Abstract
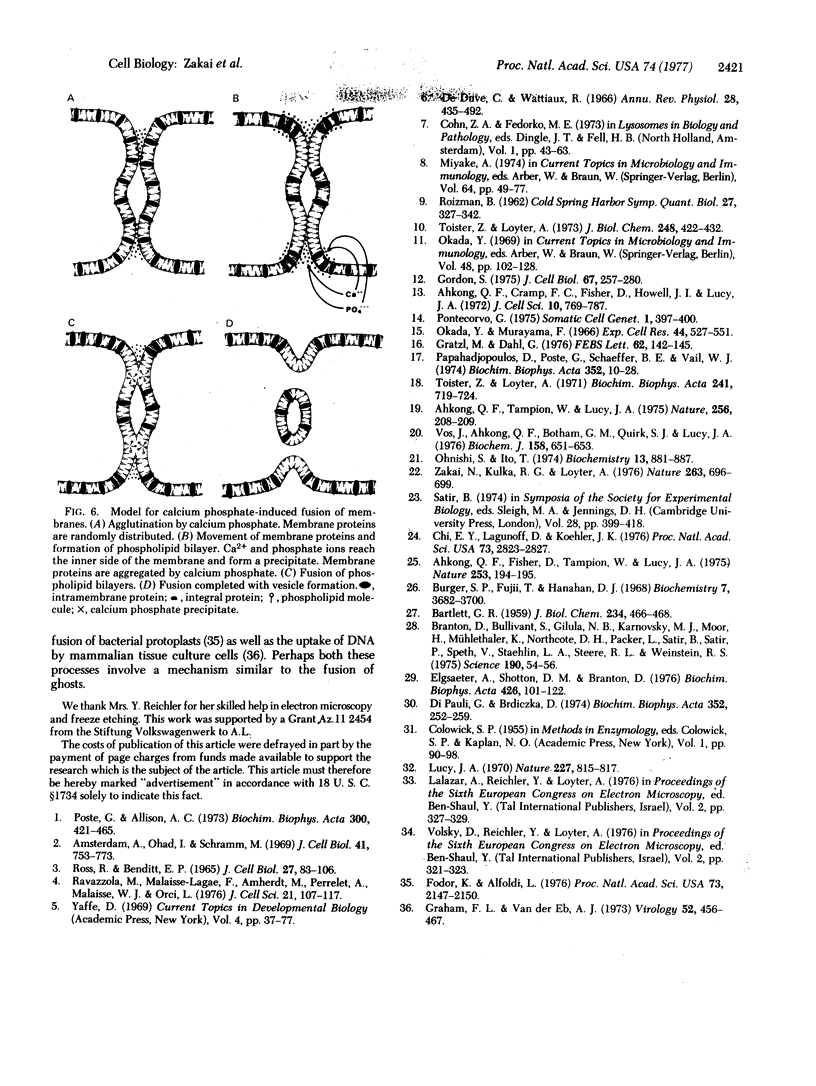
Nascent calcium phosphate promotes the agglutination and fusion of human erythrocyte ghosts. Membrane phospholipids of erythrocyte ghosts treated with Ca2+ and phosphate ions become exposed to attack by phospholipase C (phosphatidylcholine cholinephosphohydrolase, EC 3.1.4.3) (Bacillus cereus). Freeze-fracture pictures of fused erythrocyte ghosts show the presence of regions deficient in intramemebrane particles in the protoplasmic face which we believe to be regions of fusion. Discontinuous regions of the protoplasmic and exoplasmic faces are observed, which are apparently intermediate stages in the process of fusion. TH-in-section electron micrographs reveal deposits of calcium phosphate in areas of contact and fusion of ghosts. Ca2+ in the presence of N-[tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl]glycine (Tricine) buffer causes the formation of blebs in the membrane but does not cause changes in the intramembrane particle pattern or induce fusion. It is suggested that nascent calcium phosphate acts by forming protein-free regions of phospholipid bilayer which can fuse readily.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahkong Q. F., Cramp F. C., Fisher D., Howell J. I., Lucy J. A. Studies on chemically induced cell fusion. J Cell Sci. 1972 May;10(3):769–787. doi: 10.1242/jcs.10.3.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahkong Q. F., Fisher D., Tampion W., Lucy J. A. Mechanisms of cell fusion. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):194–195. doi: 10.1038/253194a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahkong Q. F., Tampion W., Lucy J. A. Promotion of cell fusion by divalent cation ionophores. Nature. 1975 Jul 17;256(5514):208–209. doi: 10.1038/256208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsterdam A., Ohad I., Schramm M. Dynamic changes in the ultrastructure of the acinar cell of the rat parotid gland during the secretory cycle. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jun;41(3):753–773. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Bullivant S., Gilula N. B., Karnovsky M. J., Moor H., Mühlethaler K., Northcote D. H., Packer L., Satir B., Satir P. Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science. 1975 Oct 3;190(4209):54–56. doi: 10.1126/science.1166299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger S. P., Fujii T., Hanahan D. J. Stability of the bovine erythrocyte membrane. Release of enzymes and lipid components. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3682–3700. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi E. Y., Lagunoff D., Koehler J. K. Freeze-fracture study of mast cell secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2823–2827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Pauli G., Brdiczka D. Localization of glycoproteins within erythrocyte membranes of sheep. A freeze-etching and biochemical study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):252–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgsaeter A., Shotton D. M., Branton D. Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. II. The influence of spectrin aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):101–122. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90433-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor K., Alföldi L. Fusion of protoplasts of Bacillus megaterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2147–2150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon S. Cell fusion and some subcellular properties of heterokaryons and hybrids. J Cell Biol. 1975 Nov;67(2PT1):257–280. