Abstract
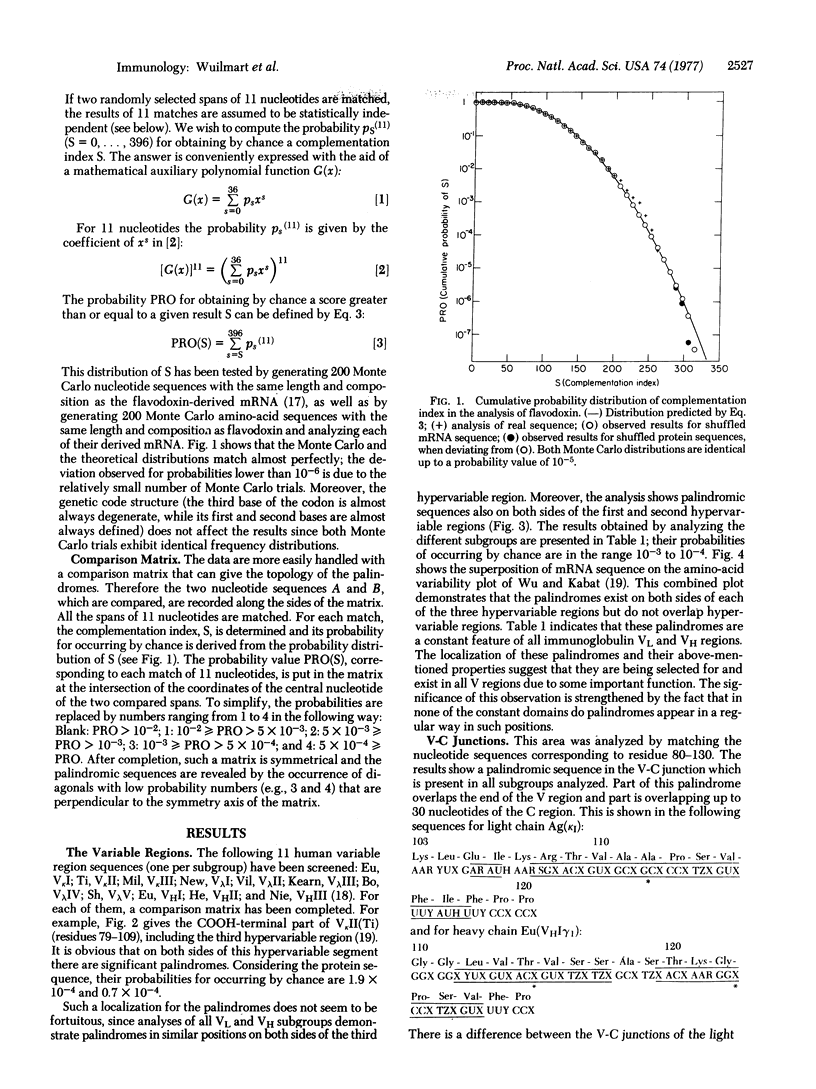
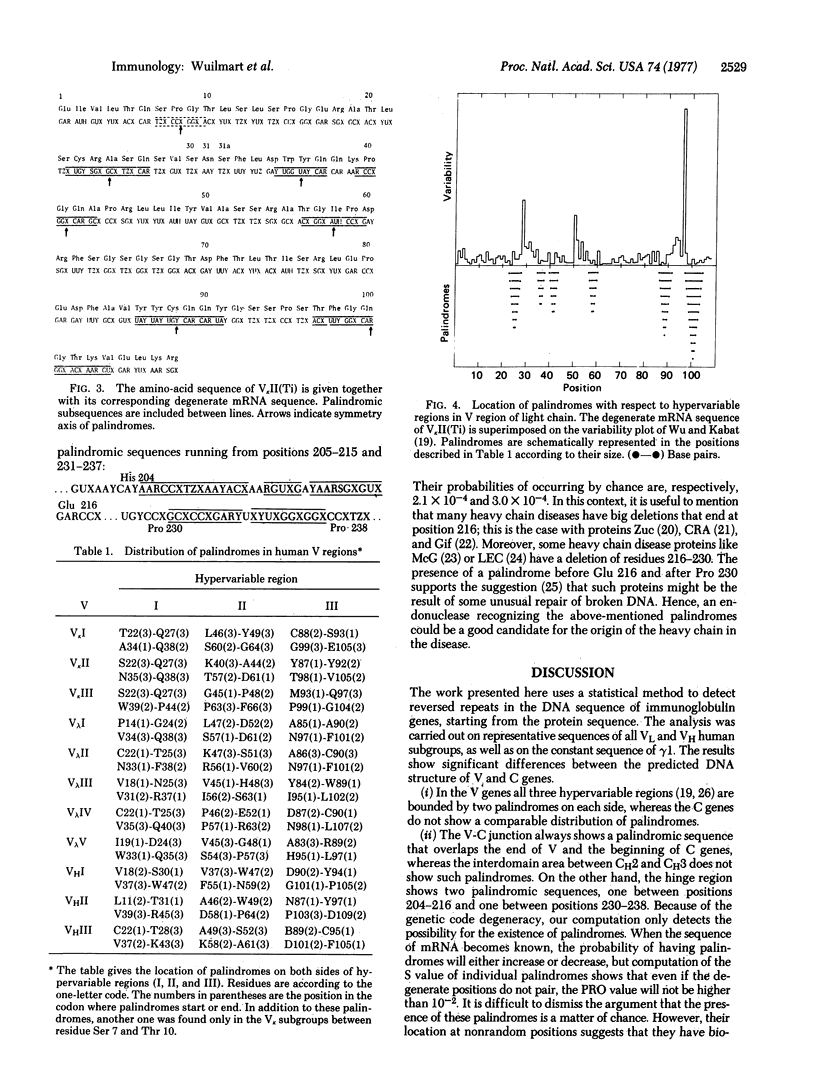
We present a statistical method for detection of palindromes in mRNA or DNA, starting from the protein sequence. Analysis of immunoglobulin genes by this method demonstrates that palindromic sequences are not randomly distributed. They are located at each side of the hypervariable regions in the variable (V) genes, whereas no such regular design is observed in the constant (C) genes. In addition, palindromic sequences overlap the V-C junction in all immunoglobulin classes and significant palindromes are present near residue 216 of the heavy chain, which is the end of deletions in many heavy chain diseases. The relevance of these palindromes to gene translocation and generation of diversity in antibodies is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner S., Milstein C. Origin of antibody variation. Nature. 1966 Jul 16;211(5046):242–243. doi: 10.1038/211242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Hypervariable regions, idiotypy, and the antibody-combining site. Adv Immunol. 1975;20:1–40. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60205-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N. Transposable genetic elements and plasmid evolution. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):731–738. doi: 10.1038/263731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. M., Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Molecular defect in a gamma-2 heavy chain. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):187–189. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Deutsch H. F., Smithies O. Hinge-region deletion localized in the IgG-globulin Mcg. Immunochemistry. 1973 Feb;10(2):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. An improved method of testing for evolutionary homology. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsheit A. B., Ray D. S. Conformations of the single-stranded DNA of bacteriophage M13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1534–1541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fougereau M., Bourgois A., de Preval C., Rocca-Serra J., Schiff C. The complete sequence of the murine monoclonal immunoglobulin MOPC 173 (IgG2a): genetic implications. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Sep-Oct;127(5):607–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Frangione B. The molecular defect in a protein (CRA) found in gamma-1 heavy chain disease, and its genetic implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):187–191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. Somatic translocation of antibody genes. Nature. 1970 Jul 25;227(5256):341–348. doi: 10.1038/227341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. The genetic control of immunoglobulin synthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:1–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Maxam A. The nucleotide sequence of the lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3581–3584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Campbell J. H., Elgin S. C. The organization, expression, and evolution of antibody genes and other multigene families. