Abstract
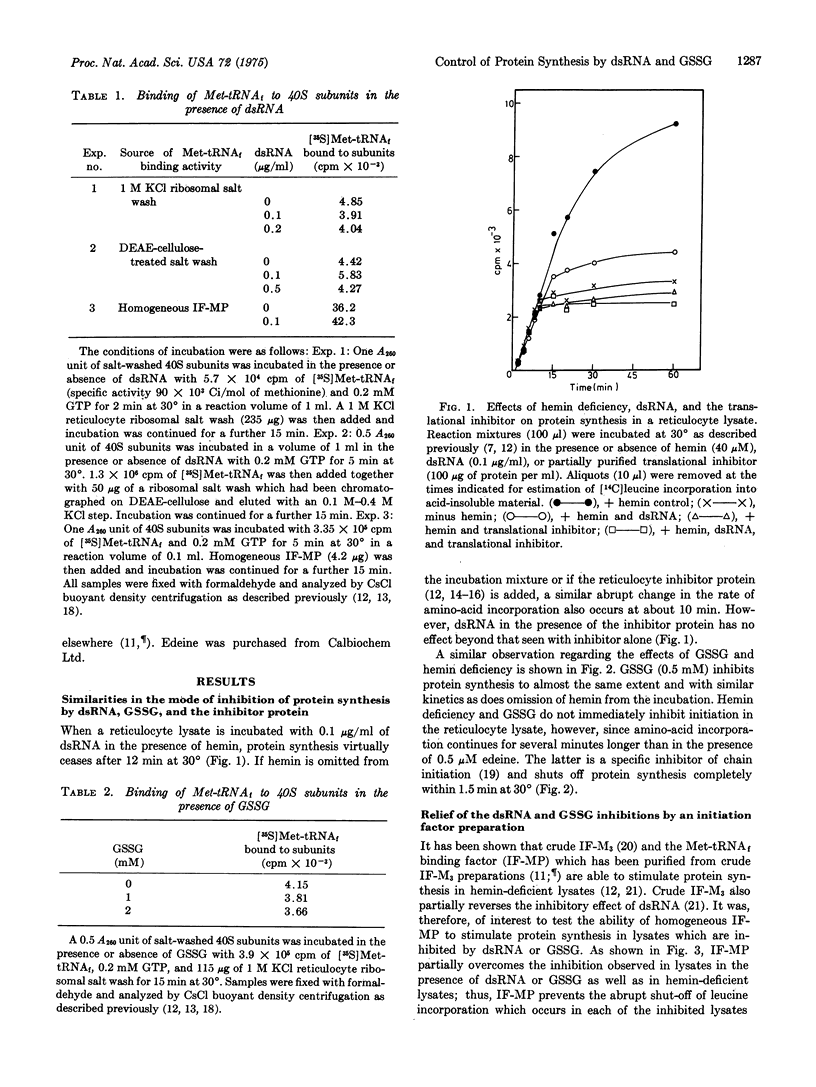
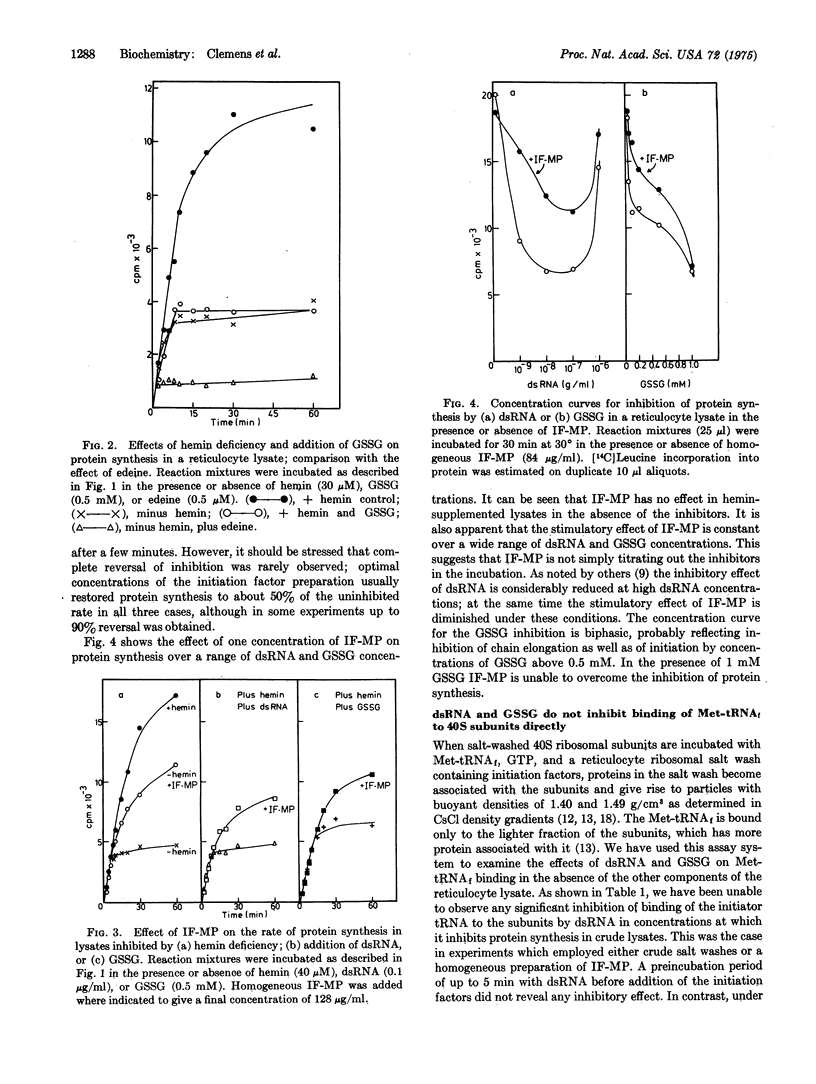
In the presence of added double-stranded RNA or oxidized glutathione, protein synthesis in heminsupplemented reticulocyte lysates declines abruptly after 8-12 min of incubation at 30 degrees. The kinetics of amino-acid incorporation are very similar to those seen when lysates incorporation are very similar to those seen when lysates are incubated in the absence of added hemin. The inhibitory effects of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and oxidized glutathione (GSSG) are partially overcome by a homogeneous initiation factor, IF-MP, which also stimulates protein synthesis in hemin-deficient lysates. This factor is involved in the binding of Met-tRNAfmet to 40S ribosomal subunits during protein chain initiation. However, neither dsRNA alone nor GSSG alone significantly inhibits formation of [40S subunit-Met-tRNAf] complexes induced in reticulocyte lysates by dsRNA or GSSG involves one or more components present in the lysates but absent from the fractionated in vitro system. Such components may be related to the translational inhibitor that is active in hemin-deficient lysates.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beuzard Y., London I. M. The effects of hemin and double-stranded RNA on alpha and beta globin synthesis in reticulocyte and Krebs II ascites cell-free systems and the relationship of these effects to an initiation factor preparation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2863–2866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashion L. M., Stanley W. M., Jr Comparative studies on the properties of the eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor IF-I from several sources. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 26;324(3):410–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90285-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Henshaw E. C., Rahamimoff H., London I. M. Met-tRNAfMet binding to 40S ribosomal subunits: a site for the regulation of initiation of protein synthesis by hemin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dettman G. L., Stanley W. M., Jr Recognition of eukaryotic initiator tRNA by an initiation factor and the transfer of the methionine moiety into peptide linkage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 16;287(1):124–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Hunt T. Double-stranded poliovirus RNA inhibits initiation of protein synthesis by reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Rabinovitz M. Control of globin synthesis in cell-free preparations of reticulocytes by formation of a translational repressor that is inactivated by hemin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1565–1568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta N. K., Woodley C. L., Chen Y. C., Bose K. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes. Assays, purification, and properties of different ribosomal factors and their roles in peptide chain initiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4500–4511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch C. A., Cox M. A., van Venrooij W. J., Henshaw E. C. The ribosome cycle in mammalian protein synthesis. II. Association of the native smaller ribosomal subunit with protein factors. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4377–4385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. A., Adamson S. D., Herbert E. Studies on cessation of protein synthesis in a reticulocyte lysate cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 16;213(1):237–240. