Abstract
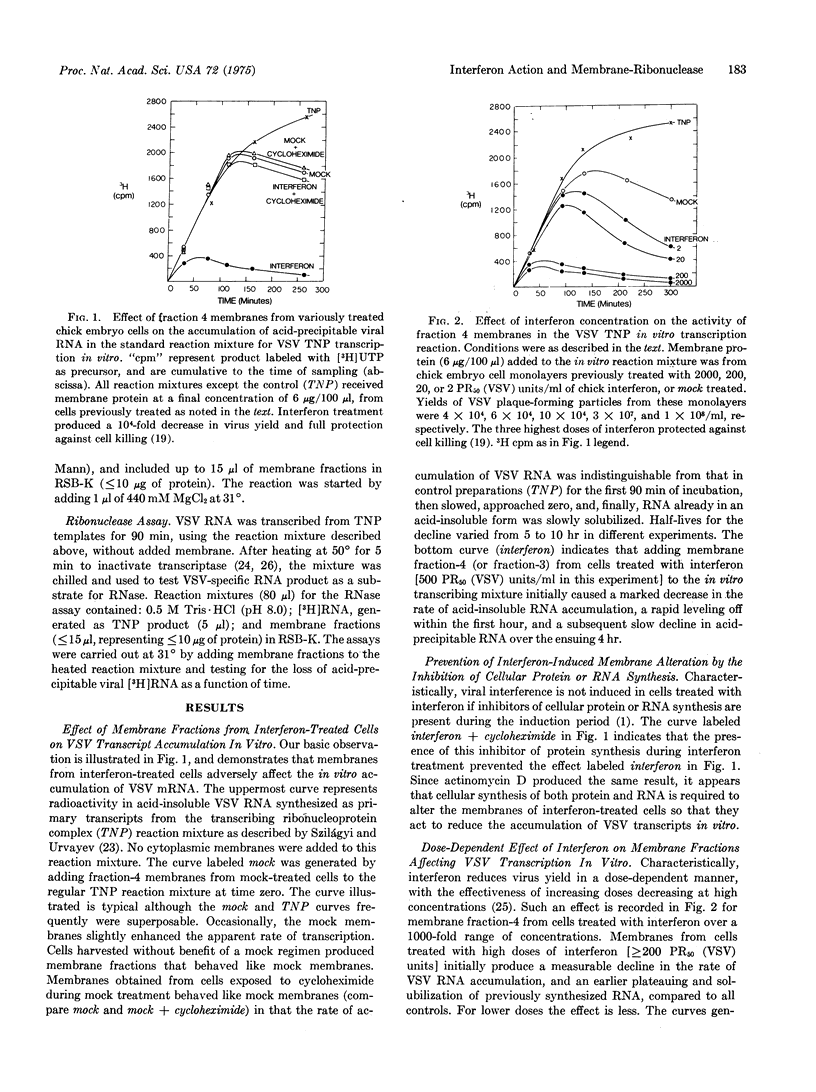
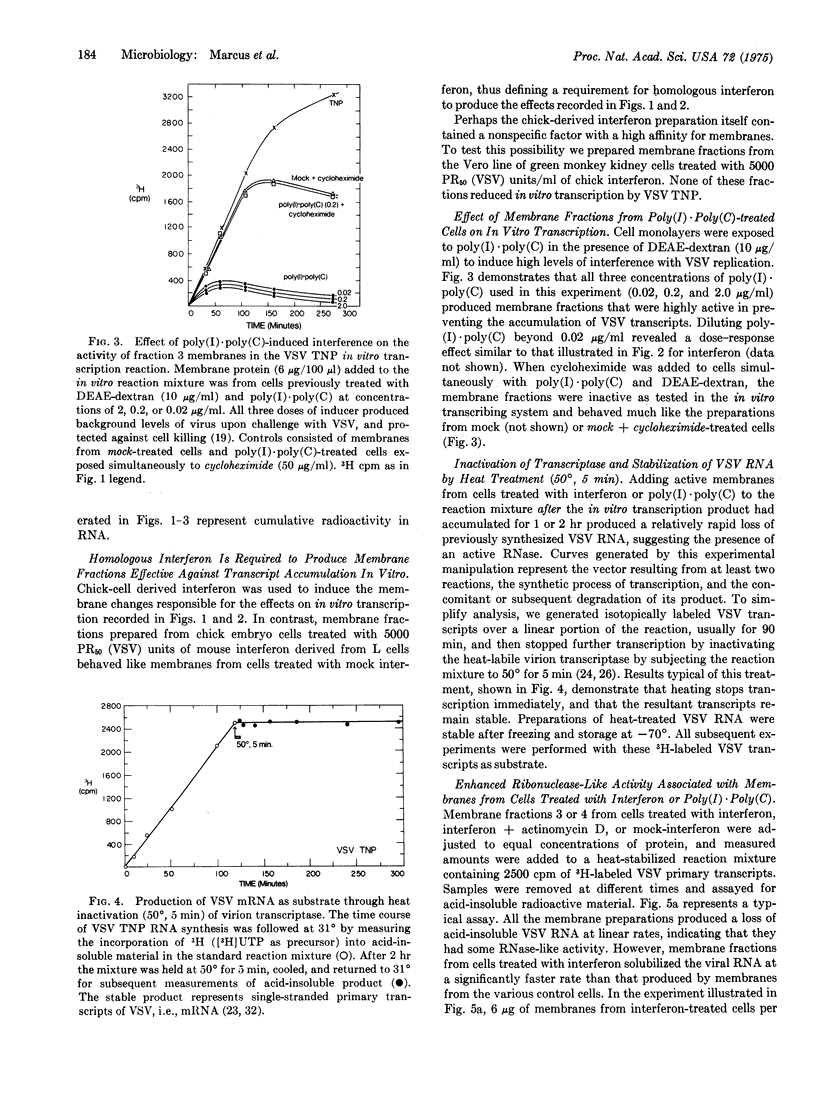
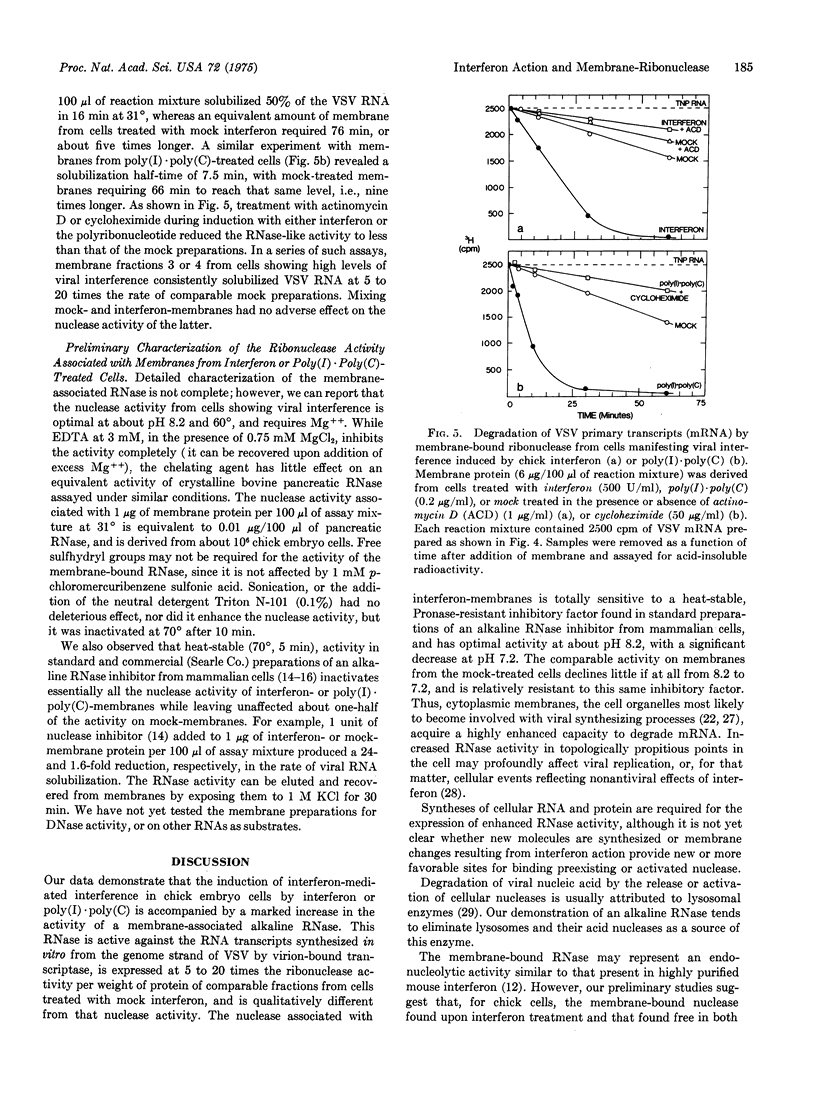
Membrane fractions from chick embryo cells manifesting viral interference mediated by interferon or poly(I)-poly(C) contain high levels of an alkaline ribonuclease. Enhanced RNase activity is not observed when inhibitors of cell protein or RNA synthesis are present during interferon treatment, or when heterologous interferon is used. The RNase associated with comparable membrane fractions from cells treated with mock-interferon is about 1/10 as active, and shows qualitative differences. In principle, divergent views of interferon action may be reconciled to a common mode of action by postulating that viral interference results from a newly induced or activated RNase of cellular origin and proper specificity that acts to reduce the accumulation and functional capacity of newly synthesized viral RNAs, particularly mRNA. Previous data in support of interferon's acting to inhibit virion-derived transcription in vivo are now interpreted as demonstrating enhanced degradation of viral transcripts (mRNA).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean W. J., Jr, Simpson R. W. Primary transcription of the influenza virus genome in permissive cells. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):646–651. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialy H. S., Colby C. Inhibition of early vaccinia virus ribonucleic acid synthesis in interferon-treated chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Virol. 1972 Feb;9(2):286–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.2.286-289.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Roy P. Properties of the product synthesized by vesicular stomatitis virus particles. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):799–814. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in poliovirus biosynthesis. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcoff E., Falcoff R., Lebleu B., Revel M. Correlation between the antiviral effect of interferon treatment and the inhibition of in vitro mRNA translation in noninfected L cells. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):421–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.421-430.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszman M. Y., Bucchini D., Girard M., Lwoff A. Inhibition of poliovirus RNA synthesis by supraoptimal temperatures. J Gen Virol. 1970 Feb;6(2):293–304. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A., Bishop D. H. Primary in vivo transcription of vesicular stomatitis virus and temperature-sensitive mutants of five vesicular stomatitis virus complementation groups. