Abstract
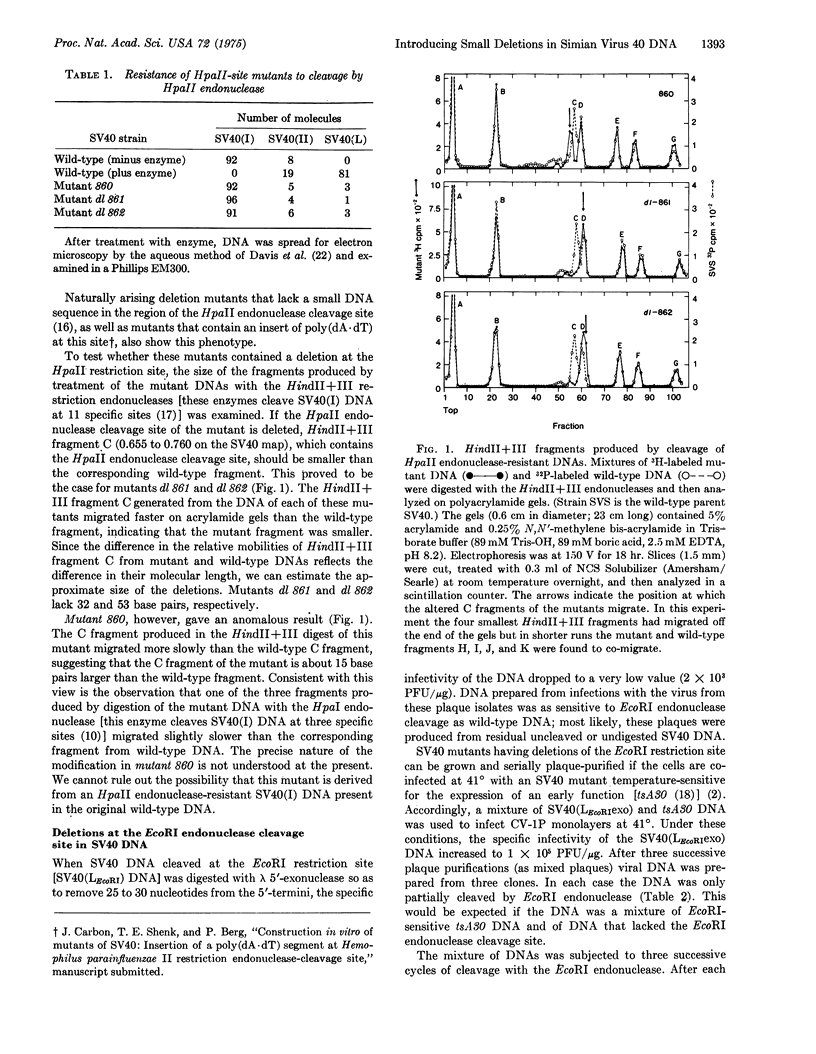
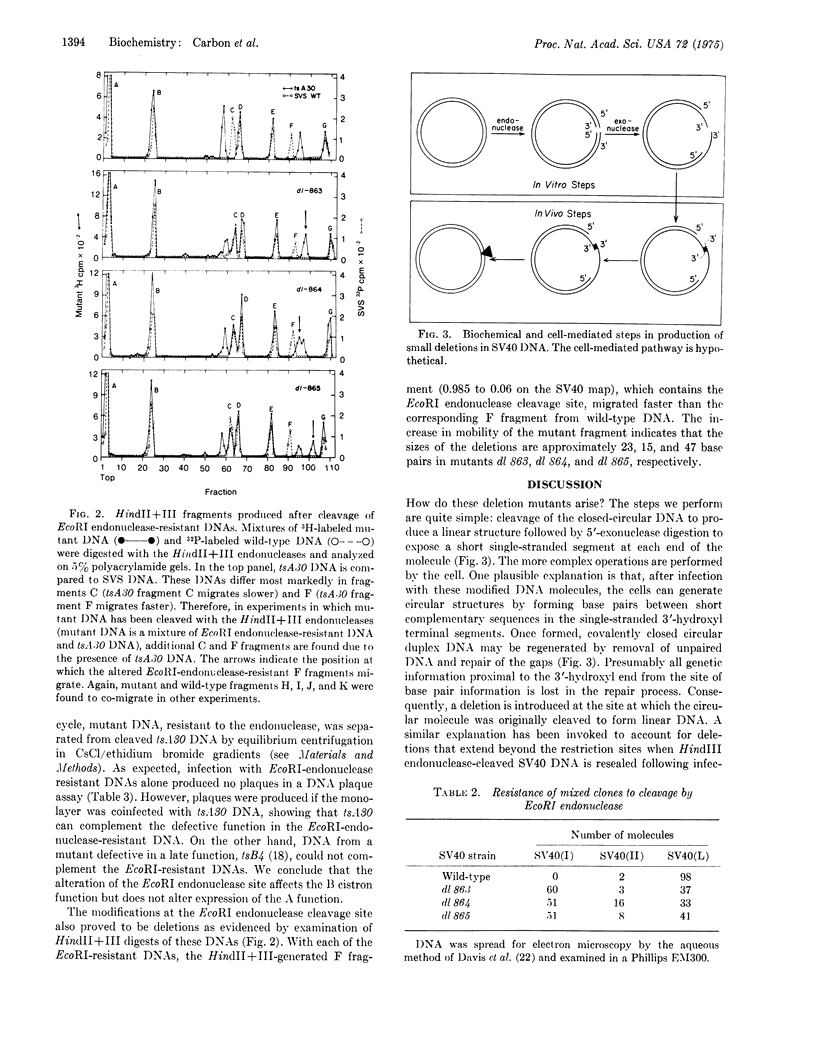
A simple biochemical procedure for producing small deletions (15 to 50 base pairs) at virtually any location in simian virus 40 DNA has been developed. The steps involved are: cleavage of the closed-circular DNA to produce a linear structure followed by 5'-exonuclease digestion to expose a short single-stranded segment at each 3' end of the molecule. Mutants containing deletions at the site of the cleavage are obtained by infecting permissive monkey kidney cells with the exonuclease-treated DNA in the presence or absence of a helper DNA (depending upon whether or not the site of cleavage and therefore the deletion occurred in a gene required for vegetative multiplication). In this paper viable mutants with deletions at the HpaII endonuclease cleavage site (0.735 map position) and defective trans-complementable mutants with deletions at the EcoRI endonuclease cleavage site (0/1.0 map position) were isolated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaij C., Borst P. The gel electrophoresis of DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 10;269(2):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman W. W., Nathans D. The isolation of simian virus 40 variants with specifically altered genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):942–946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K., Nathans D. Specific cleavage of simian virus 40 DNA by restriction endonuclease of Hemophilus influenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2913–2917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedgpeth J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. DNA nucleotide sequence restricted by the RI endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3448–3452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN F. C., GIRARDI A. J., GILDEN R. V., KOPROWSKI H. INFECTION OF HUMAN AND SIMIAN TISSUE CULTURES WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:53–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., Symons R. H., Berg P. Biochemical method for inserting new genetic information into DNA of Simian Virus 40: circular SV40 DNA molecules containing lambda phage genes and the galactose operon of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2904–2909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Nathans D. Deletion mutants of simian virus 40 generated by enzymatic excision of DNA segments from the viral genome. