Abstract
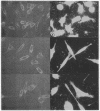
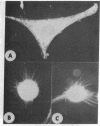
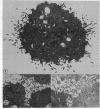
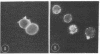
We have utilized dark field microscopy to observe the surface microstructure of living cultured cells. Using this method, we have found that dibutyryl cAMP treatment causes regression of the numerous, long cell surface microvilli present on L929 cells. Thirty minutes after removal of dibutyryl cAMP, microvilli reappear. An inhibitor of phosphodiesterase (methylisobutylxanthine) and a stimulator of adenylate cyclase (prostaglandin E1), both of which raise cAMP levels, cause regression of microvilli in 15 min. Untransformed 3T3 cells show very few microvilli when viewed still attached to their substratum or after removal with EDTA. Treatment of these cells with trypsin causes the formation of numerous microvilli on their surface. When clumps of cells agglutinated by concanavalin A are examined by thin section electron microscopy, the cells are seen to be held together by a "forest" of interdigitating microvilli and only rarely is there apposition of the areas of membrane between microvilli. At the same time the distribution of surface-bound concanavalin A was examined using immunofluorescent light microscopy, and concanavalin A was found to be uniformly distributed over the cell surface. We propose that agglutinability of mouse and rat fibroblasts is regulated through the modulation of cell surface microvilli by cAMP, and that transformed cells are highly agglutinable because their low cAMP levels result in the formation of numerous surface microvilli.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burger M. M., Bombik B. M., Breckenridge B. M., Sheppard J. R. Growth control and cyclic alterations of cyclic AMP in the cell cycle. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 11;239(93):161–163. doi: 10.1038/newbio239161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsie A. W., Jones C., Puck T. T. Further changes in differentiation state accompanying the conversion of Chinese hamster cells of fibroblastic form by dibutyryl adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsie A. W., Puck T. T. Morphological transformation of Chinese hamster cells by dibutyryl adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and testosterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. S., Friedman R. M., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP-treated sarcoma cells acquire several morphological characteristics of normal fibroblasts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 30;185:413–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb45267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. S., Friedman R. M., Pastan I. Restoration of several morphological characteristics of normal fibroblasts in sarcoma cells treated with adenosine-3':5'-cyclic monphosphate and its derivatives. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):425–429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. S., Morgan W. D., Pastan I. Regulation of cell motility by cyclic AMP. Nature. 1972 Jan 7;235(5332):54–56. doi: 10.1038/235054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. S., Pastan I. Role of 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate in regulation of morphology and growth of transformed and normal fibroblasts. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 May;48(5):1377–1387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurth R., Bauer H. Influence of dibutyryl cyclicAMP and theophylline on cell surface antigens on oncornavirus transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):243–245. doi: 10.1038/newbio243243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Temperature-dependent mobility of concanavalin A sites on tumour cell surfaces. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 13;243(128):218–220. doi: 10.1038/newbio243218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten J., Johnson G. S., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP levels in fibroblasts: relationship to growth rate and contact inhibition of growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Sep;44(5):1192–1198. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten J., Johnson G. S., Pastan I. Regulation of cell growth by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. Effect of cell density and agents which alter cell growth on cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):7082–7087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K., Prescott D., Frye J. Changes in surface morphology of Chinese hamster ovary cells during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):815–836. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblith J. Z., Ukena T. E., Yin H. H., Berlin R. D., Karnovsky M. J. A comparative evaluation of the distribution of concanavalin A-binding sites on the surfaces of normal, virally-transformed, and protease-treated fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1625–1629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins: cell-agglutinating and sugar-specific proteins. Science. 1972 Sep 15;177(4053):949–959. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4053.949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R. Difference in the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in normal and transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 1;236(61):14–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio236014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R., Prescott D. M. Cyclic AMP levels in synchronized mammalian cells. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Nov;75(1):293–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90554-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R. Restoration of contact-inhibited growth to transformed cells by dibutyryl adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1316–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smets L. A. Contact inhibition of transformed cells incompletely restored by dibutyryl cyclic AMP. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):123–124. doi: 10.1038/newbio239123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller N. K. Visualization of concanavalin A-binding sites with scanning electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):699–707. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Carchman R. A., Pastan I. H. A mutant of 3T3 cells with cyclic AMP metabolism sensitive to temperature change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2906–2910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Ostlund R. E., Pastan I. Myosin is a component of the cell surface of cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4144–4148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Cyclic AMP mediates the concanavalin A agglutinability of mouse fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1974 Oct;63(1):288–294. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]