Abstract
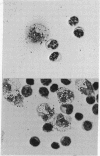
Insulin receptors have been demonstrated on mononuclear leukocytes prepared by centrifugation of buffy coats from normal blood donors on Ficoll-Hypaque gradients. The cell type that specifically binds insulin in this mixture of lymphocytes and monocytes has never been clearly identified, although it was assumed to be the lymphocyte since this cell constitutes about 80% of the population. In the present studies, insulin-binding assays were performed on the mononuclear leukocyte preparation before and after selective depletion or enrichment for monocytes using glass wool or Sephadex G-10 adherence columns. The amount of 125-I-labeled insulin specifically bound correlated significantly with the number of monocytes but not with the number of B or T lymphocytes. Approximately 90% of the specific insulin binding of this preparation could be accounted for by its content of monocytes. The amount of binding was unaffected by phagocytosis of latex particles or by metabolic inhibitors added to prevent endocytosis. Autoradiograms made on smears of whole peripheral blood and mononuclear leukocytes demonstrated that all of the cells that bound 125-I-labeled insulin were large mononulcear cells, 85-90% of which could be identified as monocytes by morphological criteria or by the functional criterion of latex particle ingestion. Since insulin receptor concentration may be altered in disease states in man, it is essential, when using this cell population for detecting such changes, to quantitate the number of monocytes in the preparation so that the insulin-binding data can be appropriately interpreted.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer J. A., Gorden P., Gavin J. R., 3rd, Lesniak M. A., Roth J. Insulin receptors in human circulating lymphocytes: application to the study of insulin resistance in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Apr;36(4):627–633. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-4-627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrt P., Ada G. L. An in vitro reaction between labelled flagellin or haemocyanin and lymphocyte-like cells from normal animals. Immunology. 1969 Oct;17(4):503–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Lehrer R. I. Phagocytosis by human monocytes. Blood. 1968 Sep;32(3):423–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. The regulation of pinocytosis in mouse macrophages. I. Metabolic requirements as defined by the use of inhibitors. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):557–571. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. M., Paul W. E. Receptors on immunocompetent cells. II. Specificity and nature of receptors on dinitrophenylated guinea pig albumin- 125 I-binding lymphocytes of normal guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1971 Aug 1;134(2):495–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickler H. B., Kunkel H. G. Interaction of aggregated -globulin with B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):191–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen S. A., Wedner H. J., Parker C. W. Isolation of pure human peripheral blood T-lymphocytes using nylon wool columns. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(6):571–577. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Laudat M. H., Laudat P., Rosselin G., Kahn C. R., Gorden P., Roth J. Impairment of insulin binding to the fat cell plasma membrane in the obese hyperglycemic mouse. FEBS Lett. 1972 Sep 15;25(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L., KNIGHT E. J. THE ROUTE OF RE-CIRCULATION OF LYMPHOCYTES IN THE RAT. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1964 Jan 14;159:257–282. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1964.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Gorden P., Roth J., Archer J. A., Buell D. N. Characteristics of the human lymphocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Jen P., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in human circulating cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Gardner J. D., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin action in isolated rat thymocytes. I. Binding of 125 I-insulin and stimulation of -aminoisobutyric acid transport. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6919–6926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G. Purification of human T and B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):420–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Neville D. M., Jr, Roth J. Insulin-receptor interaction in the obese-hyperglycemic mouse. A model of insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug U., Krug F., Cuatrecasas P. Emergence of insulin receptors on human lymphocytes during in vitro transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2604–2608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ly I. A., Mishell R. I. Separation of mouse spleen cells by passage through columns of sephadex G-10. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Reaven G. M. The human lymphocyte: a model for the study of insulin-receptor interaction. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Apr;38(4):554–560. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-4-554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Leventhal B. G., Hersh E. M. The transformation of column-purified lymphocytes with nonspecific and specific antigenic stimuli. J Immunol. 1968 Aug;101(2):262–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak C. A., Warmsley A. M., Thomas D. B. Structural alterations in the surface membrane during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):562–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Smith R. W., Gerber P. B-cell characteristics of human peripheral and cord blood lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Apr;52(4):1081–1086. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.4.1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Herberman R., Frank M. M., Green I. Receptors for complement and immunoglobulin on human leukemic cells and human lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1933–1938. doi: 10.1172/JCI106999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. W., Woody J. N. The immunosuppressive potency of antilymphocyte serum is related to activity against human thymic lymphocyte-specific antigens. Transplantation. 1974 May;17(5):503–507. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197405000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner M. S., Bianco C., Nussenzweig V. Enhanced binding of neuraminidase-treated sheep erythrocytes to human T lymphocytes. Blood. 1973 Dec;42(6):939–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D. The percentage of monocytes among "mononuclear" cell fractions obtained from normal human blood. J Immunol. 1974 Jan;112(1):234–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]