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1238–1252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1238-1252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Metz D. H., Esteban R. M., Tovell D. R., Ball L. A., Kerr I. M. Mechanism of interferon action: inhibition of viral messenger ribonucleic acid translation in L-cell extracts. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1184–1198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1184-1198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Sreevalsan T. Membrane binding of input arbovirus ribonucleic acid: effect of interferon or cycloheximide. J Virol. 1970 Aug;6(2):169–175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.2.169-175.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravell M., Cromeans T. L. Inhibition of early viral ribonucleic acid synthesis in interferon-treated cells infected with frog polyhedral cytoplasmic deoxyribovirus. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):916–919. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90447-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziadei W. D., 3rd, Weideli H., Lengyel P. Endonuclease of high specific activity in a purified mouse interferon preparation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90885-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Graziadei W. D., 3rd, Weideli H., Sopori M. L., Lengyel P. Selective inhibition of viral protein accumulation in interferon-treated cells; nondiscriminate inhibition of the translation of added viral and cellular messenger RNAs in their extracts. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):49–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Sopori M. L., Lengyel P. Release of the inhibition of messenger RNA translation in extracts of interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells by added transfer RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 8;57(3):763–770. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90612-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft N., Shortman K. The phylogeny of the ribonuclease-ribonuclease inhibitor system: its distribution in tissues and its response during leukaemogenesis and aging. Aust J Biol Sci. 1970 Feb;23(1):175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manders E. K., Tilles J. G., Huang A. S. Interferon-mediated inhibition of virion-directed transcription. Virology. 