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:305–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Evidence for somatic rearrangement of immunoglobulin genes coding for variable and constant regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3628–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Wu T. T. Attempts to locate complementarity-determining residues in the variable positions of light and heavy chains. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:382–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl J. W. N- and C-terminal sequences of a heavy chain disease protein and its genetic implications. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1386–1387. doi: 10.1038/2151386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Backman K., Humayun M. Z., Jeffrey A., Maurer R., Meyer B., Sauer R. T. Autoregulation and function of a repressor in bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):156–161. doi: 10.1126/science.959843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reanney D. Extrachromosomal elements as possible agents of adaptation and development. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):552–590. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.552-590.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivat C., Schiff C., Rivat L., Ropartz C., Fougereau M. Deletion of hinge region of human myeloma IgG1 molecule (protein LEC) associated with nonexpression of G1m (3) and Km (1, 2) allotypes. A possible genetic explanation at the DNA level. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):545–551. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. J. Restriction endonucleases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1976 Nov;4(2):123–164. doi: 10.3109/10409237609105456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryskov A. P., Saunders G. F., Farashyan V. R., Georgiev G. P. Double-helical regions in nuclear precursor of mRNA (pre-mRNA). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 8;312(1):152–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H., Voss H., Gucker S. Structure of the DNA of bacteriophage fd. II. Isolation and characterization of a DNA fraction with double strand-like properties. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):445–458. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Cohen S. N., Davidson N. Electron microscope heteroduplex studies of sequence relations among plasmids of Escherichia coli. II. Structure of drug resistance (R) factors and F factors. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):235–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D. M., Fanning E. M., Percy M. E., Parr D. M., Connell G. E. Deletions in immunoglobulin polypeptide chains as evidence for breakage and repair in DNA. Science. 1971 May 7;172(3983):574–577. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3983.574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. Molecular mechanism for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2483–2487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Haniu M., Yasunobu K. T., Mayhew S., Massey V. Amino acid sequence of the Peptostreptococcus elsdenii flavodoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):886–892. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90794-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. E., Jr, Radman M. A mechanism for initiation of genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3619–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