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.2.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzl M., Dahl G. Ca2+-induced fusion of golgi-derived secretory vesicles isolated from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1976 Feb 15;62(2):142–145. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucy J. A. The fusion of biological membranes. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):815–817. doi: 10.1038/227815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Murayama F. Requirement of calcium ions for the cell fusion reaction of animal cells by HVJ. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Nov-Dec;44(2):527–551. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi S., Ito T. Calcium-induced phase separations in phosphatidylserine--phosphatidylcholine membranes. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 26;13(5):881–887. doi: 10.1021/bi00702a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papahadjopoulos D., Poste G., Schaeffer B. E., Vail W. J. Membrane fusion and molecular segregation in phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 30;352(1):10–28. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontecorvo G. Production of mammalian somatic cell hybrids by means of polyethylene glycol treatment. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):397–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01538671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Allison A. C. Membrane fusion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 28;300(4):421–465. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(73)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B. Polykaryocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:327–342. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravazzola M., Malaisse-Lagae F., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Malaisse W. J., Orci L. Patterns of calcium localization in pancreatic endocrine cells. J Cell Sci. 1976 Jun;21(1):107–117. doi: 10.1242/jcs.21.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Benditt E. P. Wound healing and collagen formation. V. Quantitative electron microscope radioautographic observations of proline-H3 utilization by fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1965 Oct;27(1):83–106. doi: 10.1083/jcb.27.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toister Z., Loyter A. Ca 2+ -induced fusion of avian erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):719–724. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toister Z., Loyter A. The mechanism of cell fusion. II. Formation of chicken erythrocyte polykaryons. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):422–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J., Ahkong Q. F., Botham G. M., Quirk S. J., Lucy J. A. Changes in the distribution of intramembranous particles in hen erythrocytes during cell fusion induced by the bivalent-cation ionophore A23187. Biochem J. 1976 Sep 15;158(3):651–653. doi: 10.1042/bj1580651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakai N., Kulka R. G., Loyter A. Fusion of human erythrocyte ghosts promoted by the combined action of calcium and phosphate ions. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):696–699. doi: 10.1038/263696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