1972 Aug;49(2):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90508-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Engelhardt D. L., Hunt J. M., Sekellick M. J. Interferon action: inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus RNA synthesis induced by virion-bound polymerase. Science. 1971 Nov 5;174(4009):593–598. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4009.593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Salb J. M. Molecular basis of interferon action: inhibition of viral RNA translation. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):502–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus P. I., Sekellick M. J. Cell killing by viruses. I. Comparison of cell-killing, plaque-forming, and defective-interfering particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):321–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Friedman R. M. Stimulation of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction in cell cultures by interferon. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):193–197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.193-197.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxman M. N., Levin M. J. Interferon and transcription of early virus-specific RNA in cells infected with simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):299–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH J. S. Ribonuclease. IX. Further studies on ribonuclease inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:903–915. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH J. S. Ribonuclease. V. Studies on the properties and distribution of ribonuclease inhibitor in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Jul;21(1):34–43. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Joklik W. K. A protein synthesizing system from interferon-treated cells that discriminates between cellular and viral messenger RNAs. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):476–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi J. F., Pringle C. R. Effect of temperature-sensitive mutations on the virion-associated RNA transcriptase of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90351-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilágyi J. F., Uryvayev L. Isolation of an infectious ribonucleoprotein from vesicular stomatitis virus containing an active RNA transcriptase. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):279–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.279-286.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Spandidos D., Georgatsos J. G. An endonuclease activity associated with preparations of chick interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 2;43(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


