Abstract
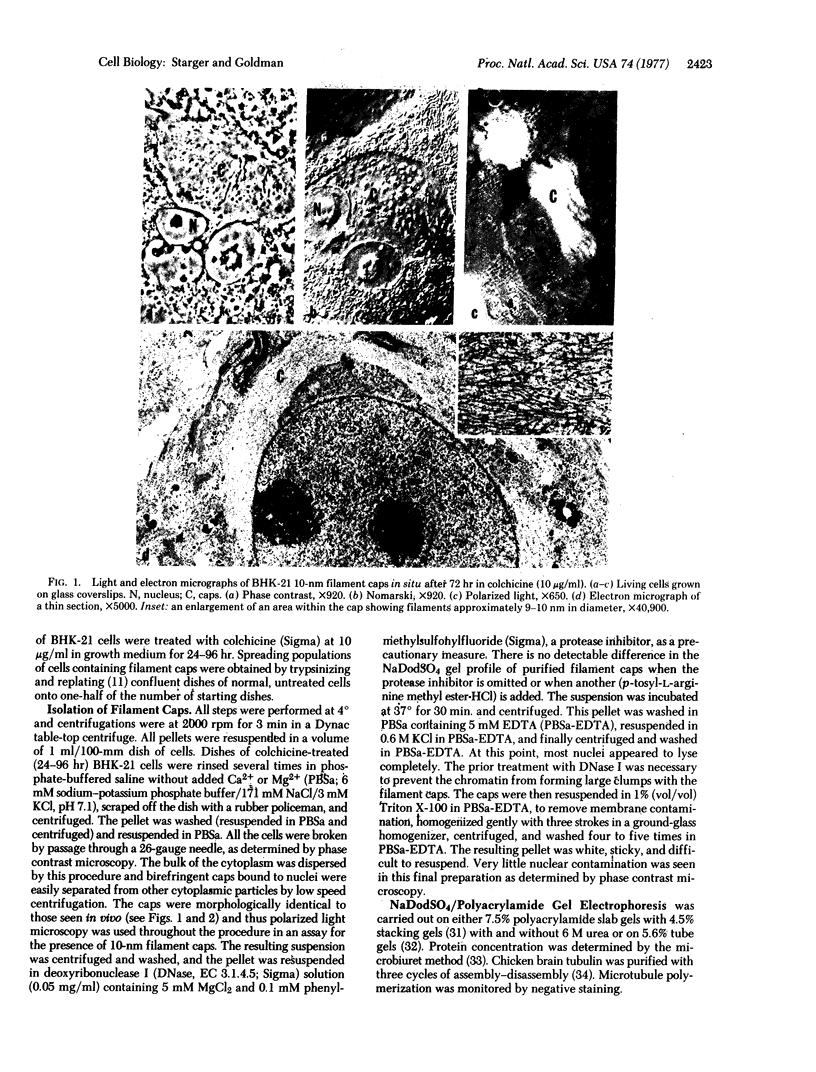
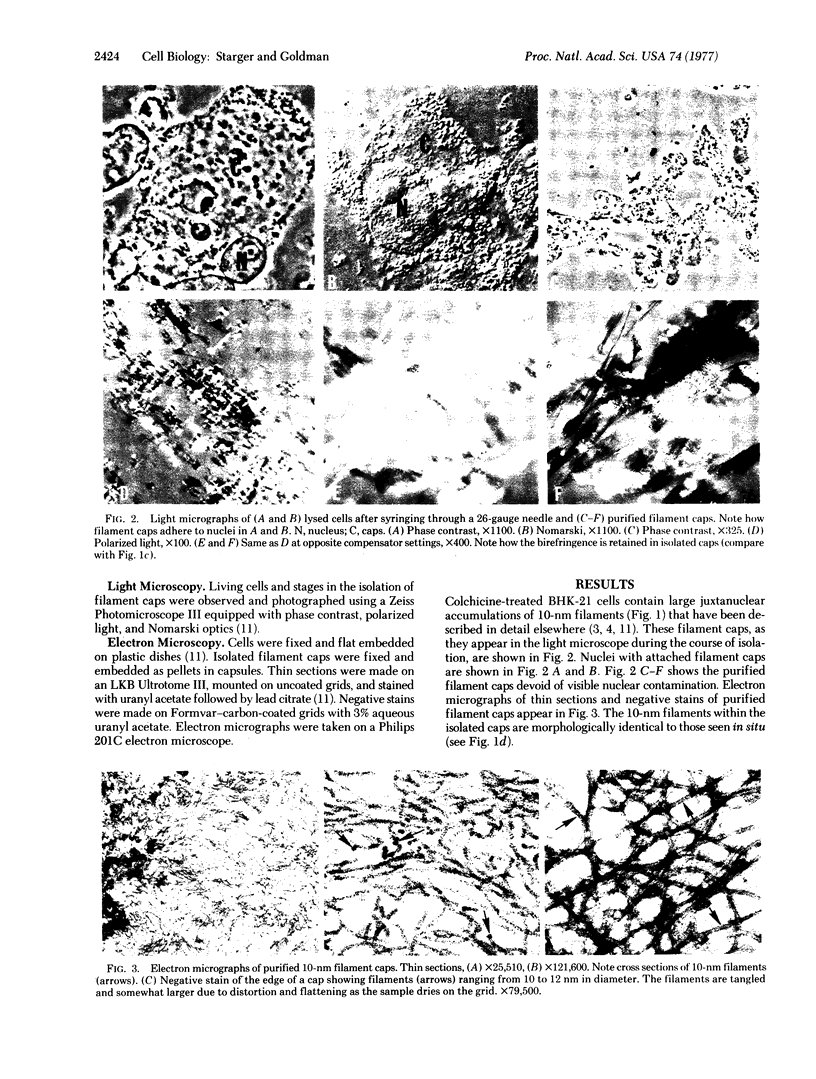
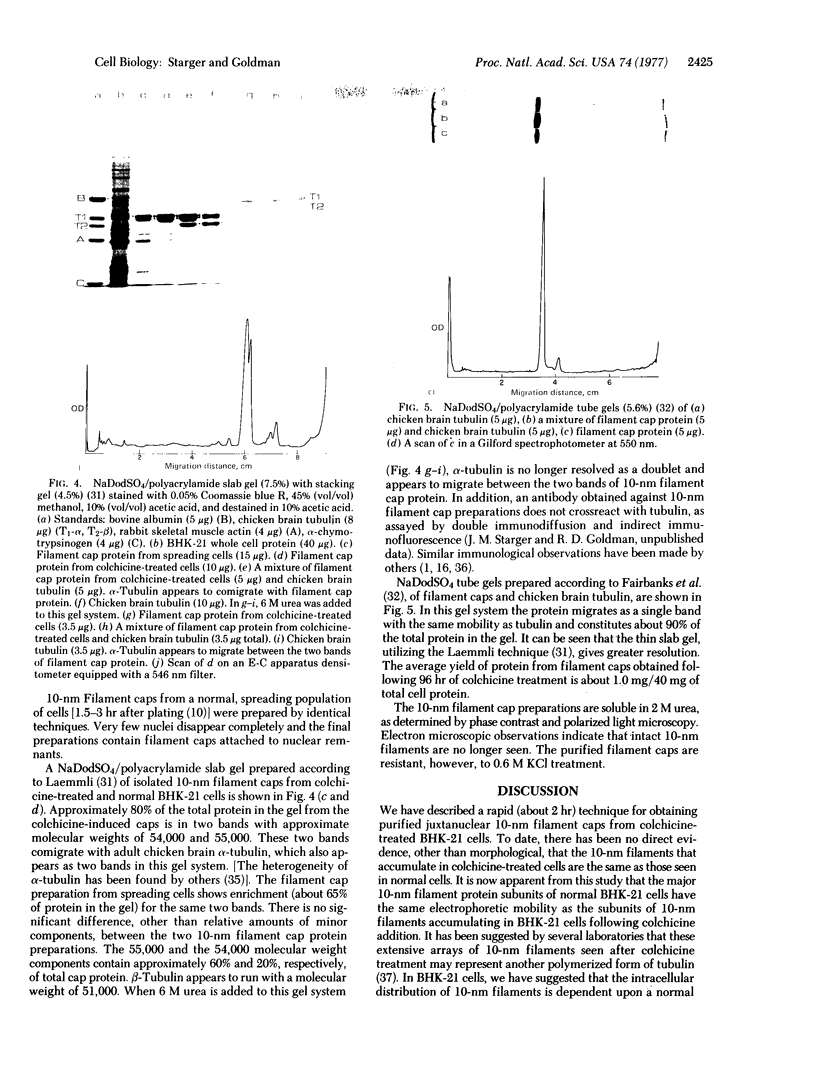
A procedure for isolating 10-nm filaments as juxtanuclear caps from normal and colchicine-treated BHK-21 cells is described. These aggregates of 10-nm filaments retain their birefringence and their structural integrity. The major proteins comprising the filament preparations can be resolved as two bands on sodium dodecyl sulfate gels, corresponding to approximate molecular weights of 54,000 and 55,000.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett D., Angelo G. M. Maternal characteristics of hatching enzymes in hybrid sea urchin embryos. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Oct;57(2):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibring T., Baxandall J., Denslow S., Walker B. Heterogeneity of the alpha subunit of tubulin and the variability of tubulin within a single organism. J Cell Biol. 1976 May;69(2):301–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blose S. H., Chacko S. Rings of intermediate (100 A) filament bundles in the perinuclear region of vascular endothelial cells. Their mobilization by colcemid and mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):459–466. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecher S. The occurrence and possible role of 80-100 A filaments in PtKl cells. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Dec;96(2):303–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90261-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke P. H., Chase R. H. Potassium chloride-insoluble myofilaments in vertebrate smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jun;66(2):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke P. A filamentous cytoskeleton in vertebrate smooth muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):539–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F., Winslow B. The protein subunit of calf brain neurofilament. J Neurobiol. 