Abstract
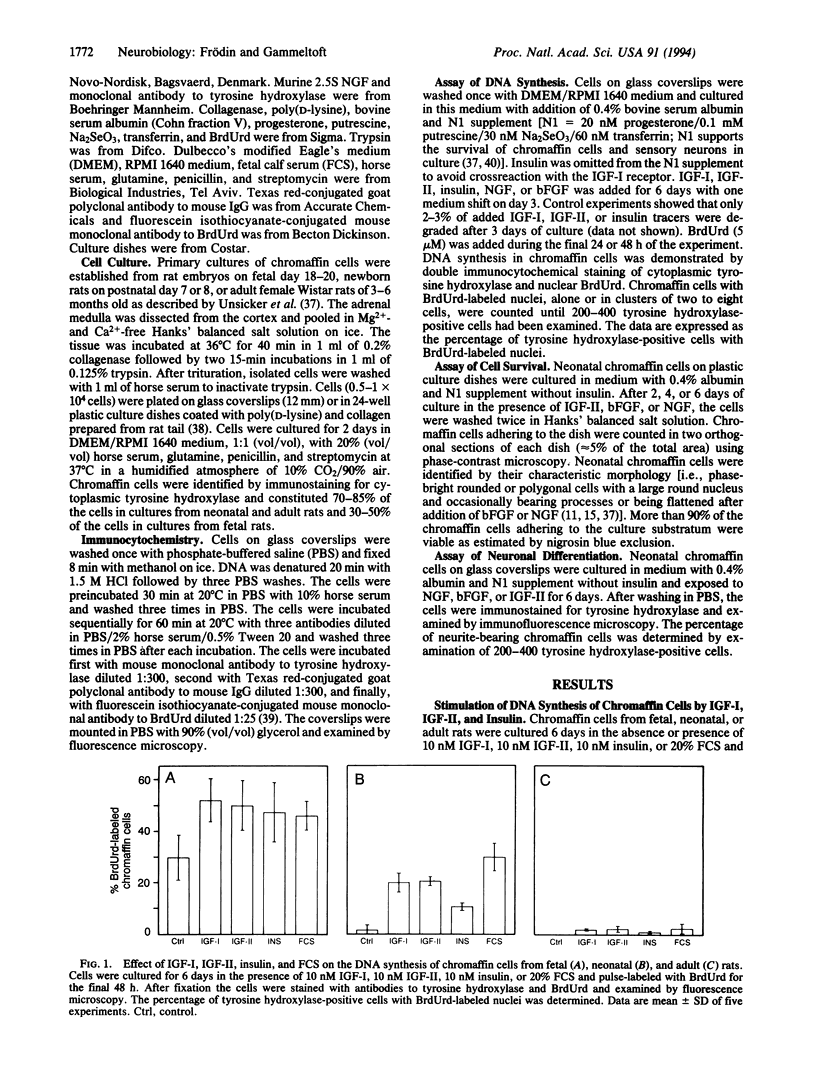
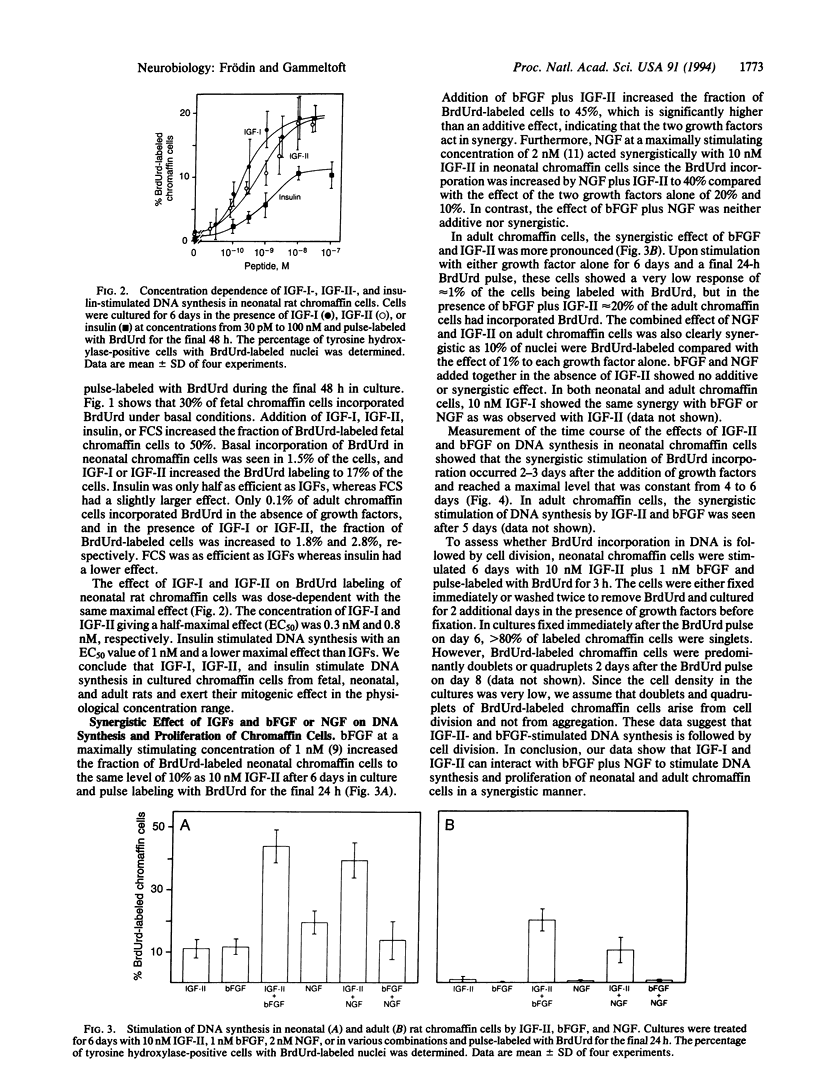
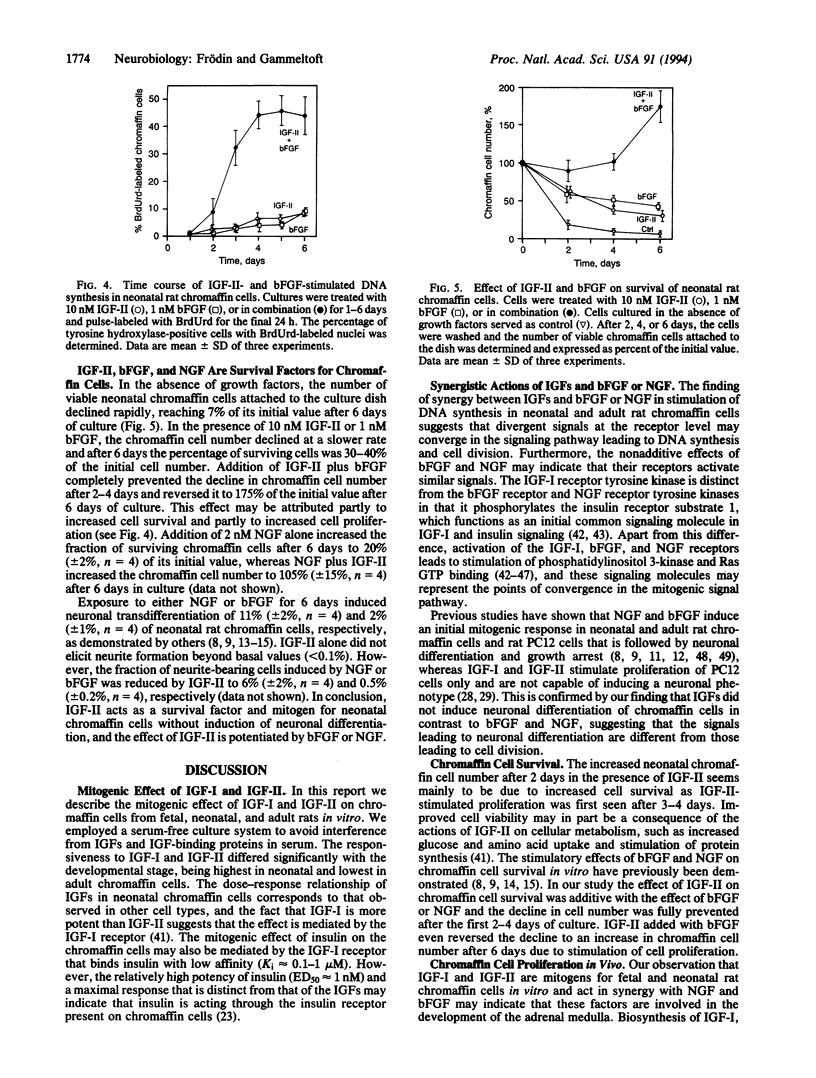
We have investigated the effects of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), and nerve growth factor (NGF) on DNA synthesis in cultured chromaffin cells from fetal, neonatal, and adult rats by using 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdUrd) pulse labeling for 24 or 48 h and immunocytochemical staining of cell nuclei. After 6 days in culture in the absence of growth factors, nuclear BrdUrd incorporation was detected in 30% of fetal chromaffin cells, 1.5% of neonatal cells, and 0.1% of adult cells. Addition of 10 nM IGF-I or IGF-II increased the fraction of BrdUrd-labeled nuclei to 50% of fetal, 20% of neonatal, and 2% of adult chromaffin cells. The ED50 value of IGF-I- and IGF-II-stimulated BrdUrd labeling in neonatal chromaffin cells was 0.3 nM and 0.8 nM, respectively. In neonatal and adult chromaffin cells, addition of 1 nM bFGF or 2 nM NGF stimulated nuclear BrdUrd incorporation to approximately the same level as 10 nM IGF-I or IGF-II. However, the response to bFGF or NGF in combination with either IGF-I or IGF-II was more than additive, indicating that the combined effect of the IGFs and bFGF or NGF is synergistic. The degree of synergism was 2- to 4-fold in neonatal chromaffin cells and 10- to 20-fold in adult chromaffin cells compared with the effect of each growth factor alone. In contrast, the action of bFGF and NGF added together in the absence of IGFs was not synergistic or additive. IGF-II acted also as a survival factor on neonatal chromaffin cells and the cell survival was further improved when bFGF or NGF was added together with IGF-II. In conclusion, we propose that IGF-I and IGF-II act in synergy with bFGF and NGF to stimulate proliferation and survival of chromaffin cells during neonatal growth and adult maintenance of the adrenal medulla. Our findings may have implications for improving the survival of chromaffin cell implants in diseased human brain.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen G. S., Burns R. S., Tulipan N. B., Parker R. A. Adrenal medullary transplantation to the caudate nucleus in Parkinson's disease. Initial clinical results in 18 patients. Arch Neurol. 1989 May;46(5):487–491. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1989.00520410021016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORNSTEIN M. B. Reconstituted rattail collagen used as substrate for tissue cultures on coverslips in Maximow slides and roller tubes. Lab Invest. 1958 Mar-Apr;7(2):134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn M. C., Goldstein M., Black I. B. Role of glucocorticoids in expression of the adrenergic phenotype in rat embryonic adrenal gland. Dev Biol. 1981 Feb;82(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90423-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Moolenaar W. H., Harrison P. H., Moed P., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Ionic responses and growth stimulation induced by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):92–98. