Abstract
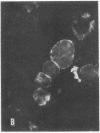
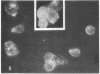
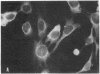
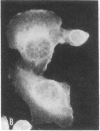
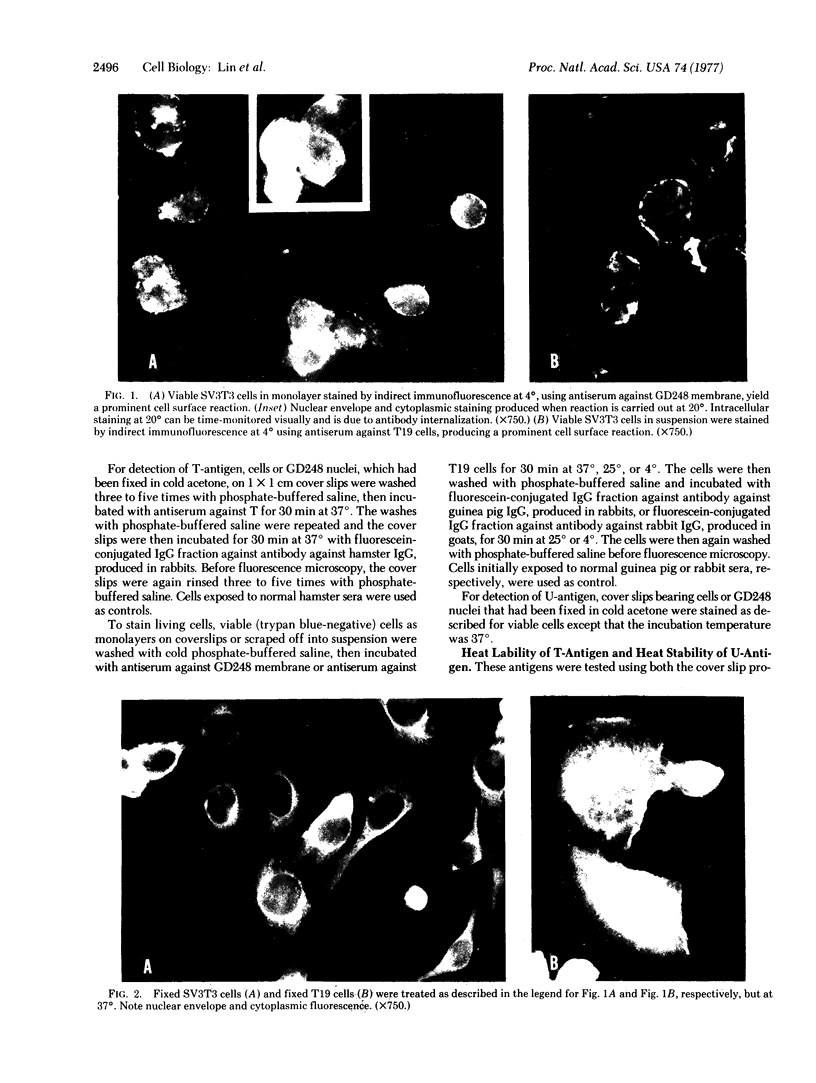
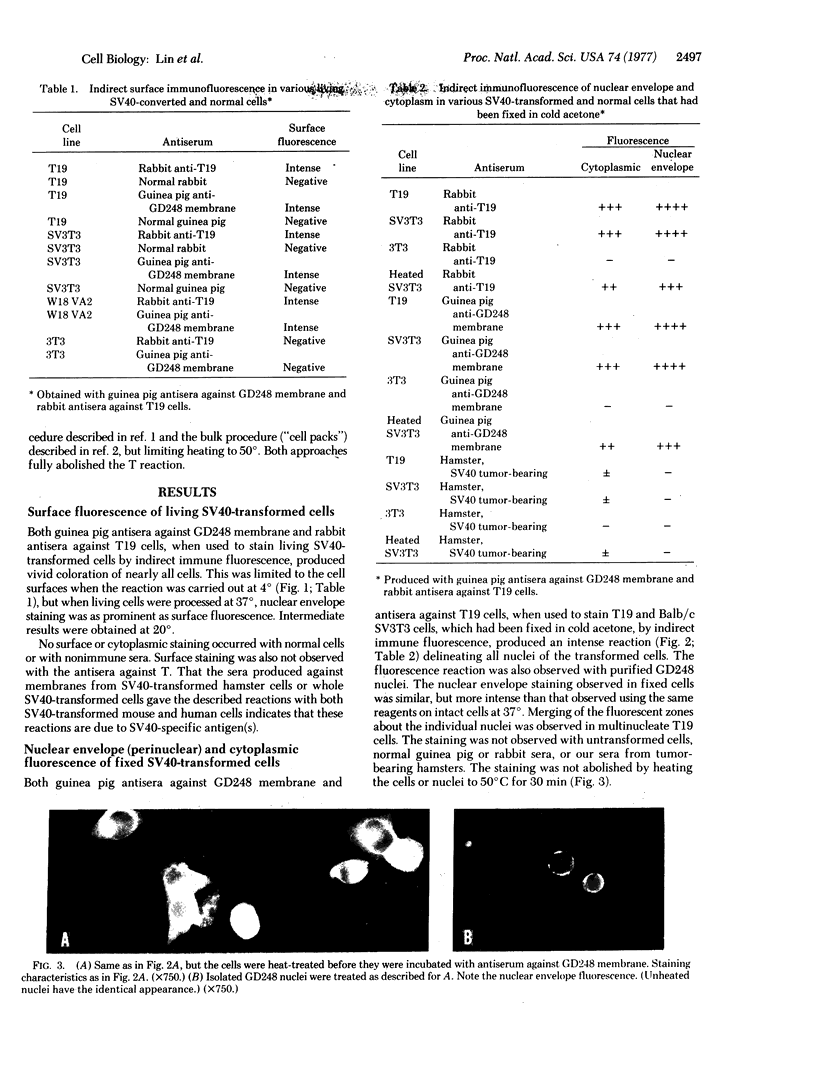
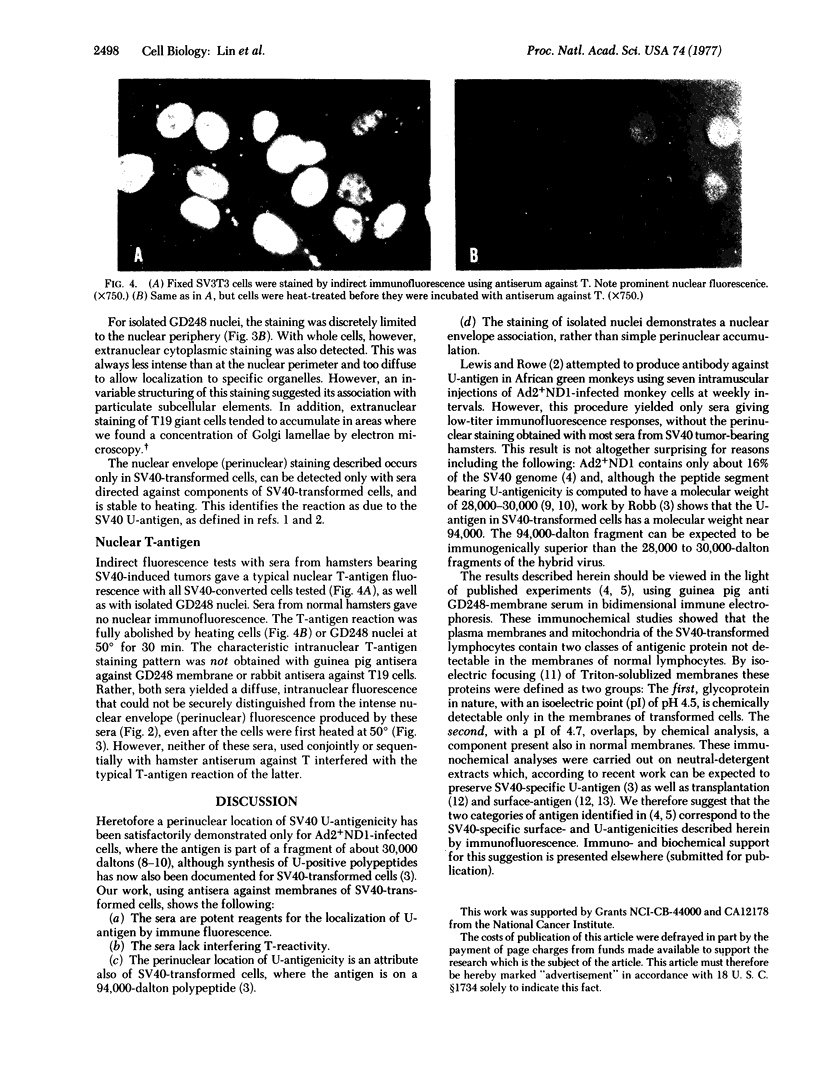
Nucleus- and mitochondrion-free membranes from hamster lymphocytes transformed by simian virus 40 (SV40), GD248 cells, cause guinea pigs to produce immune sera that reveal the presence in GD248 plasma membranes and mitochondria of two types of glycoprotein that are not detected in membranes of normal lymphocytes [Schmidt-Ullrich, R., Thompson, W. S. & Wallach, D. F. H. (1977) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 643-647]. Indirect immune fluorescence of living, SV40-transformed T19 hamster reticulum cells, Balb/c 3T3 mouse fibroblasts, and W18 VA2 human fibroblasts, using the antisera against GD248 membrane, at 4° produced a distinct cell surface fluorescence; however, above 20°, staining at the nuclear perimeter, the SV40 U-antigen reaction, becomes equally prominent. In SV40-transformed cells that had been fixed in cold acetone, as well as in purified GD248 nuclei, thermostable U-antigen staining is dramatic, but there is no reaction for nuclear T-antigen. Rabbit antisera against T19 cells gave immunofluorescence reactions equivalent to those obtained with the antisera against GD248 cells. Normal guinea pig or rabbit sera and cells that had not been transformed by SV40 gave no reaction. Our sera from tumor-bearing hamsters gave only nuclear T-antigen fluorescence. The results indicate the presence of related, SV40-specific antigens in the surface membranes, nuclear envelope, and possibly other intracellular organelles of SV40-transformed cells.
Keywords: immunofluorescence, antisera against membrane, U-antigen, isolated nuclei, T-antigen
