Abstract
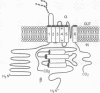
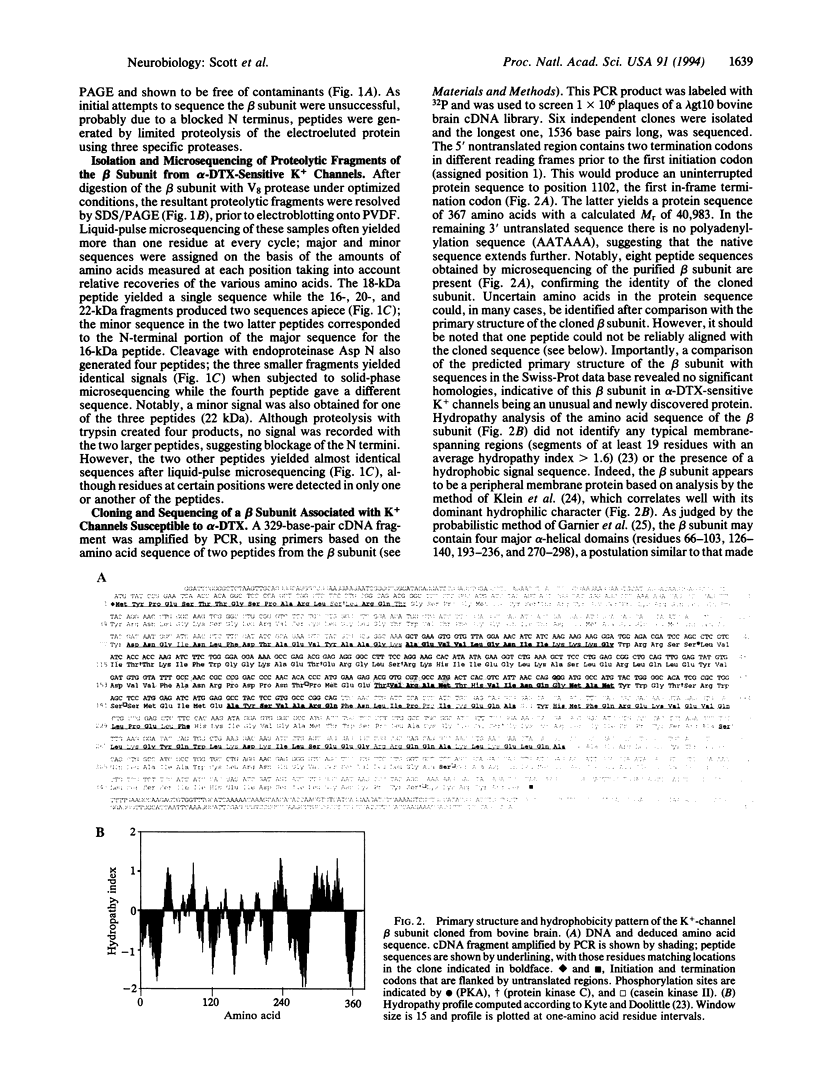
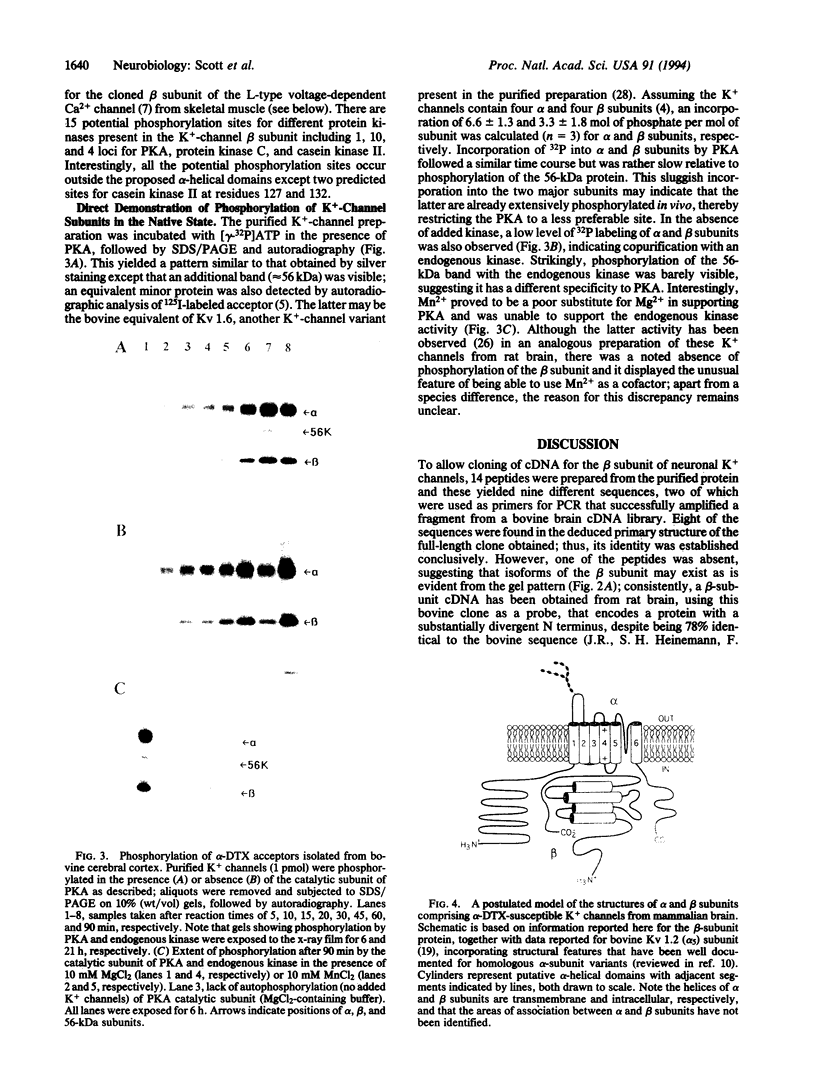
Voltage-dependent cation channels are large heterooligomeric proteins. Heterologous expression of cDNAs encoding the alpha subunits alone of K+, Na+, or Ca2+ channels produces functional multimeric proteins; however, coexpression of those for the latter two with their auxiliary proteins causes dramatic changes in the resultant membrane currents. Fast-activating, voltage-sensitive K+ channels from brain contain four alpha and beta subunits, tightly associated in a 400-kDa complex; although molecular details of the alpha-subunit proteins have been determined, little is known about the beta-subunit constituent. Proteolytic fragments of a beta subunit from bovine alpha-dendrotoxin-sensitive neuronal K+ channels yielded nine different sequences. In the polymerase chain reaction, primers corresponding to two of these peptides amplified a 329-base-pair fragment in a lambda gt10 cDNA library from bovine brain; a full-length clone subsequently isolated encodes a protein of 367 amino acids (M(r) approximately 40,983). It shows no significant homology with any known protein. Unlike the channels' alpha subunits, the hydropathy profile of this sequence failed to reveal transmembrane domains. Several consensus phosphorylation motifs are apparent and, accordingly, the beta subunit could be phosphorylated in the intact K+ channels. These results, including the absence of a leader sequence and N-glycosylation, are consistent with the beta subunit being firmly associated on the inside of the membrane with alpha subunits, as speculated in a simplified model of these authentic K+ channels. Importantly, this first primary structure of a K(+)-channel beta subunit indicates that none of the cloned auxiliary proteins of voltage-dependent cation channels, unlike their alpha subunits, belong to a super-family of genes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bidard J. N., Mourre C., Gandolfo G., Schweitz H., Widmann C., Gottesmann C., Lazdunski M. Analogies and differences in the mode of action and properties of binding sites (localization and mutual interactions) of two K+ channel toxins, MCD peptide and dendrotoxin I. Brain Res. 1989 Aug 21;495(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black A. R., Breeze A. L., Othman I. B., Dolly J. O. Involvement of neuronal acceptors for dendrotoxin in its convulsive action in rat brain. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 15;237(2):397–404. doi: 10.1042/bj2370397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S15–S48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Functional subunit structure of voltage-gated calcium channels. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1499–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.1654596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolly J. O., Halliwell J. V., Black J. D., Williams R. S., Pelchen-Matthews A., Breeze A. L., Mehraban F., Othman I. B., Black A. R. Botulinum neurotoxin and dendrotoxin as probes for studies on transmitter release. J Physiol (Paris) 1984;79(4):280–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isom L. L., De Jongh K. S., Patton D. E., Reber B. F., Offord J., Charbonneau H., Walsh K., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. Primary structure and functional expression of the beta 1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):839–842. doi: 10.1126/science.1375395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Kanehisa M., DeLisi C. The detection and classification of membrane-spanning proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 28;815(3):468–476. