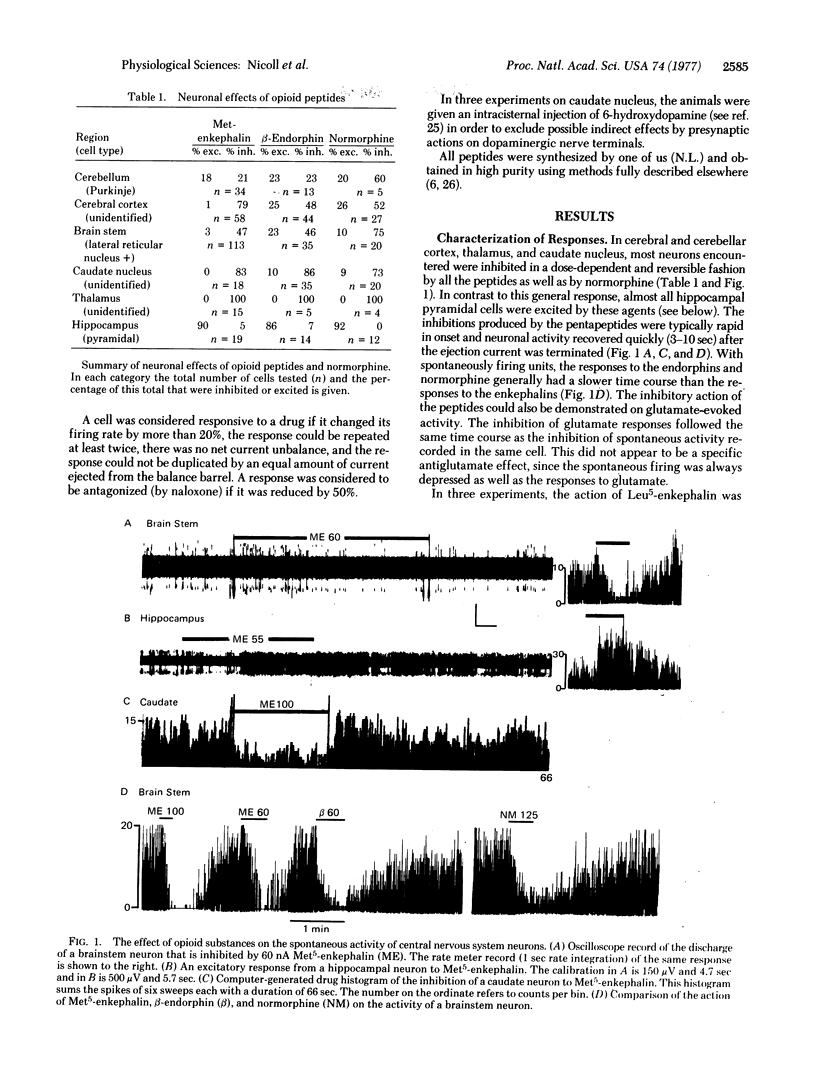
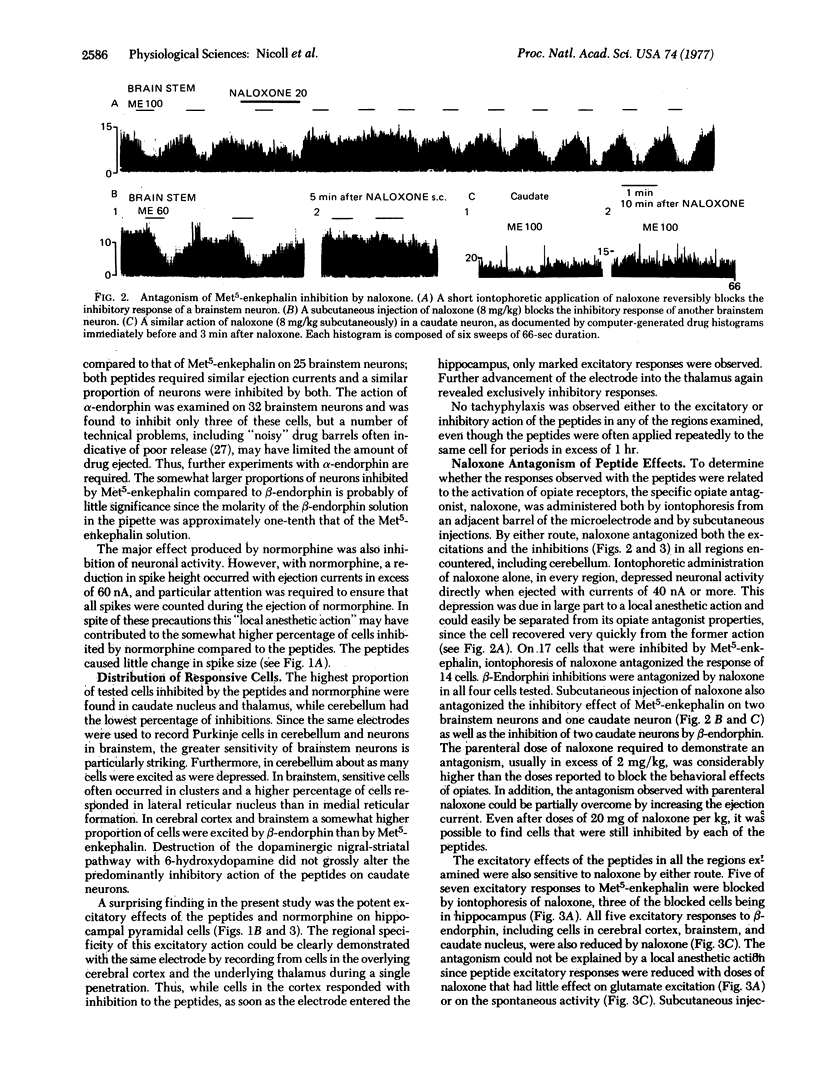
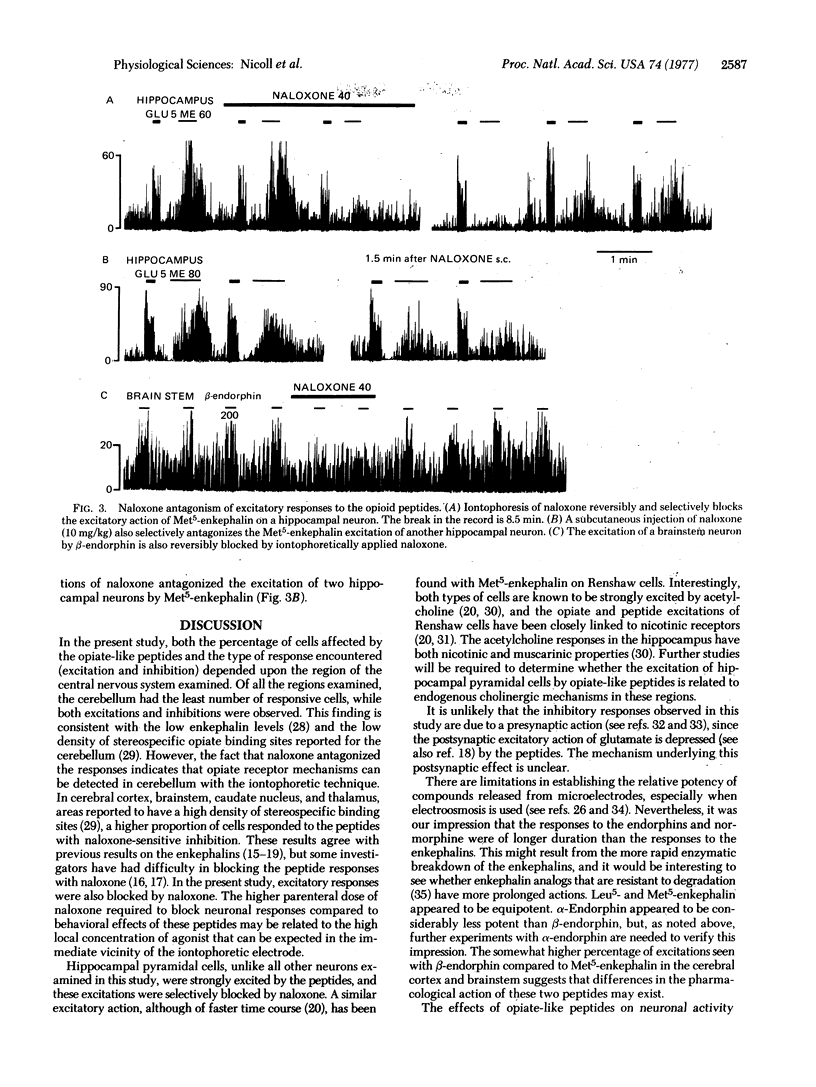
Abstract
The brain peptides alpha- and beta-endorphin, leucine- and methionine-enkephalin, as well as the opiate normorphine, have been evaluated by microiontophoresis for their effects on neuronal activity in several regions of the rat brain. In cerebral cortex, brainstem, caudate nucleus, and thalamus, most responsive cells were inhibited by the peptides and by normorphine, while in hippocampus all responsive cells were excited. Both inhibitory and excitatory responses were blocked by the narcotic antagonist naloxone. Occurrence of responsive cells encountered in a particular region was loosely correlated with density of stereospecific opiate binding sites as reported by others. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that the endorphins and enkephalins may represent a new class of central neurotransmitters; among other functions, these peptides may play a role in the regulation of behavior and the expression of psychopharmacological agents such as the opiate alkaloids.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belluzzi J. D., Grant N., Garsky V., Sarantakis D., Wise C. D., Stein L. Analgesia induced in vivo by central administration of enkephalin in rat. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):625–626. doi: 10.1038/260625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird S. J., Aghajanian G. K. The cholinergic pharmacology of hippocampal pyramidal cells: a microiontophoretic study. Neuropharmacology. 1976 May;15(5):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(76)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Hulme E. C. C fragment of lipotropin has a high affinity for brain opiate receptors. Nature. 1976 Apr 29;260(5554):793–795. doi: 10.1038/260793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E., Algeri S., Groppetti A., Revuelta A., Costa E. Lesions of central norepinephrine terminals with 6-OH-dopamine: biochemistry and fine structure. Science. 1969 Dec 5;166(3910):1284–1286. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3910.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E. To spritz or not to spritz: the doubtful value of aimless iontophoresis. Life Sci. 1974 May 16;14(10):1819–1834. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F., Segal D., Ling N., Guillemin R. Endorphins: profound behavioral effects in rats suggest new etiological factors in mental illness. Science. 