Abstract
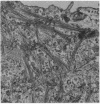
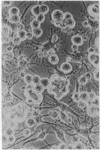
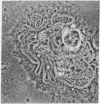
Muscle cultures treated with cytochalasin B yield mono- and oligonucleated cells of two kinds: (i) arborized, replicating precursor myogenic cells and fibroblasts; and (ii) round, post-mitotic, terminally differentiating myoblasts and myotubes. The arborized cells do not bind fluorescein-labeled antibody against myosin, do not contract rhythmically, and do not display hexagonally stacked thick and thin filaments. The round, mono-nucleated myoblasts and round, oligonucleated myotubes bind the fluorescein-labeled antibody against myosin, contract rhythmically, and display clusters of hexagonally-stacked thick and thin filaments. When cytochalasin B is removed and replaced by colcemide, the arborized cells, but not the post-mitotic muscle cells, acquire a radial symmetry and are induced to assemble massive, meandering cables that may occupy over 25% of the cell volume. These tortuous calbes are positively birefringent and consist exclusively of enormous numbers of 100-A, intermediate-sized filaments.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott J., Schiltz J., Dienstman S., Holtzer H. The phenotypic complexity of myogenic clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamburg J. R., Shooter E. M., Wilson L. Developmental changes in microtubule protein of chick brain. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1476–1482. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K. G., Malawista S. E. Microtubular crystals in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jan;40(1):95–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham M. E., Caput D., Cohen A., Whalen R. G., Gros F. The synthesis and stability of cytoplasmic messenger RNA during myoblast differentiation in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1466–1470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley P. A., Konigsberg I. R. Myogenic fusion and the duration of the post-mitotic gap (G1). Dev Biol. 1974 Mar;37(1):193–212. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. B. Effects of cytochalasins on mammalian cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 21;213(5073):261–264. doi: 10.1038/213261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. B. The cytochalasins as research tools in cytology. Endeavour. 1972 May;31(113):77–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstman S. R., Biehl J., Holtzer S., Holtzer H. Myogenic and chondrogenic lineages in developing limb buds grown in vitro. Dev Biol. 1974 Jul;39(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(74)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doering J. L., Fischman D. A. The in vitro cell fusion of embryonic chick muscle without DNA synthesis. Dev Biol. 1974 Feb;36(2):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLTZER H., MARSHALL J. M., Jr, FINCK H. An analysis of myogenesis by the use of fluorescent antimyosin. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Sep 25;3(5):705–724. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka S. D. Clonal analysis of vertebrate myogenesis. 3. Developmental changes in the muscle-colony-forming cells of the human fetal limb. Dev Biol. 1974 Apr;37(2):345–368. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90154-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtrop M. E., Raisz L. G., Simmons H. A. The effects of parathyroid hormone, colchicine, and calcitonin on the ultrastructure and the activity of osteoclasts in organ culture. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):346–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer H., Croop J., Gershon M., Somlyo A. Effects of cytochalasin-B and colcimide on cells in muscle cultures. Am J Anat. 1974 Oct;141(2):291–296. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001410210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Formation of arrowhead complexes with heavy meromyosin in a variety of cell types. J Cell Biol. 1969 Nov;43(2):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Mitosis and intermediate-sized filaments in developing skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1968 Sep;38(3):538–555. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg I. R. Diffusion-mediated control of myoblast fusion. Dev Biol. 1971 Sep;26(1):133–152. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishan A. Cytochalasin-B: time-lapse cinematographic studies on its effects on cytokinesis. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):657–664. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. F., Godman G. C., Deitch A. D., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. I. Early events. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):481–500. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C., Stockdale F. E. Differentiation without cell division in cultured skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1972 Dec;29(4):410–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M., Strohman R. C. Studies of the decline of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity during embryonic muscle cell fusion in vitro. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 7;9(14):2832–2839. doi: 10.1021/bi00816a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M., Strohman R. C. Studies of the decline of deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity during embryonic muscle cell fusion in vitro. Biochemistry. 1970 Jul 7;9(14):2832–2839. doi: 10.1021/bi00816a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson B., Strohman R. C. Myosin synthesis in cultures of differentiating chicken embryo skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1972 Oct;29(2):113–138. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives J. M., Paterson B. M. Differentiation of cell membranes in cultures of embryonic chick breast muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3208–3211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przybyla A., Strohman R. C. Myosin heavy chain messenger RNA from myogenic cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):662–666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein N. A., Chi J. C., Holtzer H. Actin and myosin in a variety of myogenic and non-myogenic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 25;57(2):438–446. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Holtzer H. Cytochalasin B: effects on cell morphology, cell adhesion, and mucopolysaccharide synthesis (cultured cells-contractile microfilaments-glycoproteins-embryonic cells-sorting-out). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):253–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger J. W., Holtzer S., Holtzer H. Effects of cytochalasin B on muscle cells in tissue culture. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 27;229(4):121–123. doi: 10.1038/newbio229121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E. Actin in dividing cells: contractile ring filaments bind heavy meromyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1688–1692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainberg A., Yagil G., Yaffe D. Alterations of enzymatic activities during muscle differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1971 May;25(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale F. E., O'Neill M. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis, mitosis, and skeletal muscle differentiation. In Vitro. 1972 Nov-Dec;8(3):212–227. doi: 10.1007/BF02619501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H., Shelanski M. L., Terry R. D. Effects of mitotic spindle inhibitors on neurotubules and neurofilaments in anterior horn cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):224–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Developmental changes preceding cell fusion during muscle differentiation in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1971 May;66(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]