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Ehrenfeld E. Cytoplasm from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells inhibits cell-free haemoglobin synthesis. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):91–94. doi: 10.1038/newbio230091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Vanderhoff G., London I. M. Control of globin synthesis: the role of heme. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R., Kaufman J. Inhibition of cellular protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA: inactivation of an initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1222–1226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R., Kaufman J. Translational control of hemoglobin synthesis by an initiation factor required for recycling of ribosomes and for their binding to messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower N. S., Vanderhoff G. A., Benerofe B., Hunt T., Kosower E. M. Inhibition of protein synthesis by glutathione disulfide in the presence of glutathione. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):816–821. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90490-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower N. S., Vanderhoff G. A., Kosower E. M. Glutathione. 8. The effects of glutathione disulfide on initiation of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 31;272(4):623–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Brayley A., Hunt T., Jackson R. J. The effect of cyclic AMP and related compounds on the control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Feb 4;56(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Control of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates by haemin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 31;241(109):150–152. doi: 10.1038/newbio241150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Kyner D., Acs G. Protein initiation in eukaryotes: formation and function of a ternary complex composed of a partially purified ribosomal factor, methionyl transfer RNA, and guanosine triphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell C. R., Kamper C. S., Rabinovitz M. Hemin control of globin synthesis: an assay for the inhibitor formed in the absence of hemin and some characteristics of its formation. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T., Irvin J., Culp W., Hardesty B. Inhibition of peptide initiation on reticulocyte ribosomes by edeine. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 15;21(1):31–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard P. M., Picciano D. J., Laycock D. G., Anderson W. F. Translation of exogenous messenger RNA for hemoglobin on reticulocyte and liver ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2752–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Staehelin T. Initiation of eukaryotic protein synthesis: (Met-tRNA f -40S ribosome) initiation complex catalysed by purified initiation factors in the absence of mRNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 14;242(115):35–38. doi: 10.1038/newbio242035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker W. V., Schulman H. M. Stimulation of globin-chain initiation by hemin in the reticulocyte cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):582–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