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90169-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobban P. E., Kaiser A. D. Enzymatic end-to end joining of DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 15;78(3):453–471. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Berg P. Defective simian virus 40 genomes: isolation and growth of individual clones. Virology. 1974 Nov;62(1):112–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertz J. E., Berg P. Viable deletion mutants of simian virus 40: selective isolation by means of a restriction endonuclease from Hemophilus parainfluenzae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4879–4883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. F., Berg P. Cleavage of Simian virus 40 DNA at a unique site by a bacterial restriction enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder C., Delius H. Specificity of the break produced by restricting endonuclease R 1 in Simian virus 40 DNA, as revealed by partial denaturation mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3215–3219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Murray K. Manipulation of restriction targets in phage lambda to form receptor chromosomes for DNA fragments. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):476–481. doi: 10.1038/251476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Rhodes C., Rigby P. W., Berg P. Biochemical method for mapping mutational alterations in DNA with S1 nuclease: the location of deletions and temperature-sensitive mutations in simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki H., Takanami M. DNA sequence restricted by restriction endonuclease AP from Haemophilus aphirophilus. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 5;246(153):138–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio246138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabak H. F., Griffith J., Geider K., Schaller H., Kornberg A. Initiation of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. VII. A unique location of the gap in the M13 replicative duplex synthesized in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3049–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto K. K., Kirschstein R. L., Habel K. Mutants of simian virus 40 differing in plaque size, oncogenicity, and heat sensitivity. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):990–994. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.990-994.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


