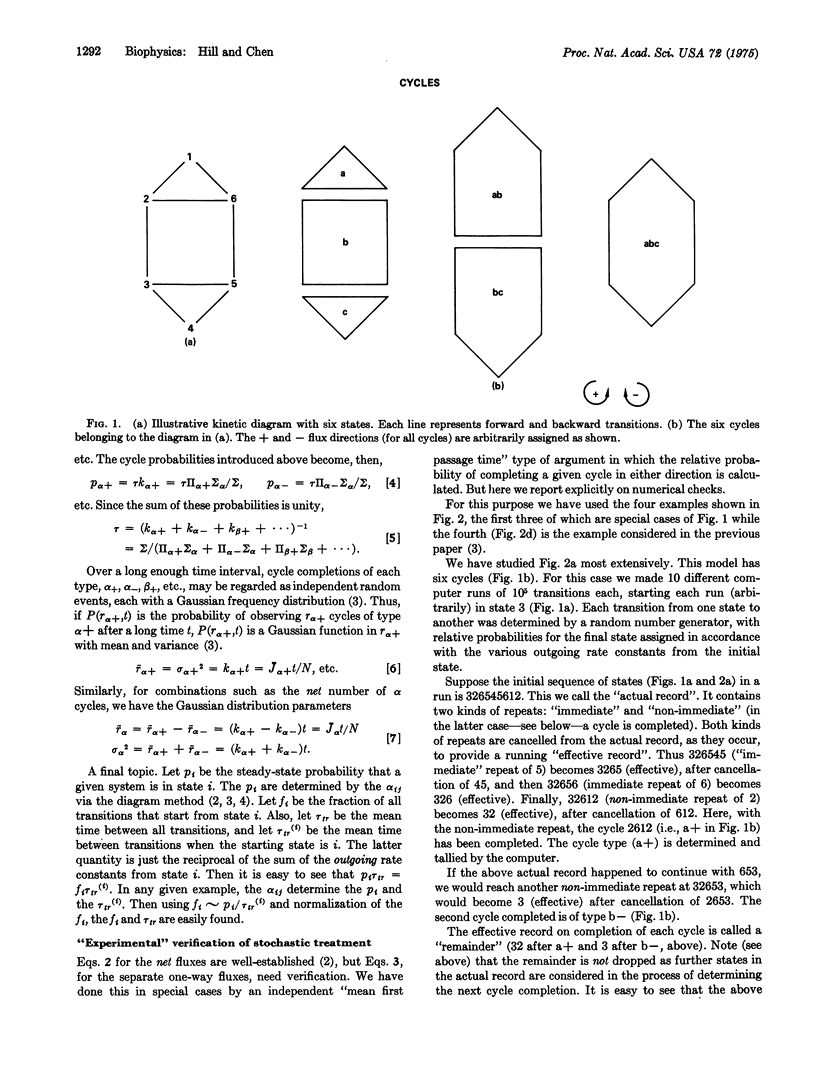
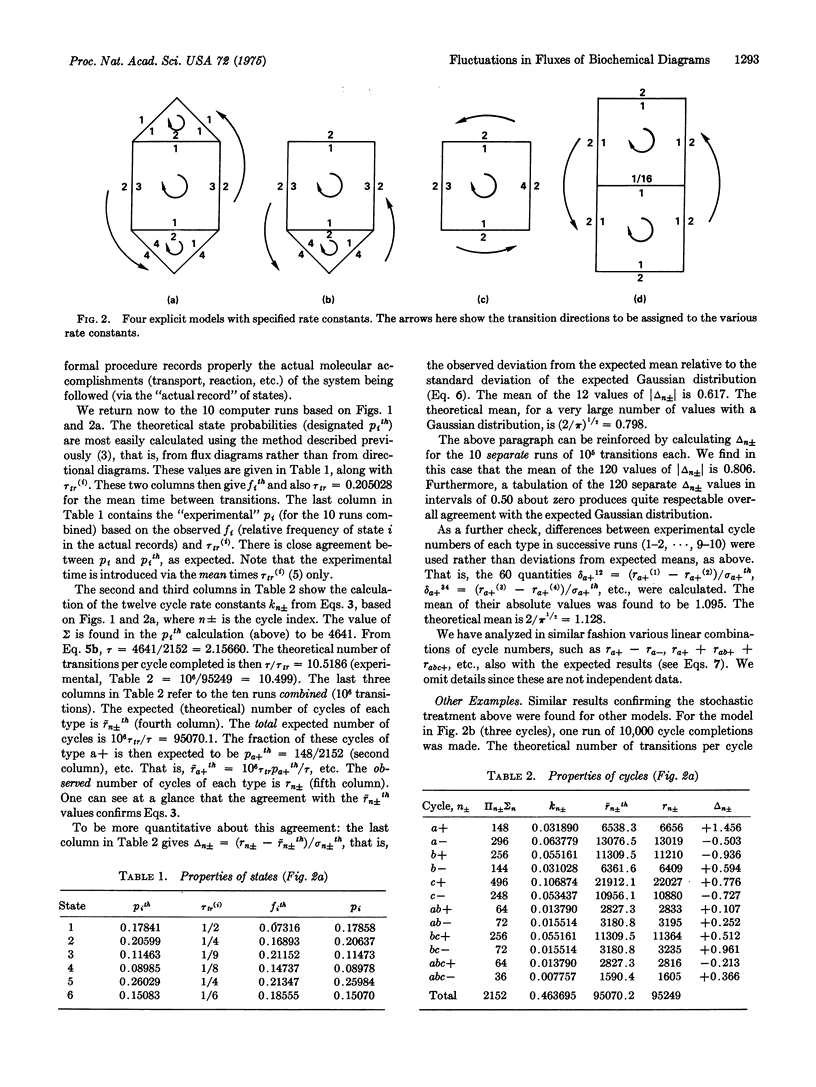
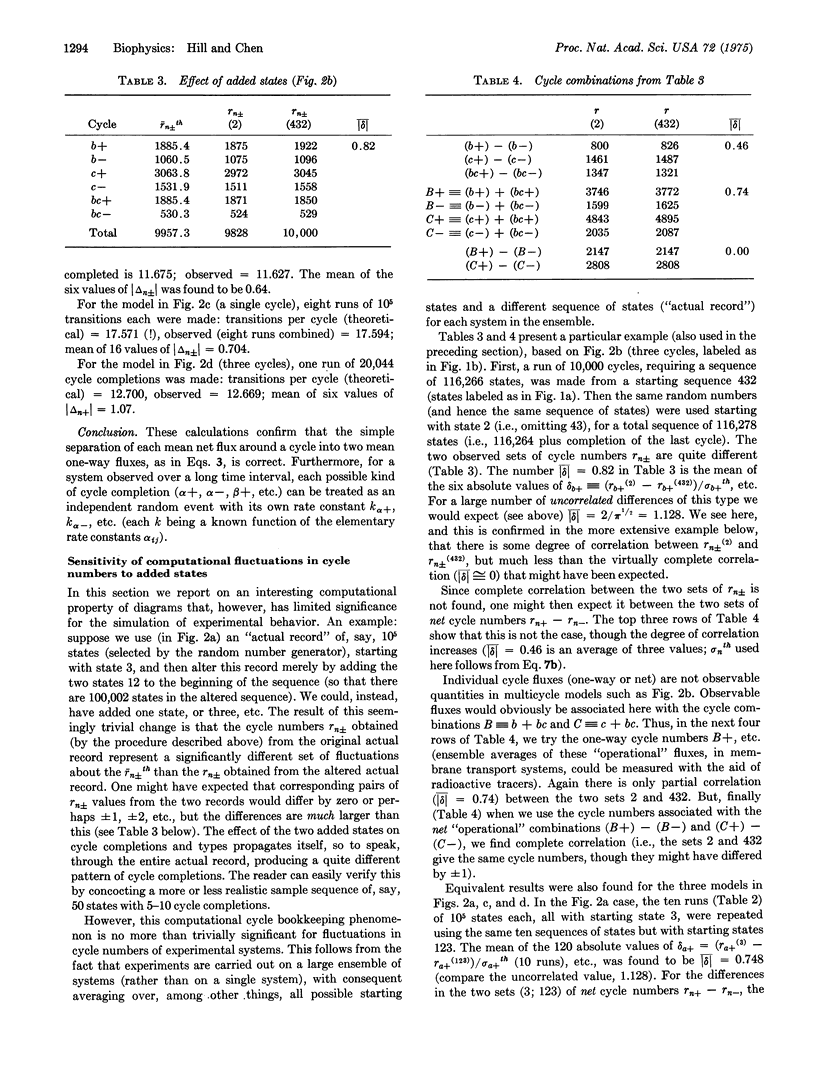
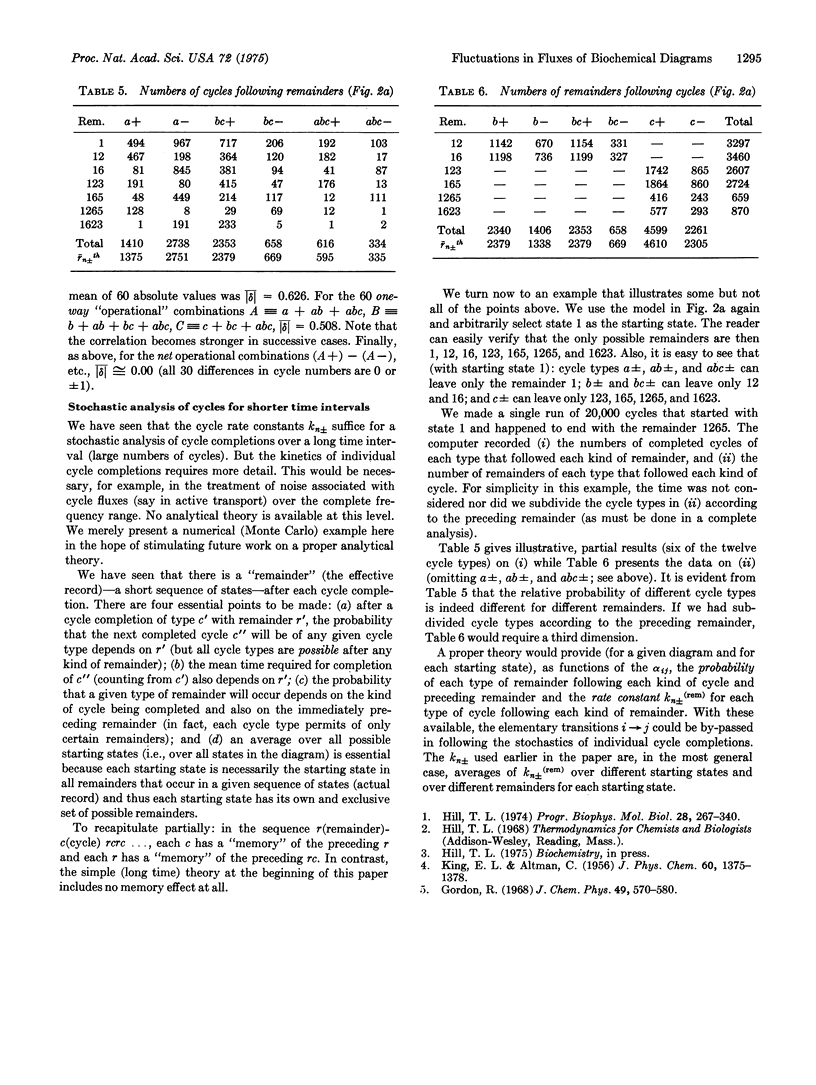
Abstract
Over a long time period, the rate constants for cycle completions (one-way fluxes) in steady-state biochemical diagrams can be expressed explicitly in terms of the elementary rate constants for transitions between states of the diagram. These cycle rate constants determine the mean one-way fluxes in the diagram and also fluctuations about the means. These properties are confirmed by Monte Carlo computer simulations on special cases. Two other topics are considered briefly: the effect of the starting state or states on the numbers of cycle completions in computer simulation runs; and the more detailed stochastic approach required if individual cycle completions are to be followed (i.e., if the "long time" restriction is removed).
Full text
PDF