Abstract
Purified lambda repressor protein is shown to reduce the lambda DNA-directed synthesis of proteins in vitro as determined both by net amino-acid incorporation and by analysis of specific lambda-coded proteins resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis. By means of different lambda DNA templates carrying deletion and point mutations in the operators o-L or o-R, it has been possible to demonstrate repression of the synthesis of two classes of lambda proteins. The synthesis of one, class c, appears to be controlled from the operator o-L and is more efficiently repressed at low concentrations of the repressor than that of the other class of repressible lambda proteins, class d, which is controlled from the operator o-R. Several other proteins synthesized in vitro are not repressible. Some of these are coded by the J-att region. In addition, the repressor appears to have another activity, that of stimulating the synthesis of a protein identified as the repressor itself. Lambda repressor appears to stimulate its own synthesis by acting at prm, a site defined by the cis-acting mutation prm 116.
Full text
PDF

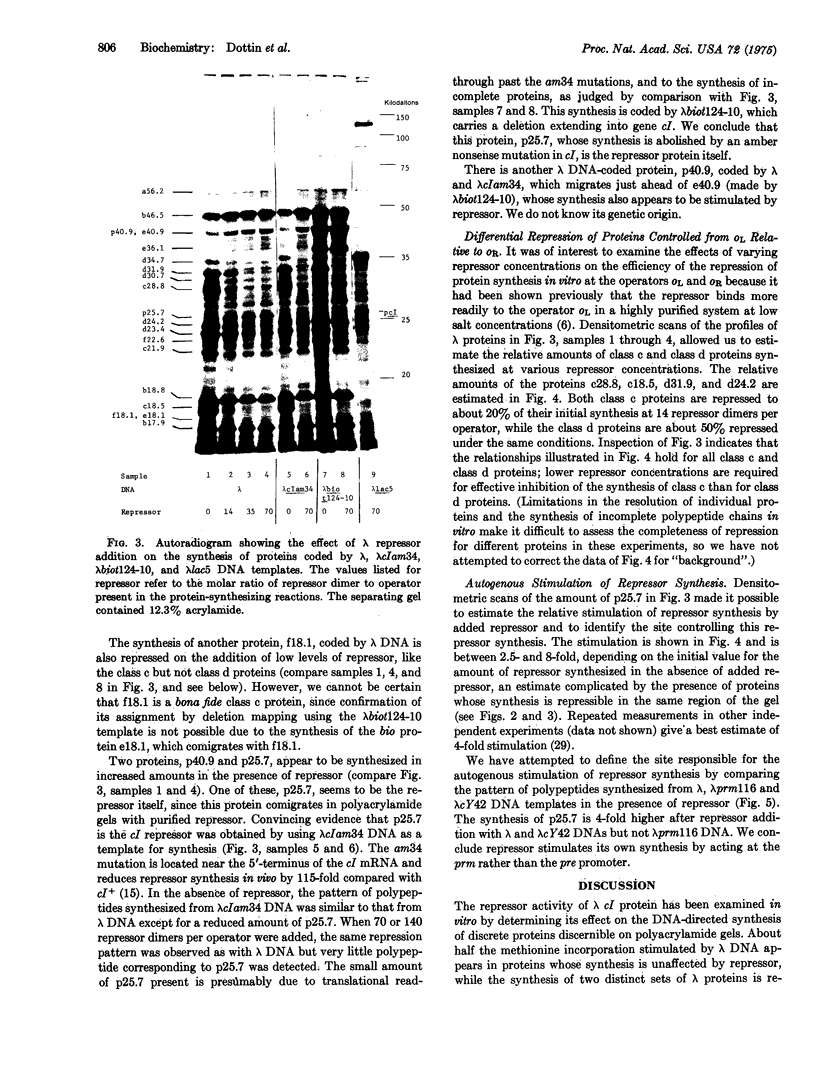

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allet B., Katagiri K. J., Gesteland R. F. Characterization of polypeptides made in vitro from bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 25;78(4):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Wulff D. The roles of the lambda c3 gene and the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activation system in the establishment of lysogeny by bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):779–782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E. RNA synthesis startpoints in bacteriophage lambda: are the promoter and operator transcribed? Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):227–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio237227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Parkinson J. S. Deletion mutants of bacteriophage lambda. 3. Physical structure of att-phi. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):403–423. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90473-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dottin R. P., Pearson M. L. Regulation by N gene protein of phage lambda of anthranilate synthetase synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1078–1082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H., Brachet P., Pereira da Silva L., Jacob F. Regulation of repressor expression in lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):855–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Jr, Levinthal C., Reeder R. H. Analysis of C14-labeled proteins by disc electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Aug 16;20(4):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90589-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F., Kahn C. Synthesis of bacteriophage lambda proteins in vitro. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 1;240(96):3–6. doi: 10.1038/newbio240003a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R., Howe M. New mutations in the S cistron of bacteriophage lambda affecting host cell lysis. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):200–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ippen K., Shapiro J. A., Beckwith J. R. Transposition of the lac region to the gal region of the Escherichia coli chromosome: isolation of lambda-lac transducing bacteriophages. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):5–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.5-9.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D. Mutations in a temperate bacteriophage affecting its ability to lysogenize Escherichia coli. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):42–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamy M. H., Fiandt M., Szybalski W. Electron microscopy of polar insertions in the lac operon of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;119(3):207–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00333859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M. Multiple repressor binding at the operators in bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1531–1535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
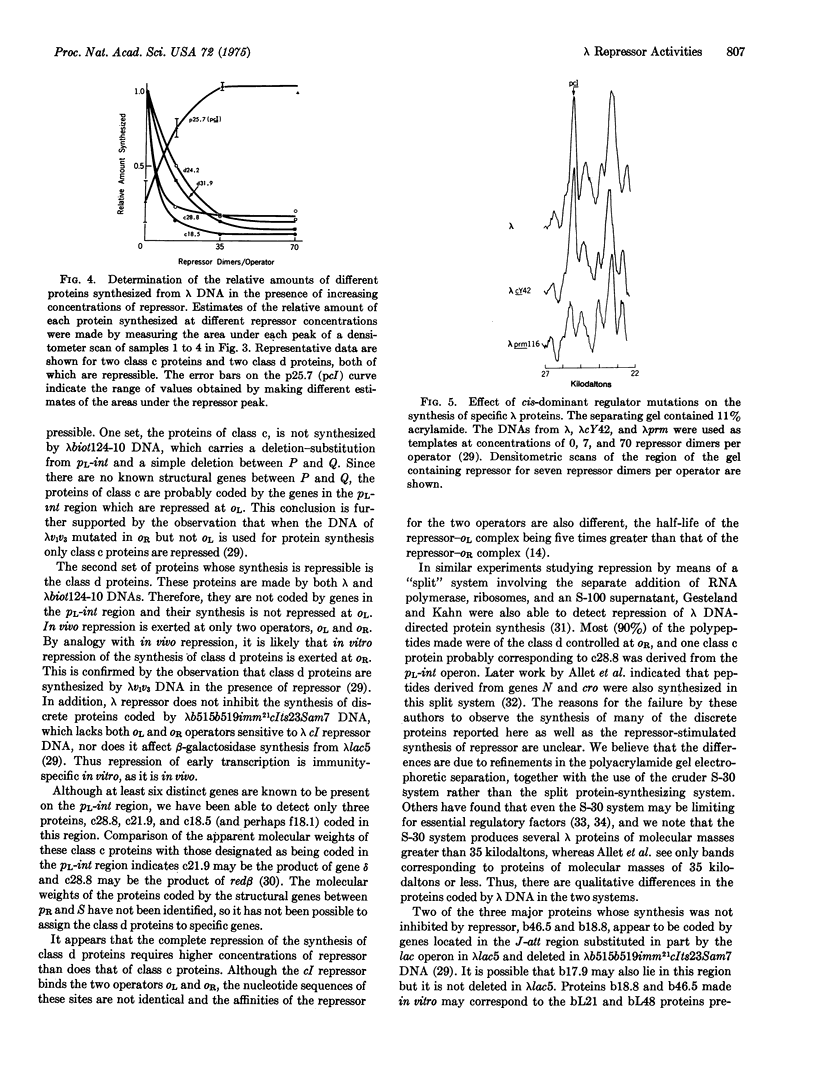
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M. Structure of the lambda operators. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):133–136. doi: 10.1038/246133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer Z., Calef E. Immunity phase-shift in defective lysogens: non-mutational hereditary change of early regulation of lambda prophage. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 14;51(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90265-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Hopkins N. The operators controlled by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1282–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. ISOLATION OF THE lambda PHAGE REPRESSOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):306–313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L., Kaiser A. D. Control of lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2185–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Haruna I., Holland I. B., Beaudreau G., Mills D. The synthesis of a self-propagating and infectious nucleic acid with a purified enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):919–927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman W. G., Reichardt L. F., Yaniv M., Heinemann S. F., Kaiser A. D., Eisen H. Bidirectional transcription and the regulation of Phage lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3156–3160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Analysis of bacteriophage T7 early RNAs and proteins on slab gels. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 15;79(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetekam W., Ehring R. A role for the product of gene suA in restoration of polarity in vitro. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Aug 28;124(4):345–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00267663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Ghosh S., Echols H., Spiegelman W. G. Repression by the cI protein of phage lambda: in vitro inhibition of RNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):407–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gussin G. N. Genetic characterization of a prm- mutant of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):300–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]