Abstract
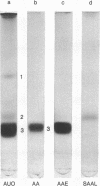
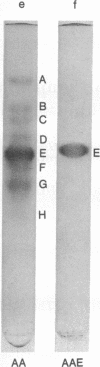
An amyloid fibril protein of unknown origin from a patient with systemic amyloidosis has been purified to homogeneous charge and size by gel filtration and two step isoelectric focusing. From crude antisera to the initial heterogeneous fibril protein, monospecific antibodies have been obtained by immunoabsorption with the immobilized purified amyloid protein. These antibodies have been used to identify an antigenically related serum component in whole sera of patients with and without amyloidosis. Chromatography on Sephadex G-200 in phosphate buffered saline of a patient's whole serum yields a component with an apparent molecular weight of approximately 200,000. Guanidine denaturation of this high-molecular-weight serum component followed by Sephadex G-100 column chromatography in 5 M guanidine affords an antigenically reactive protein with an apparent molecular weight of about 12,500. The antigenic similarity and molecular weight of the latter protein indicates that it could act as the smallest serum precursor of the tissue fibril protein in this group of cases of amyloidosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. Estimation of the molecular weights of proteins by Sephadex gel-filtration. Biochem J. 1964 May;91(2):222–233. doi: 10.1042/bj0910222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benditt E. P., Eriksen N., Hermodson M. A., Ericsson L. H. The major proteins of human and monkey amyloid substance: Common properties including unusual N-terminal amino acid sequences. FEBS Lett. 1971 Dec 1;19(2):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80506-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ein D., Kimura S., Terry W. D., Magnotta J., Glenner G. G. Amino acid sequence of an amyloid fibril protein of unknown origin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 10;247(17):5653–5655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Terry W. D., Isersky C. Amyloidosis: its nature and pathogenesis. Semin Hematol. 1973 Jan;10(1):65–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husby G., Natvig J. B. A serum component related to nonimmunoglobulin amyloid protein AS, a possible precursor of the fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1054–1061. doi: 10.1172/JCI107642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isersky C., Ein D., Page D. L., Harada M., Glenner G. G. Immunochemical cross-reactions of human amyloid proteins with human immunoglobulin light polypeptide chains. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):486–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Franklin E. C., Frangione B., Pras M. The amino acid sequence of a major nonimmunoglobulin component of some amyloid fibrils. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2773–2776. doi: 10.1172/JCI107098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Pras M., Franklin E. C. Immunologic studies of the major nonimmunoglobulin protein of amyloid. I. Identification and partial characterization of a related serum component. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):373–380. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletten K., Husby G. The complete amino-acid sequence of non-immunoglobulin amyloid fibril protein AS in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):117–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesterberg O. Physicochemical properties of the carrier ampholytes and some biochemical applications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Jun 15;209:23–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb47516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]