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang C., Pancake S. J., Luborsky S. W., Mora P. T. Detergent solubilization and partial purification of tumor specific surface and transplantation antigens from SV40-virus-transformed mouse cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Feb 15;19(2):258–266. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamandopoulos G. T. Induction of lymphocytic leukemia, lymphosarcoma, reticulum cell sarcoma, and osteogenic sarcoma in the Syrian golden hamster by oncogenic DNA simian virus 40. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 May;50(5):1347–1365. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.5.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Anderson C., Sharp P. A., Sambrook J. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. I. Host range mutants of Ad2+ND1. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1237–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1237-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodzicker T., Lewis J. B., Anderson C. W. Conditional lethal mutants of adenovirus type 2-simian virus 40 hybrids. II. Ad2+ND1 host-range mutants that synthesize fragments of the Ad2+ND1 30K protein. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):559–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.559-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarasch E. D., Reilly C. E., Comes P., Kartenbeck J., Franke W. W. Isolation and characterization of nuclear membranes from calf and rat thymus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1973 Aug;354(8):974–986. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1973.354.2.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Levin M. J., Wiese W. H., Crumpacker C. S., Henry P. H. A nondefective (competent) adenovirus-SV40 hybrid isolated from the AD.2-SV40 hybrid population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1128–1135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Rowe W. P. Studies on nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. I. A newly characterized simian virus 40 antigen induced by the Ad2+ND 1 virus. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):189–197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.189-197.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luborsky S. W., Chang C., Pancake S. J., Mora P. T. Detergent solubilized and molecular weight estimation of tumor specific surface antigen from SV40 virus transformed cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):990–996. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90752-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A. Identification of simian virus 40 tumor and U antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Thompson W. S., Wallach D. F. Antigenic distinctions of glycoproteins in plasma and mitochondrial membranes of lymphoid cells neoplastically transformed by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):643–647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Verma S. P., Wallach D. F. Anomalous side chain amidation in plasma membrane proteins of simian virus 40-transformed lymphocytes indicated by isoelectric focussing and laser Raman spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 1;67(3):1062–1069. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90782-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Wallach D. F., Davis F. D., 2nd Membranes of normal hamster lymphocytes and lymphoid cells neoplastically transformed by simian virus 40. II. Plasma membrane proteins analyzed by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and two-dimensional immune electrophoresis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Nov;57(5):1117–1126. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.5.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Martin H. Simian virus 40-specific proteins in HeLa cells infected with nondefective adenovirus 2-simian virus 40 hybrid viruses. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1236–1247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1236-1247.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]