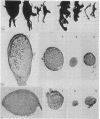
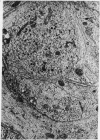
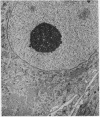
Abstract
Concomitant daily treatment of newborn rats for a 2-week to 1-month period with 10 mug/g of body weight of nerve growth factor and 100 mug/g of body weight of 6-hydroxydopamine produces in the cell bodies of adrenergic neurons the characteristic effects of the growth factor but in the nerve terminals the characteristic effects of 6-hydroxydopamine. The dual opposite effects result in a striking volume increase of sympathetic ganglia which far exceeds that produced by nerve growth factor alone. The selective induction of tyrosine hydroxylase [L-tyrosine, tetrahydropteridine:oxygen oxidoreductase (3-hydroxylating), EC 1.14.16.2] in these chemically axotomized adrenergic neurons is even more pronounced than that produced by nerve growth factor alone in intact neurons.
Full text
PDF

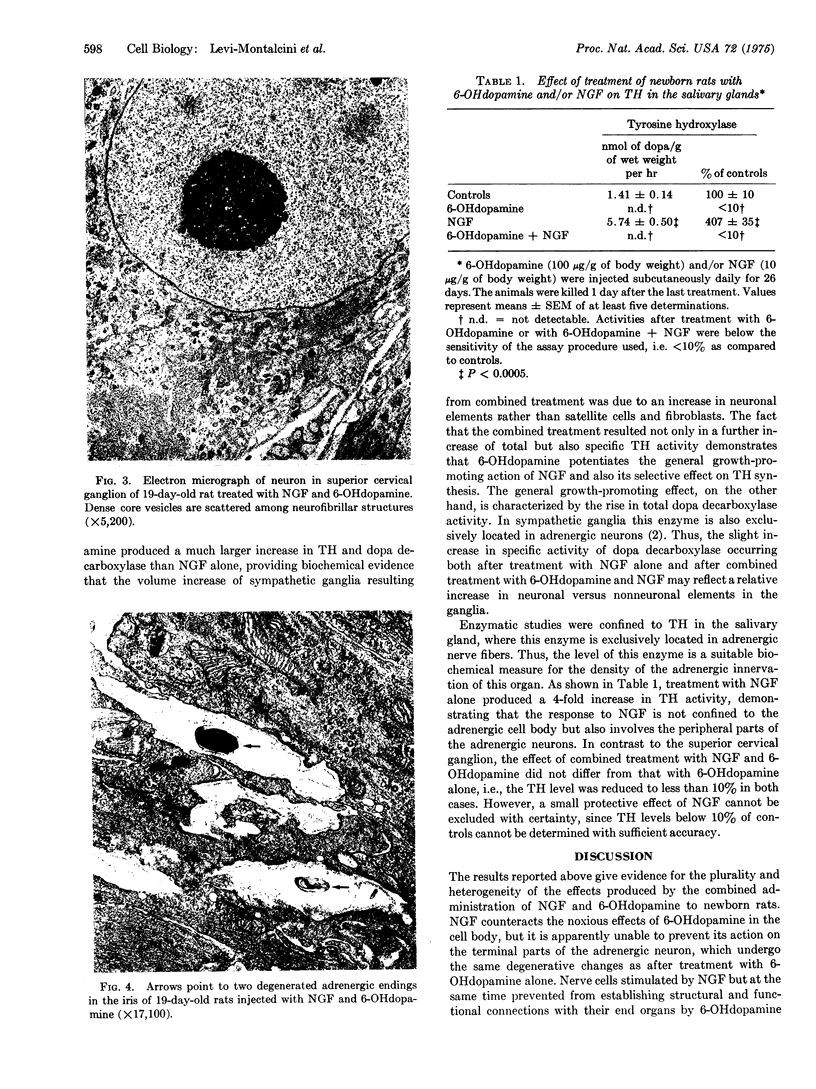

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angeletti P. U., Levi-Montalcini R. Sympathetic nerve cell destruction in newborn mammals by 6-hydroxydopamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jan;65(1):114–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapeller K., Mayor D. An electron microscopic study of the early changes proximal to a constriction in sympathetic nerves. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Mar 11;172(1026):39–51. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R. GROWTH CONTROL OF NERVE CELLS BY A PROTEIN FACTOR AND ITS ANTISERUM: DISCOVERY OF THIS FACTOR MAY PROVIDE NEW LEADS TO UNDERSTANDING OF SOME NEUROGENETIC PROCESSES. Science. 1964 Jan 10;143(3602):105–110. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3602.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: its mode of action on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:217–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Gibb J. W., Daly J. W., Lipton M., Udenfriend S. A new class of tyrosine hydroxylase inhibitors and a simple assay of inhibition in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Jul 7;16(7):1313–1321. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Axelrod J. Biochemistry of catecholamines. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:465–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller R. A., Thoenen H., Axelrod J. Increase in tyrosine hydroxylase activity after reserpine administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Sep;169(1):74–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OWMAN C. EFFECT OF DENERVATION AND ENZYME INHIBITION ON DOPA DECARBOXYLASE AND MONOAMINE OXIDASE ACTIVITIES OF RAT PINEAL GLAND. J Neurochem. 1965 May;12:417–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb04242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch F., Otten U., Thoenen H. Relationship between the rate of axoplasmic transport and subcellular distribution of enzymes involved in the synthesis of norepinephrine. J Neurochem. 1973 Jun;20(6):1691–1706. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peracchia C., Mittler B. S. Fixation by means of glutaraldehyde-hydrogen peroxide reaction products. J Cell Biol. 1972 Apr;53(1):234–238. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Angeletti P. U., Levi-Montalcini R., Kettler R. Selective induction by nerve growth factor of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine- -hydroxylase in the rat superior cervical ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1598–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Tranzer J. P. Chemical sympathectomy by selective destruction of adrenergic nerve endings with 6-Hydroxydopamine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1968;261(3):271–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00536990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Tranzer J. P. The pharmacology of 6-hydroxydopamine. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1973;13:169–180. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.13.040173.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranzer J. P., Thoenen H. Electronmicroscopic localization of 5-hydroxydopamine (3,4,5-trihydroxy-phenyl-ethylamine), a new 'false' sympathetic transmitter. Experientia. 1967 Sep 15;23(9):743–745. doi: 10.1007/BF02154151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]