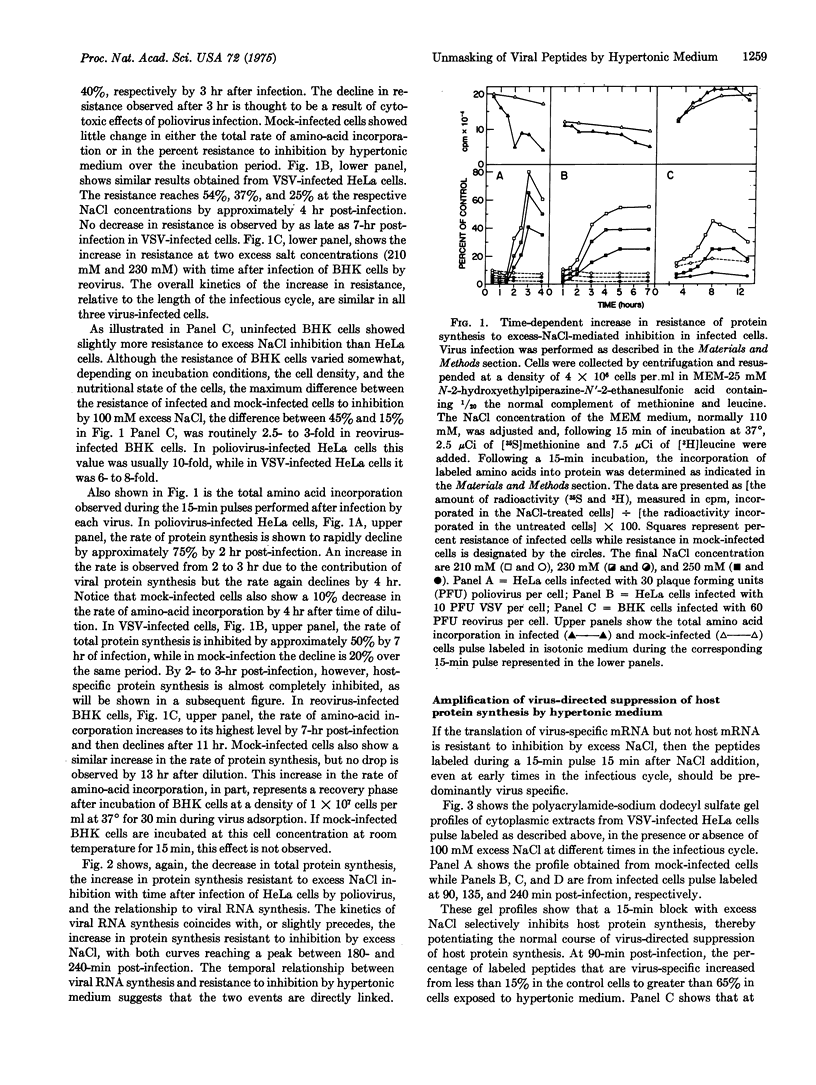
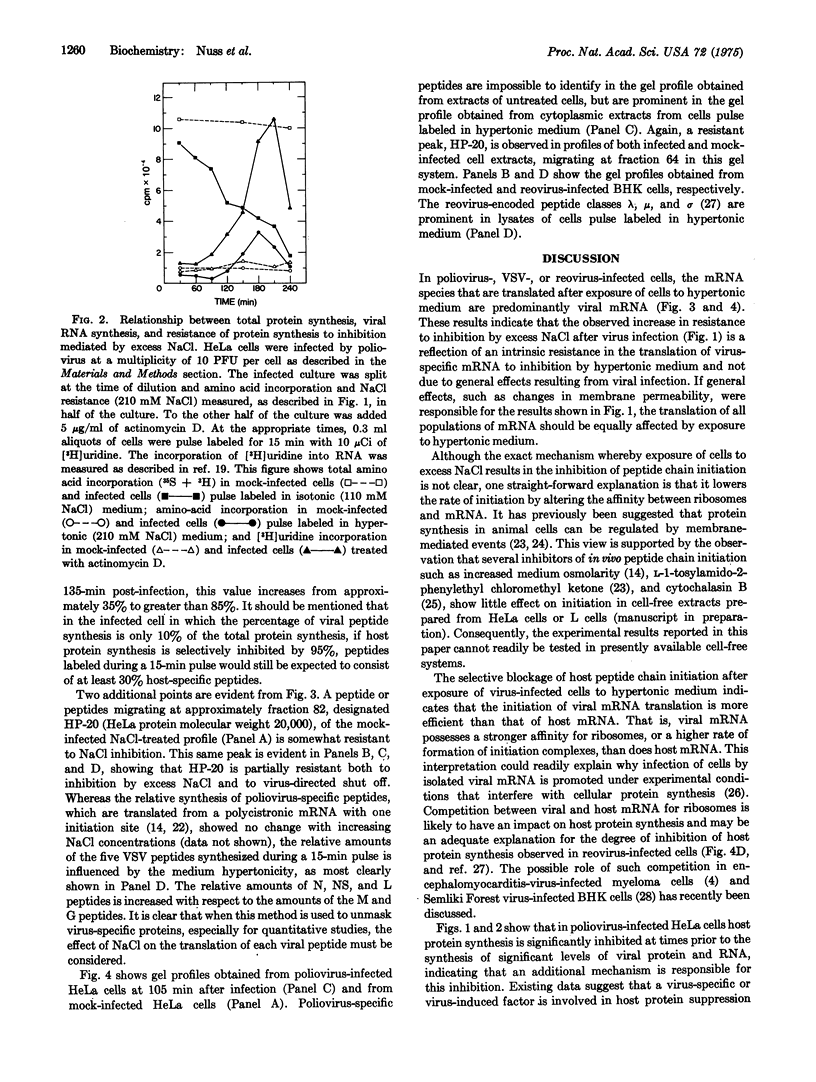
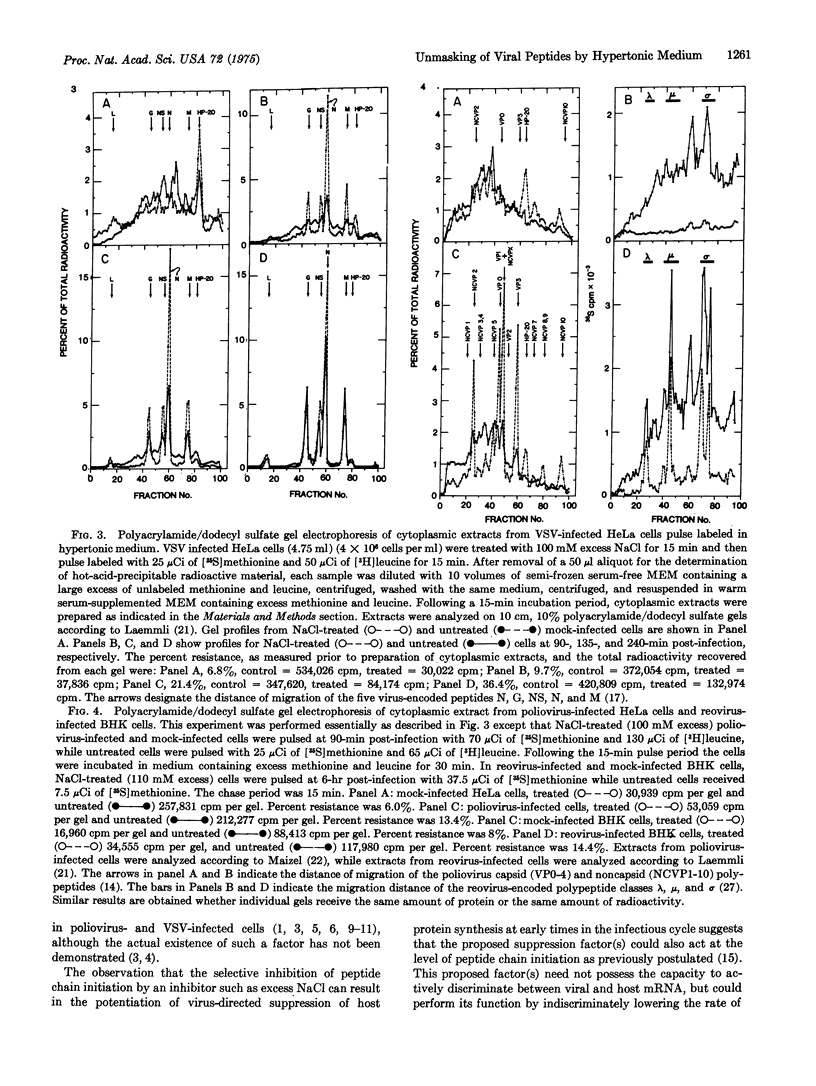
Abstract
Poliovirus mRNA and mRNA transcribed from vesicular stomatitis virus and reovirus genomes efficiently direct protein synthesis in vivo under experimental conditions where the initiation of host protein synthesis is selectively blocked. The selective blockage of host peptide chain initiation after exposure to hypertonic medium indicates that the translation of viral mRNA is more efficiently initiated than is the translation of host mRNA. It further suggests that virus directed suppression of host protein synthesis could proceed by a mechanism involving a nonspecific decrease in the rate of peptide chain initiation. Exposure of infected cells to hypertonic medium provides a unique tool with which to study early events in the infectious cycle by permitting the efficient unmasking of virus-specific poly-peptide synthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BABLANIAN R., EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISM OF POLIOVIRUS-INDUCED CELL DAMAGE. I. THE RELATION BETWEEN POLIOVIRUS,-INDUCED METABOLIC AND MORPHOLOGICAL ALTERATIONS IN CULTURED CELLS. Virology. 1965 May;26:100–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D., FRANKLIN R. M., CALLENDER J. MENGOVIRUS-INDUCED INHIBITION OF HOST RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 22;76:425–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Huang A. S. The formation of poliovirus proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:741–746. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DARNELL J. E., Jr, LEVINTOW L. Poliovirus protein: source of amino acids and time course of synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jan;235:74–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. INHIBITION OF HOST CELL MACROMOLECULAR SYNTHESIS BY HIGH MULTIPLICITIES OF POLIOVIRUS UNDER CONDITIONS PREVENTING VIRUS SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:574–581. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., PETERSON J. A. NUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DURING POLIOVIRUS INFECTION OF HUMAN CELLS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:556–575. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg M., Breitbart H., Atlan H. Interactions between membrane functions and protein synthesis in reticulocytes. Effects of valinomycin and dicyclohexyl-18-crown-6. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 1;45(1):161–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G. Differential effect of phleomycin on the infectivity of poliovirus and poliovirus-induced ribonucleic acids. J Virol. 1971 Jul;8(1):28–34. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.1.28-34.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C., Thach R. E. Encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mouse plasmacytoma cells. I. Inhibition of cellular protein synthesis. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):598–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.598-610.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz R., Penman S. Regulation of protein synthesis in HeLa cells. 3. Inhibition during poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):661–668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.661-668.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Model for the regulation of mRNA translation applied to haemoglobin synthesis. Nature. 1974 Oct 4;251(5474):385–388. doi: 10.1038/251385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd J. A., Summers D. F. Protein synthesis in vesicular stomatitis virus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Summers D. Effects on host cell metabolism following synchronous infection with poliovirus. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pong S. S., Nuss D. L., Koch G. Inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian tissue culture cells by L-1-tosylamido-2-phenylethyl chloromethyl ketone. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saborio J. L., Pong S. S., Koch G. Selective and reversible inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 15;85(2):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90360-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Jr, Burge B. W., Darnell J. E. Sindbis virus infection of chick and hamster cells: synthesis of virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1969 Mar;37(3):367–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trown P. W., Bilello J. A. Mechanism of action of gliotoxin: elimination of activity by sulfhydryl compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Oct;2(4):261–266. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.4.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELOCK E. F., TAMM I. Biochemical basis for alterations in structure and function of HeLa cells infected with Newcastle disease virus. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:617–632. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Youngner J. S. Inhibition of protein synthesis in L cells infected with vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):85–89. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.85-89.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. J., Cooper P. D. Poliovirus proteins associated with ribosomal structures in infected cells. Virology. 1974 May;59(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN E. F., HEETER M., DARNELL J. E. RNA synthesis in poliovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1963 Mar;19:400–408. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J., Joklik W. K. Studies on the intracellular synthesis of reovirus-specified proteins. Virology. 1970 Jul;41(3):501–518. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


