Abstract
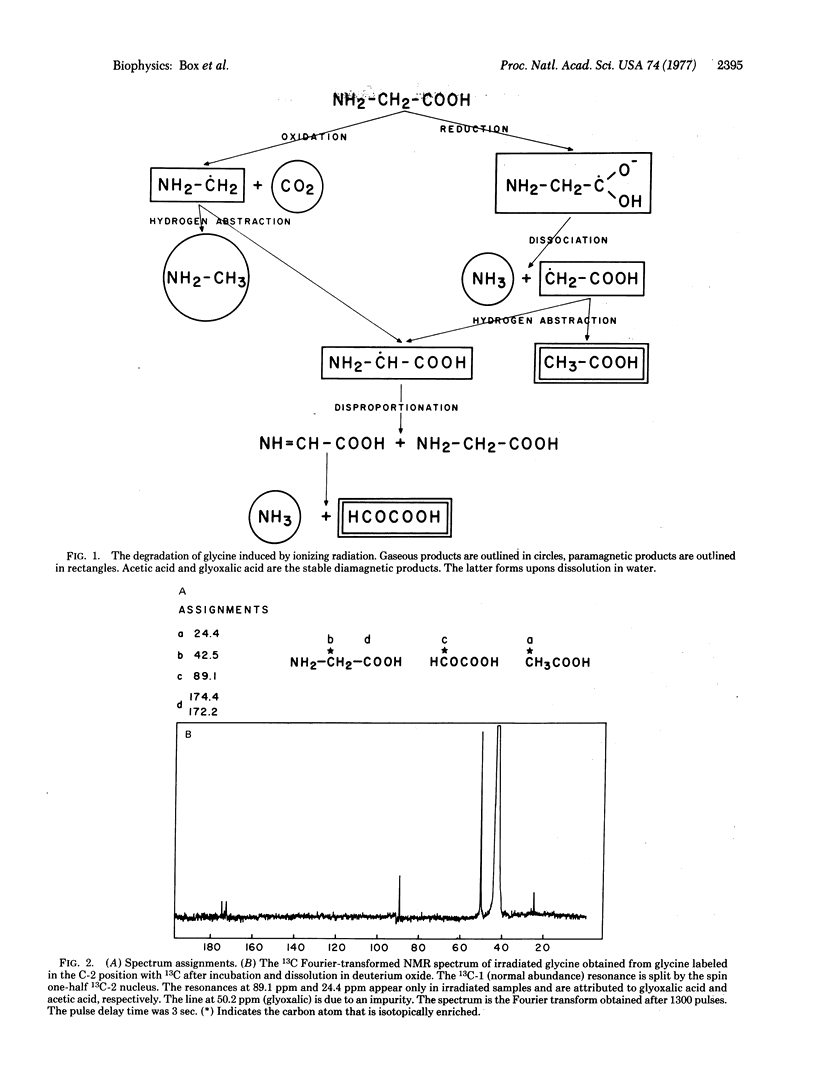
The stable products generated in polycrystalline glycine exposed to ionizing radiation and subsequently dissolved in water were identified by using 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The study was done on isotopically enriched samples. The results can be correlated with the results of many other studies on irradiated glycine using other methods.
Keywords: electron spin resonance spectroscopy, free radicals, radiation effects, 13C isotopes, electron nuclear double resonance spectroscopy
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Box H. C., Freund H. G., Budzinski E. E. Paramagnetic absorption of irradiated glycine. J Am Chem Soc. 1966 Feb 20;88(4):658–661. doi: 10.1021/ja00956a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordy W., Ard W. B., Shields H. MICROWAVE SPECTROSCOPY OF BIOLOGICAL SUBSTANCES. I. PARAMAGNETIC RESONANCE IN X-IRRADIATED AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Nov 15;41(11):983–996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.11.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