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacerda A. E., Kim H. S., Ruth P., Perez-Reyes E., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Normalization of current kinetics by interaction between the alpha 1 and beta subunits of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channel. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):527–530. doi: 10.1038/352527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muniz Z. M., Parcej D. N., Dolly J. O. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies against voltage-dependent K+ channels raised using alpha-dendrotoxin acceptors purified from bovine brain. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 15;31(49):12297–12303. doi: 10.1021/bi00164a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappin D. J., Coull J. M., Köster H. Solid-phase sequence analysis of proteins electroblotted or spotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Anal Biochem. 1990 May 15;187(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90410-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
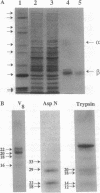
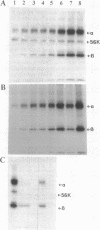
- Parcej D. N., Dolly J. O. Dendrotoxin acceptor from bovine synaptic plasma membranes. Binding properties, purification and subunit composition of a putative constituent of certain voltage-activated K+ channels. Biochem J. 1989 Feb 1;257(3):899–903. doi: 10.1042/bj2570899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parcej D. N., Scott V. E., Dolly J. O. Oligomeric properties of alpha-dendrotoxin-sensitive potassium ion channels purified from bovine brain. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 17;31(45):11084–11088. doi: 10.1021/bi00160a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelchen-Matthews A., Dolly J. O. Distribution in the rat central nervous system of acceptor sub-types for dendrotoxin, a K+ channel probe. Neuroscience. 1989;29(2):347–361. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongs O. Molecular biology of voltage-dependent potassium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S69–S88. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehm H. Enzymatic deglycosylation of the dendrotoxin-binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Apr 10;247(1):28–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81233-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehm H., Lazdunski M. Purification and subunit structure of a putative K+-channel protein identified by its binding properties for dendrotoxin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4919–4923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid P. F., Pongs O., Dolly J. O. Cloning of a bovine voltage-gated K+ channel gene utilising partial amino acid sequence of a dendrotoxin-binding protein from brain cortex. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 4;302(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80277-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott V. E., Parcej D. N., Keen J. N., Findlay J. B., Dolly J. O. Alpha-dendrotoxin acceptor from bovine brain is a K+ channel protein. Evidence from the N-terminal sequence of its larger subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20094–20097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer D., Biel M., Lotan I., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F., Dascal N. The roles of the subunits in the function of the calcium channel. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1553–1557. doi: 10.1126/science.1716787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Ruppersberg J. P., Schröter K. H., Sakmann B., Stocker M., Giese K. P., Perschke A., Baumann A., Pongs O. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3235–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]