1974;5(2):119–133. doi: 10.1002/neu.480050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felix H., Strauli P. Different distribution pattern of 100-A filaments in resting and locomotive leukaemia cells. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):604–606. doi: 10.1038/261604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. S., Newby B. J. Neurofilament disguise, destruction and discipline. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):586–589. doi: 10.1038/256586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Berg G., Bushnell A., Chang C. M., Dickerman L., Hopkins N., Miller M. L., Pollack R., Wang E. Fibrillar systems in cell motility. Ciba Found Symp. 1973;14:83–107. doi: 10.1002/9780470719978.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Follett E. A. Birefringent filamentous organelle in BHK-21 cells and its possible role in cell spreading and motility. Science. 1970 Jul 17;169(3942):286–288. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3942.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Lazarides E., Pollack R., Weber K. The distribution of actin in non-muscle cells. The use of actin antibody in the localization of actin within the microfilament bundles of mouse 3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Feb;90(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D. The role of three cytoplasmic fibers in BHK-21 cell motility. I. Microtubules and the effects of colchicine. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):752–762. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D. The use of heavy meromyosin binding as an ultrastructural cytochemical method for localizing and determining the possible functions of actin-like microfilaments in nonmuscle cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Jul;23(7):529–542. doi: 10.1177/23.7.1095652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huneeus F. C., Davison P. F. Fibrillar proteins from squid axons. I. Neurofilament protein. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):415–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITZHAKI R. F., GILL D. M. A MICRO-BIURET METHOD FOR ESTIMATING PROTEINS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Dec;9:401–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Mitosis and intermediate-sized filaments in developing skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1968 Sep;38(3):538–555. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. S., Sinex F. M. On the relationship of brain filaments to microtubules. J Neurochem. 1974 Mar;22(3):321–326. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb07594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. O., Subrahmanyan L., Turnbull C., Kalnins V. I. Localization of the neurofilament protein in neuroblastoma cells by immunofluorescent staining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3192–3196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. E. Fine structure of desmosomes. , hemidesmosomes, and an adepidermal globular layer in developing newt epidermis. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jan;28(1):51–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Hubbard B. D. Immunological characterization of the subunit of the 100 A filaments from muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4344–4348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Albert S., DeVries G. H., Norton W. T. Isolation of filaments from brain. Science. 1971 Dec 17;174(4015):1242–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4015.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Gaskin F., Cantor C. R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):765–768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H., Shelanski M. L., Terry R. D. Effects of mitotic spindle inhibitors on neurotubules and neurofilaments in anterior horn cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):224–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Dahl D., Schachner M., Shelanski M. L. Biochemistry of the filaments of brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):529–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]