Abstract
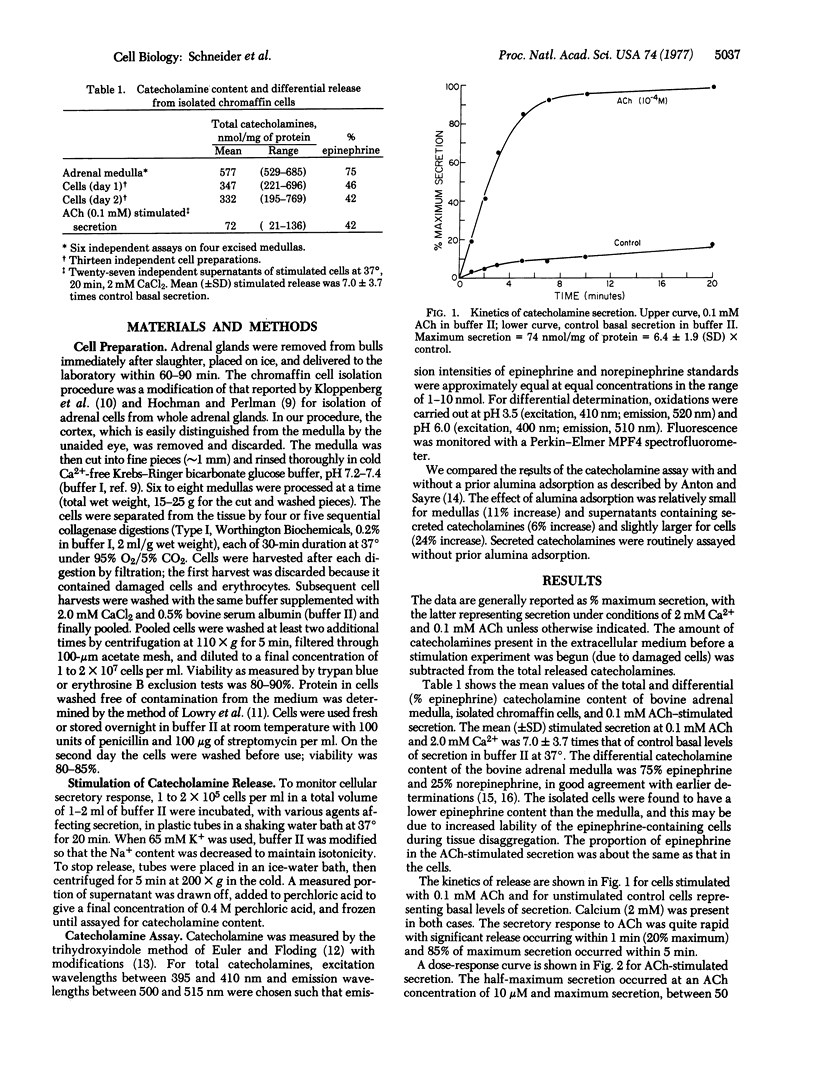
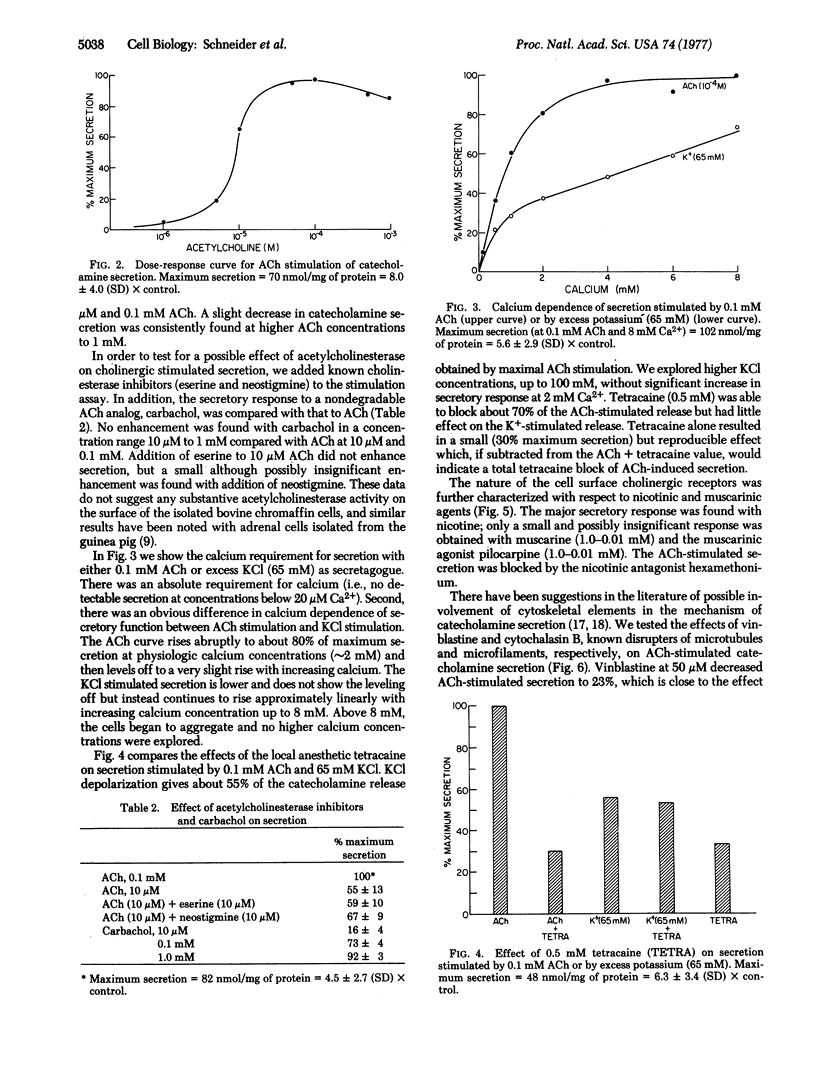
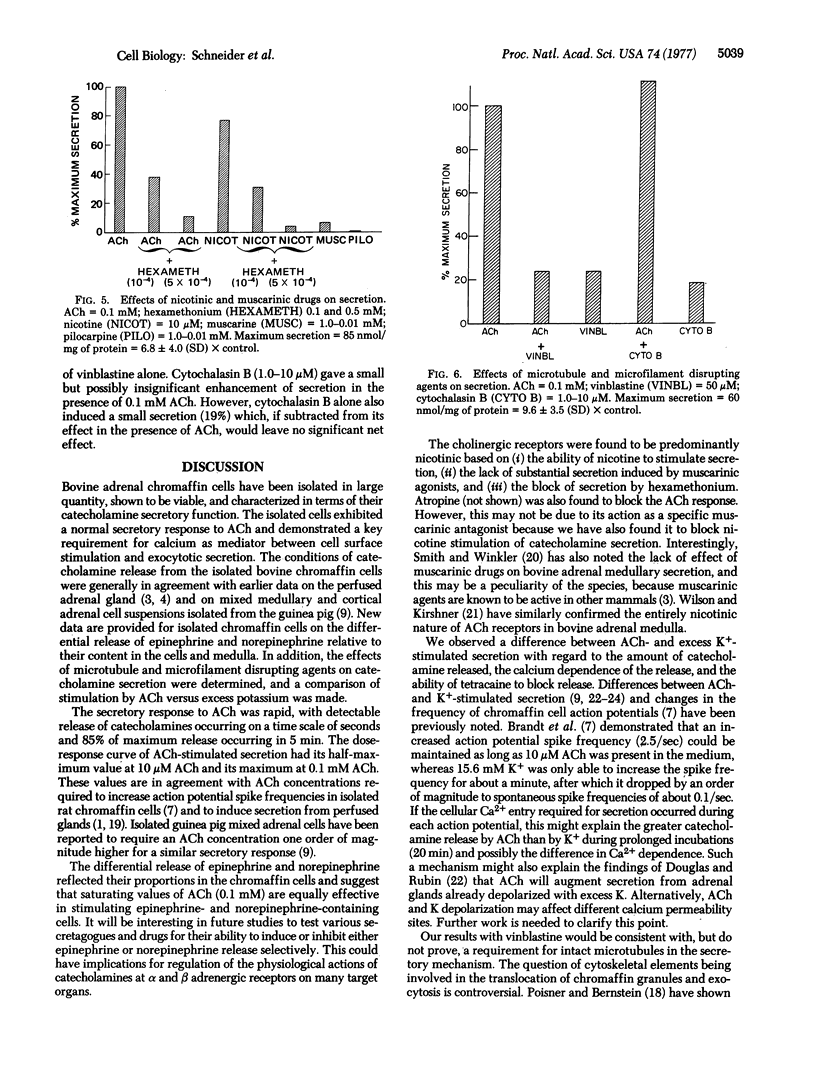
Bovine adrenal chromaffin cells were isolated by removal of the cortex and sequential collagenase digestion of the medulla. The catecholamine secretory function of these cells was characterized with respect to acetylcholine stimulation, cation requirements, and cytoskeletal elements. The dose-response curve for stimulated release had its half-maximum value at 10-5 M acetylcholine, and maximum secretion was on the average 7 times that of control basal secretion. The differential release of epinephrine versus norepinephrine after stimulation with 0.1 mM acetylcholine occurred in proportion to their distribution in the cell suspension. The cholinergic receptors were found to be predominantly nicotinic. The kinetics of catecholamine release were rapid, with significant secretion occurring in less than 60 sec and 85% of maximum secretion within 5 min. A critical requirement for calcium in the extracellular medium was demonstrated, and 80% of maximum secretion was achieved at physiologic calcium concentrations. Stimulation by excess potassium (65 mM KCl) also induced catecholamine secretion which differed from acetylcholine stimulation in being less potent, in having a different dependence on calcium concentration, and in its response to the local anesthetic tetracaine. Tetracaine, which is thought to inhibit membrane cation permeability, was able to block acetylcholine-stimulated but not KCl-stimulated secretion. The microtubule disrupting agent vinblastine was able to block catecholamine release whereas the microfilament disrupter cytochalasin B had little effect. The results show the isolated bovine chromaffin cells to be viable, functioning, and available in large quantity. These cells now provide an excellent system for studying cell surface regulation of hormone and neurotransmitter release.
Keywords: catecholamine secretion, acetylcholine receptors, K+ depolarization, calcium requirement, microtubule disruption