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J. E., Skaper S. D., Varon S. S., Sato G. H. Selective survival of neurons from chick embryo sensory ganglionic dissociates utilizing serum-free supplemented medium. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jan;125(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Parada I. M., Gordon K. A., D'Amore P. A., Wagner J. A. Acidic fibroblast growth factor stimulates adrenal chromaffin cells to proliferate and to extend neurites, but is not a long-term survival factor. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):783–790. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90126-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham L. A., Hansen J. T., Short M. P., Bohn M. C. The use of genetically altered astrocytes to provide nerve growth factor to adrenal chromaffin cells grafted into the striatum. Brain Res. 1991 Oct 11;561(2):192–202. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91595-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmer M. K., Hart P. M., Perlman R. L. Insulin-like growth factor-I enhances tyrosine hydroxylase activation in bovine chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1347–1353. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmer M. K., Hart P. M., Perlman R. L. Studies on the effect of insulin-like growth factor-I on catecholamine secretion from chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1990 Mar;54(3):931–936. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmer M. K., Perlman R. L. Bovine chromaffin cells have insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) receptors: IGF-I enhances catecholamine secretion. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):321–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmer M. K., Perlman R. L. Insulin and insulin-like growth factors stimulate deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2109–2113. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen A., Larsen E., Gammeltoft S. Chromaffin cells express two types of insulin-like growth factor receptors. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 4;518(1-2):95–100. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90958-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupe A. J., Landis S. C., Patterson P. H. Environmental influences in the development of neural crest derivatives: glucocorticoids, growth factors, and chromaffin cell plasticity. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2119–2142. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Badry O. M., Romanus J. A., Helman L. J., Cooper M. J., Rechler M. M., Israel M. A. Autonomous growth of a human neuroblastoma cell line is mediated by insulin-like growth factor II. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):829–839. doi: 10.1172/JCI114243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed C. R., Breeze R. E., Rosenberg N. L., Schneck S. A., Kriek E., Qi J. X., Lone T., Zhang Y. B., Snyder J. A., Wells T. H. Survival of implanted fetal dopamine cells and neurologic improvement 12 to 46 months after transplantation for Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 1992 Nov 26;327(22):1549–1555. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199211263272202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelato M. C., Vassalotti J. Insulin-like growth factor-II: possible local growth factor in pheochromocytoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Nov;71(5):1168–1174. doi: 10.1210/jcem-71-5-1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgetti S., Ballotti R., Kowalski-Chauvel A., Tartare S., Van Obberghen E. The insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor substrate IRS-1 associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7358–7364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz C. G., Olanow C. W., Koller W. C., Penn R. D., Cahill D., Morantz R., Stebbins G., Tanner C. M., Klawans H. L., Shannon K. M. Multicenter study of autologous adrenal medullary transplantation to the corpus striatum in patients with advanced Parkinson's disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):337–341. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gratzner H. G. Monoclonal antibody to 5-bromo- and 5-iododeoxyuridine: A new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science. 1982 Oct 29;218(4571):474–475. doi: 10.1126/science.7123245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothe C., Unsicker K. Immunocytochemical localization of basic fibroblast growth factor in bovine adrenal gland, ovary, and pituitary. J Histochem Cytochem. 1989 Dec;37(12):1877–1883. doi: 10.1177/37.12.2685112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grothe C., Unsicker K. Immunocytochemical mapping of basic fibroblast growth factor in the developing and adult rat adrenal gland. Histochemistry. 1990;94(2):141–147. doi: 10.1007/BF02440180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Lund P. K. Cellular localization of somatomedin (insulin-like growth factor) messenger RNA in the human fetus. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):193–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3563497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Irminger J. C., Zapf J., Ziegler W. H., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor II in human adrenal pheochromocytomas and Wilms tumors: expression at the mRNA and protein level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1104–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann H. D., Ebener C., Unsicker K. Age-dependent differences in 125I-nerve growth factor binding properties of rat adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18(4):574–577. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490180410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurecka W., Lassmann H., Hörandner H. The proliferation of adrenal medullary cells in newborn and adult mice. A light and electron microscopic autoradiographic study. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 May 29;189(2):305–312. doi: 10.1007/BF00209279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsching S., Auburger G., Heumann R., Scott J., Thoenen H. Levels of nerve growth factor and its mRNA in the central nervous system of the rat correlate with cholinergic innervation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1389–1393. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03791.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bowsher R. R., Apathy J. M., Smith M. C., Henry D. P. Measurement of insulin-like growth factor-II in physiological fluids and tissues. II. Extraction quantification in rat tissues. Endocrinology. 1991 Feb;128(2):815–822. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-2-815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillien L. E., Claude P. Nerve growth factor is a mitogen for cultured chromaffin cells. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):632–634. doi: 10.1038/317632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malvaldi G., Viola-Magni M. P. DNA turnover in adrenal medullary cells of different strains of rats and its enhancement after intermittent exposure to cold. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1972 Mar;5(2):103–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1972.tb01007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Sun X. J., Cheatham B., Jachna B. R., Glasheen E. M., Backer J. M., White M. F. IRS-1 is a common element in insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I signaling to the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. Endocrinology. 1993 Apr;132(4):1421–1430. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.4.8384986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Satoh T., Kaziro Y. Differentiation factors, including nerve growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, and interleukin-6, induce an accumulation of an active Ras.GTP complex in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19448–19454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen F. C., Gammeltoft S. Insulin-like growth factors are mitogens for rat pheochromocytoma PC 12 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Aug 15;154(3):1018–1023. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmichi M., Decker S. J., Saltiel A. R. Activation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase by nerve growth factor involves indirect coupling of the trk proto-oncogene with src homology 2 domains. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90039-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. Grafts and growth factors in CNS. Basic science with clinical promise. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1990;54-55:250–267. doi: 10.1159/000100220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffioni S., Bradshaw R. A. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by epidermal growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and nerve growth factor in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9121–9125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydel R. E., Greene L. A. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors promote stable neurite outgrowth and neuronal differentiation in cultures of PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Nov;7(11):3639–3653. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-11-03639.