Abstract
We have recently shown that, after the histones and most of the nonhistone proteins are gently removed from HeLa metaphase chromosomes, the chromosomal DNA is still highly organized and relatively compact. The structure of these histone-depleted chromosomes is due to the presence of a number of nonhistone proteins that form a central scaffold that retains the approximate size and shape of intact chromosomes and to which the DNA is attached, predominantly forming loops. We now demonstrate that the protein scaffold may be isolated independently of the DNA by treating HeLa chromosomes with micrococcal nuclease before removing the histones.
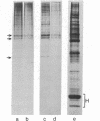
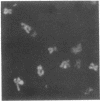
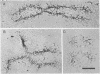
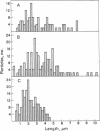
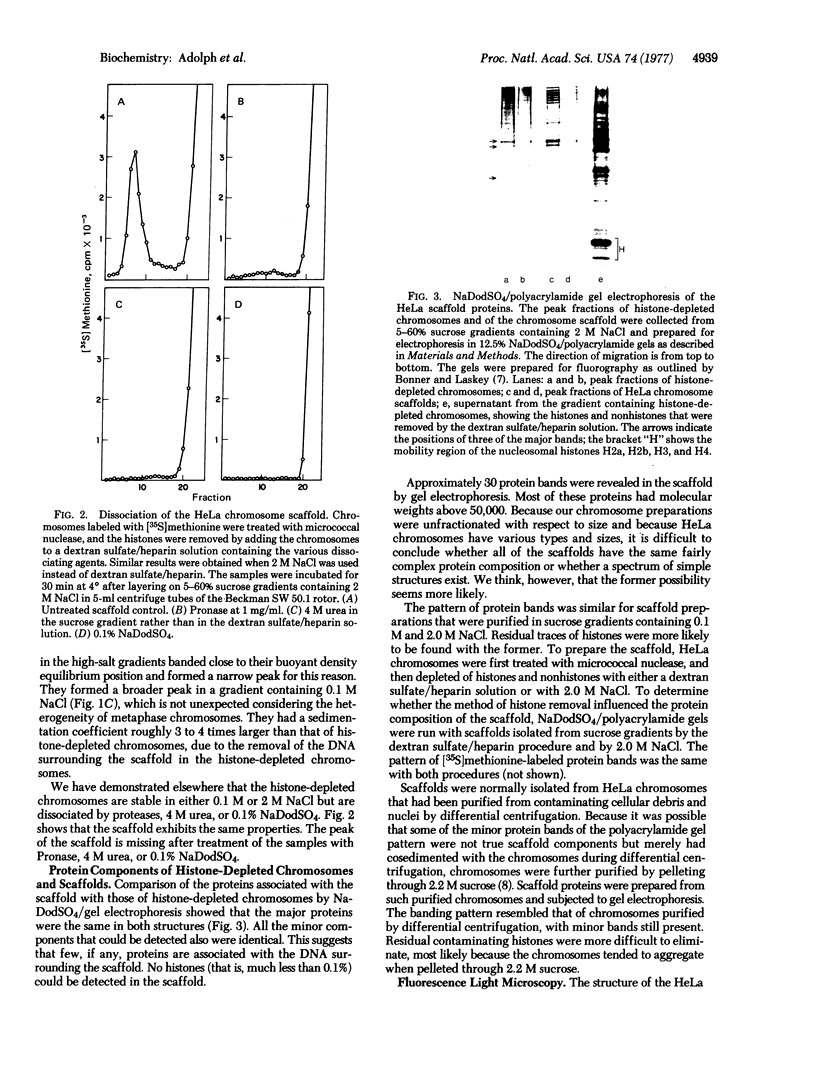
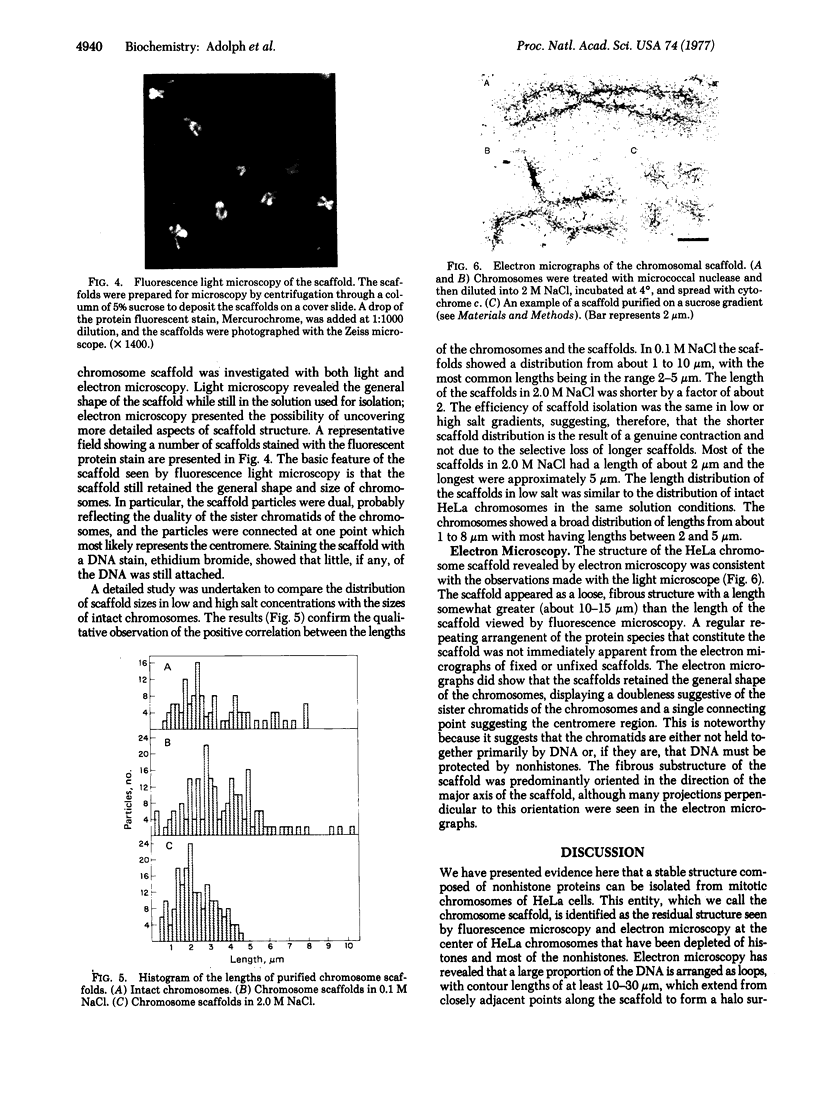
The chromosomal scaffolds may be isolated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation as a well-defined peak that is stable in 2 M sodium chloride, but is dissociated by treatment with proteases, 4 M urea, or 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis reveals that the protein content of scaffold preparations is identical to that of histone-depleted chromosomes. Fluorescence microscopy of purified scaffolds in isolation buffer shows that the particles still possess the familiar chromosome morphology. When the scaffolds are examined in the electron microscope, a fibrous structure with the approximate size and shape of intact, paired chromatids is seen. Less than 0.1% of the chromosomal DNA and virtually no histones are associated with the purified scaffold structures.
Keywords: metaphase, nonhistones, DNA superstructure, micrococcal nuclease, dextran sulfate
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolph K. W., Cheng S. M., Laemmli U. K. Role of nonhistone proteins in metaphase chromosome structure. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. R., Laemmli U. K. The structure of histone-depleted metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):817–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield E., Wray W. Architecture of the Chinese hamster metaphase chromosome. Chromosoma. 1971;32(3):262–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00284839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Stubblefield E. A new method for the rapid isolation of chromosomes, mitotic apparatus, or nuclei from mammalian fibroblasts at near neutral pH. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Mar;59(3):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90656-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]