1976 Nov 5;194(4265):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.185694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. B., Briggs I., Gayton R. J., Lambert L. A. Effects of microiontophoretically applied methionine-enkephalin on single neurones in rat brain. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):425–426. doi: 10.1038/261425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buscher H. H., Hill R. C., Römer D., Cardinaux F., Closse A., Hauser D., Pless J. Evidence for analgesic activity of enkephalin in the mouse. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):423–425. doi: 10.1038/261423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. K., Fong B. T., Pert A., Pert C. B. Opiate receptor affinities and behavioral effects of enkephalin: structure-activity relationship of ten synthetic peptide analogues. Life Sci. 1976 Jun 15;18(12):1473–1481. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Goldstein A., Hi C. H. Opioid activity of a peptide, beta-lipotropin-(61-91), derived from beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1821–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Dray A. Effects of enkephalin and morphine on Renshaw cells in feline spinal cord. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):603–604. doi: 10.1038/262603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duggan A. W., Davies J., Hall J. G. Effects of opiate agonists and antagonists on central neurons of the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jan;196(1):107–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elde R., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Terenius L. Immunohistochemical studies using antibodies to leucine-enkephalin: initial observations on the nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1976 Aug;1(4):349–351. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederickson R. C., Norris F. H. Enkephalin-induced depression of single neurons in brain areas with opiate receptors--antagonism by naloxone. Science. 1976 Oct 22;194(4263):440–442. doi: 10.1126/science.10625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R., Hoffer B. J., Woodward D. J. A quantitative microiontophoretic analysis of the responses of central neurones to noradrenaline: interactions with cobalt, manganese, verapamil and dichloroisoprenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Aug;54(4):529–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gent J. P., Wolstencroft J. H. Effects of methionine-enkephalin and leucine-enkephalin compared with those of morphine on brainstem neurones in cat. Nature. 