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTON A. H., SAYRE D. F. A study of the factors affecting the aluminum oxide-trihydroxyindole procedure for the analysis of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Dec;138:360–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biales B., Dichter M., Tischler A. Electrical excitability of cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):743–753. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt B. L., Hagiwara S., Kidokoro Y., Miyazaki S. Action potentials in the rat chromaffin cell and effects of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1976 Dec;263(3):417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. The role of calcium in the secretory response of the adrenal medulla to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:40–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Kanno T., Sampson S. R. Effects of acetylcholine and other medullary secretagogues and antagonists on the membrane potential of adrenal chromaffin cells: an analysis employing techniques of tissue culture. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(1):107–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Kanno T., Sampson S. R. Influence of the ionic environment on the membrane potential of adrenal chromaffin cells and on the depolarizing effect of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):107–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Sorimachi M. Colchicine inhibits adrenal medullary secretion evoked by acetylcholine without affecting that evoked by potassium. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 May;45(1):129–132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Costa E. Commentary: Trans-synaptic regulation of typrosine 3-mono-oxygenase biosynthesis in rat adrenal medulla. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 May 1;26(9):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90393-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman J., Perlman R. L. Catecholamine secretion by isolated adrenal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 14;421(1):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Blood F. E., Steiner A. L., Greengard P. Neurotransmitters increase cyclic nucleotides in postganglionic neurons: immunocytochemical demonstration. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):157–159. doi: 10.1126/science.241121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloppenborg P. W., Island D. P., Liddle G. W., Michelakis A. M., Nicholson W. E. A method of preparing adrenal cell suspensions and its applicability to the in vitro study of adrenal metabolism. Endocrinology. 1968 May;82(5):1053–1058. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-5-1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poisner A. M., Bernstein J. A possible role of microtubules in catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla: effect of colchicine, vinca alkaloids and deuterium oxide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):102–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poisner A. M., Cooke P. Microtubules and the adrenal medulla. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:653–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19235.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHEPHERD D. M., WEST G. B. Hydroxytyramine and the adrenal medulla. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):15–19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifaró J. M., Collier B., Lastowecka A., Stern D. Inhibition by colchicine and by vinblastine of acetylcholine-induced catecholamine release from the adrenal gland: an anticholinergic action, not an effect upon microtubules. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;8(2):264–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., FLODING I. A fluorimetric micromethod for differential estimation of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1955;33(118):45–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P., Kirshner N. The acetylcholine receptor of the adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1977 Apr;28(4):687–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von EULER U., LISHAJKO F. Improved technique for the fluorimetric estimation of catecholamines. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Apr;51:348–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


