(19):5069–5074. doi: 10.1021/ja01021a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