1976 Jun 3;261(5559):426–427. doi: 10.1038/261426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld Z., Kelly J. S., Renaud L. P. The in vivo neuropharmacology of amino-oxyacetic acid in the cerebral cortex of the cat. Brain Res. 1972 Jul 20;42(2):319–335. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90534-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Ling N., Burgus R. Endorphines, peptides, d'origine hypothalamique et neurohypophysaire à activité morphinomimétique. Isolement et structure moléculaire de l'alpha-endorphine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1976 Feb 23;282(8):783–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R. Somatostatin inhibits the release of acetylcholine induced electrically in the myenteric plexus. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1653–1654. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. G., Pepper C. M., Mitchell J. F. Depression of nociceptive and other neurones in the brain by iontophoretically applied met-enkephalin. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):604–606. doi: 10.1038/262604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Regional distribution of opiate receptor binding in monkey and human brain. Nature. 1973 Oct 26;245(5426):447–450. doi: 10.1038/245447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte C., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor binding in primate spinal cord: distribution and changes after dorsal root section. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 13;112(2):407–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus L. H., Ling N., Guillemin R. beta-Lipotropin as a prohormone for the morphinomimetic peptides endorphins and enkephalins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2156–2159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Burgus R., Guillemin R. Isolation, primary structure, and synthesis of alpha-endorphin and gamma-endorphin, two peptides of hypothalamic-hypophysial origin with morphinomimetic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3942–3946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Guillemin R. Morphinomimetic activity of synthetic fragments of beta-lipotropin and analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3308–3310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh H. H., Tseng L. F., Wei E., Li C. H. beta-endorphin is a potent analgesic agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2895–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Simantov R., Snyder S. H. Characterization of an endogenous morphine-like factor(enkephalin) in mammalian brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 May;12(3):504–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Pert A., Chang J. K., Fong B. T. (D-Ala2)-Met-enkephalinamide: a potent, long-lasting synthetic pentapeptide analgesic. Science. 1976 Oct 15;194(4262):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.968485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmoiraghi G. C., Weight F. Micromethods in neuropharmacology: an approach to the study of anesthetics. Anesthesiology. 1967 Jan-Feb;28(1):54–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker W. J., Balentine L. T., Siggins G. R., Hoffer B. J., Henriksen S. J., Bloom F. E. Characteristics of the release of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate from micropipets by microiontophoresis. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(2):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siggins G. R., Henriksen S. J. Analogs of cyclic adenosine monophosphate: correlation of inhibition of Purkinje Neurons with Protein Kinase Activation. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):559–561. doi: 10.1126/science.167439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Kuhar M. J., Pasternak G. W., Snyder S. H. The regional distribution of a morphine-like factors enkephalin in monkey brain. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 16;106(1):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snyder S. H. Morphine-like peptides in mammalian brain: isolation, structure elucidation, and interactions with the opiate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2515–2519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei E., Loh H. Physical dependence of opiate-like peptides. Science. 1976 Sep 24;193(4259):1262–1263. doi: 10.1126/science.986687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieglgänsberger W., Fry J. P., Herz A., Moroder L., Wünsch E. Enkephalin-induced inhibition of cortical neurones and the lack of this effect in morphine tolerant/dependent rats. Brain Res. 1976 Oct 8;115(1):160–164. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90832-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