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Batzer A., Li N., Lee C. H., Lowenstein E., Mohammadi M., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. The function of GRB2 in linking the insulin receptor to Ras signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1953–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.8316835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemple D. L., Mahanthappa N. K., Anderson D. J. Basic FGF induces neuronal differentiation, cell division, and NGF dependence in chromaffin cells: a sequence of events in sympathetic development. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stylianopoulou F., Efstratiadis A., Herbert J., Pintar J. Pattern of the insulin-like growth factor II gene expression during rat embryogenesis. Development. 1988 Jul;103(3):497–506. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., McClain R. M., Childers H., Downing J. Neurogenic signals regulate chromaffin cell proliferation and mediate the mitogenic effect of reserpine in the adult rat adrenal medulla. Lab Invest. 1991 Sep;65(3):374–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Riseberg J. C., Hardenbrook M. A., Cherington V. Nerve growth factor is a potent inducer of proliferation and neuronal differentiation for adult rat chromaffin cells in vitro. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1533–1542. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01533.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Ruzicka L. A., Donahue S. R., DeLellis R. A. Chromaffin cell proliferation in the adult rat adrenal medulla. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989;7(5):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0736-5748(89)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Krisch B., Otten U., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor-induced fiber outgrowth from isolated rat adrenal chromaffin cells: impairment by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3498–3502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K., Westermann R. Basic fibroblast growth factor promotes transmitter storage and synthesis in cultured chromaffin cells. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1992 Feb 21;65(2):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(92)90181-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore S. R., Ebendal T., Lärkfors L., Olson L., Seiger A., Strömberg I., Persson H. Development and regional expression of beta nerve growth factor messenger RNA and protein in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):817–821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widner H., Tetrud J., Rehncrona S., Snow B., Brundin P., Gustavii B., Björklund A., Lindvall O., Langston J. W. Bilateral fetal mesencephalic grafting in two patients with parkinsonism induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) N Engl J Med. 1992 Nov 26;327(22):1556–1563. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199211263272203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S. P. Insulin-like growth factor I enhances proenkephalin synthesis and dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity in adrenal chromaffin cells. Life Sci. 1991;49(4):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



