Abstract
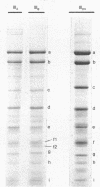
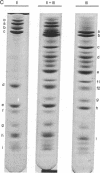
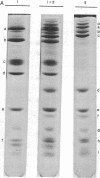
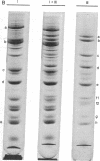
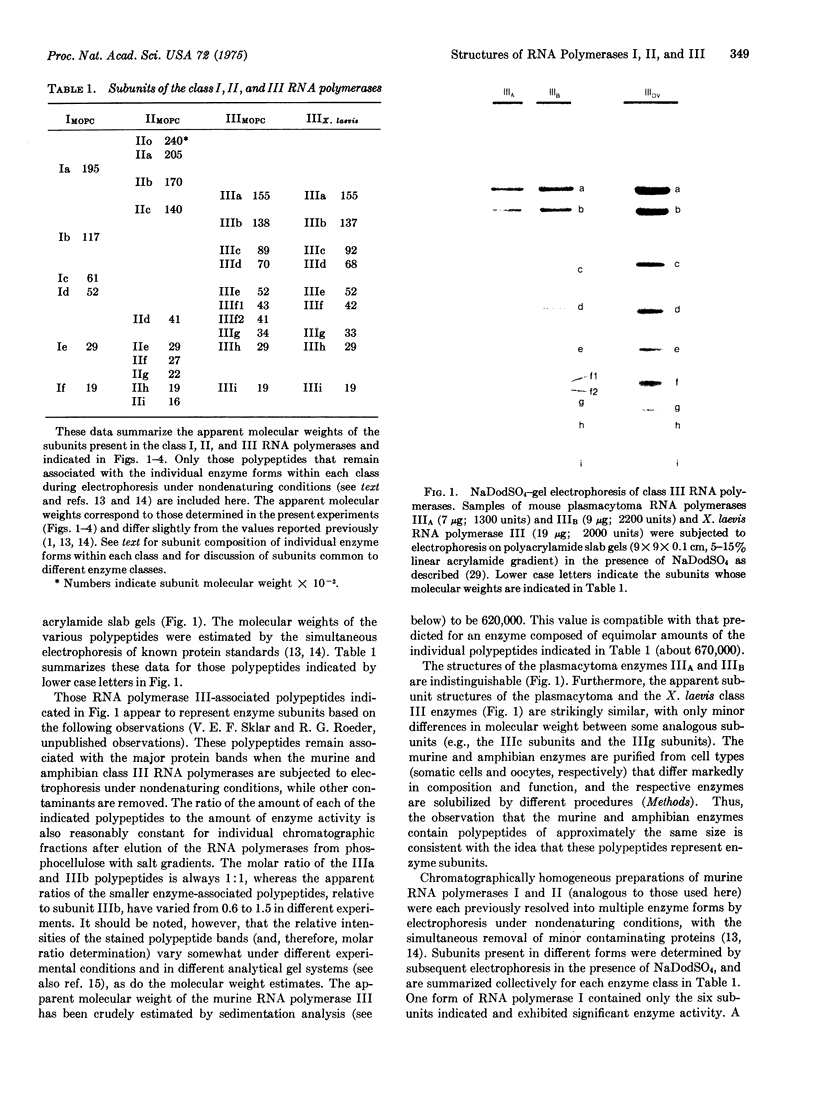
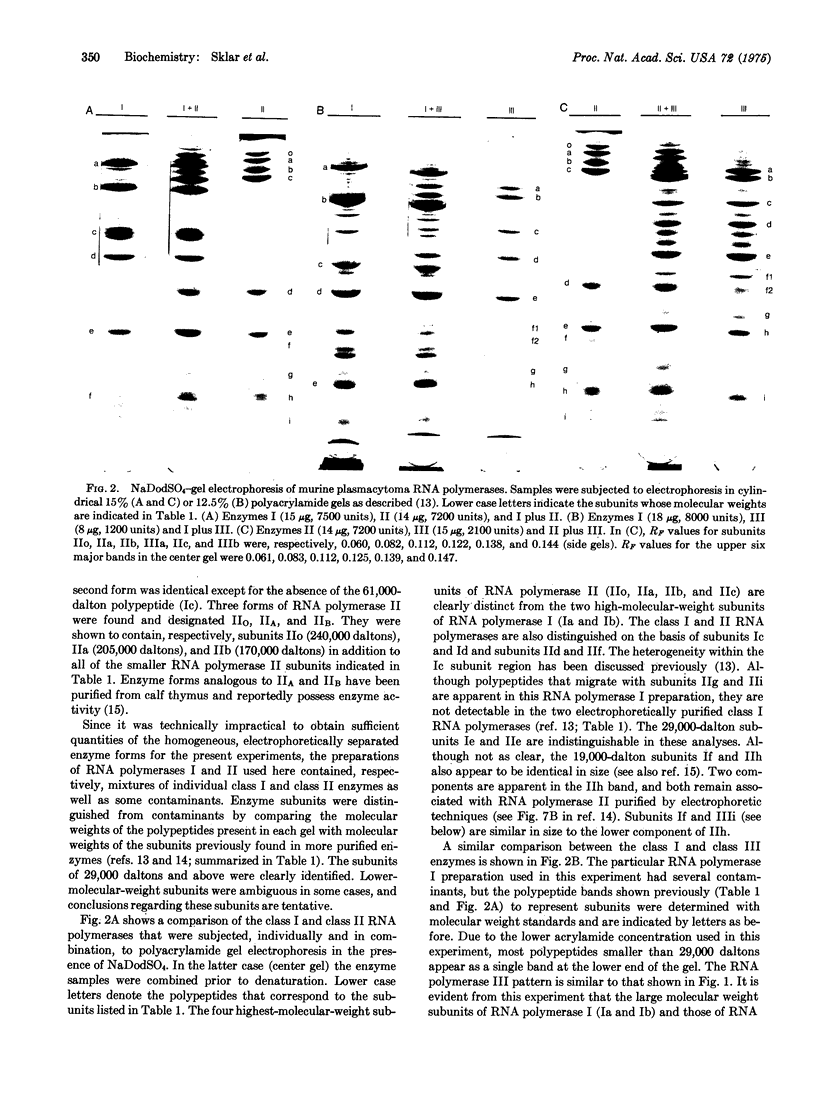
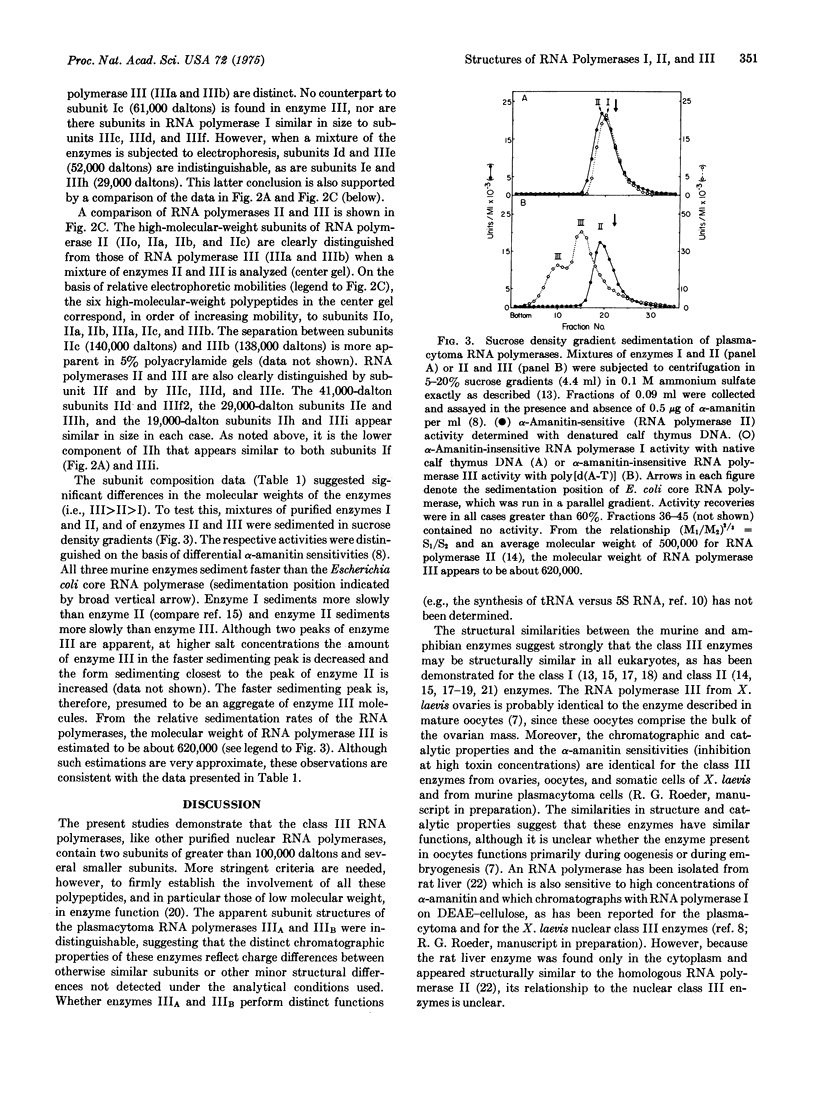
Class III RNA polymerases purified from the murine plasmacytoma MOPC 315 and from Xenopus laevis ovaries were compared. The subunit structures of the chromatographically distinct murine enzymes IIIA and IIIB were indistinguishable and were remarkably similar to that of the amphibian enzyme III. The plasmacytoma class III RNA polymerases were also compared with purified plasmacytoma RNA polymerases I and II. Sedimentation studies indicated that RNA polymerase III si significantly larger than RNA polymerase II, which is slightly larger than RNA polymerase I. Structural analyses showed that the molecular weights of the large subunits present in the class III enzymes (138,000 and 155,000) differ from those of the class II enzymes (140,000 and either 170,000, 205,000, or 240,000) and from those of the class I enzymes (117,000 and 195,000). Some low-molecular-weight subunits are also unique to each enzyme class. These results clearly distinguish the class I, II, and III enzymes on a structural basis. In addition, polypeptides of molecular weight 29,000 and 19,000 were found in all enzyme classes, a polypeptide of molecular weight 52,000 was found only in class I and III enzymes, and a polypeptide of molecular weight 41,000 was found only in class II and III enzymes. These findings are discussed in terms of the function and regulation of the RNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adman R., Schultz L. D., Hall B. D. Transcription in yeast: separation and properties of multiple FNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1702–1706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H. Selective extraction of form I DNA dependent RNA polymerase from rat liver nuclei and its separation into two species. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 11;19(2):232–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingles C. J. Antigenic homology of eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):364–371. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaehning J. A., Stewart C. C., Roeder R. G. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase levels during the response of human peripheral lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gissinger F., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Molecular structures and immunological properties of calf-thymus enzyme AI and of calf-thymus and rat-liver enzymes B. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):421–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Nuret P., Chambon P. Structural evidence for two alpha-amanitin sensitive RNA polymerases in calf thymus. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J. C., Green H. Regulation of RNA synthesis in fibroblasts during transition from resting to growing state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2819–2822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J. C., Green H. Regulation of pre-transfer RNA synthesis during transition from resting to growing state. Cell. 1974 Oct;3(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90122-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Ponta U., Wintersberger E. Purification and properties of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases from yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Aug 18;29(1):110–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in Xenopus laevis. Isolation and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):241–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in Xenopus laevis. Levels of activity during oocyte and embryonic development. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):249–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lawrence C., Thach R. E., Roeder R. G. Encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mouse plasmacytoma cells. II. Effect on host RNA synthesis and RNA polymerases. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.611-619.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase I from the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5898–5906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Sklar V. E., Jaehning J. A., Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5889–5897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifart K. H., Benecke B. J., Juhasz P. P. Multiple RNA polymerase species from rat liver tissue: possible existence of a cytoplasmic enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Aug;151(2):519–532. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90529-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergeant A., Krsmanovic V. KB cell RNA polymerases: occurrence of nucleoplasmic enzyme 3. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 15;35(2):331–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Keller W. Mammalian deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases. I. Purification and properties of an -amanitin-sensitive ribonucleic acid polymerase and stimulatory factors from HeLa and KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3777–3788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Blatti S. P., Rutter W. J. Molecular structures of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases (II) from calf thymus and rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2994–2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Raskas H. J., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases II and III in transcription of the adenovirus genome late in productive infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3426–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase 3 in the transcription of the tRNA and 5S RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1790–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. The rapid turnover of RNA polymerase of rat liver nucleolus, and of its messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]