Abstract
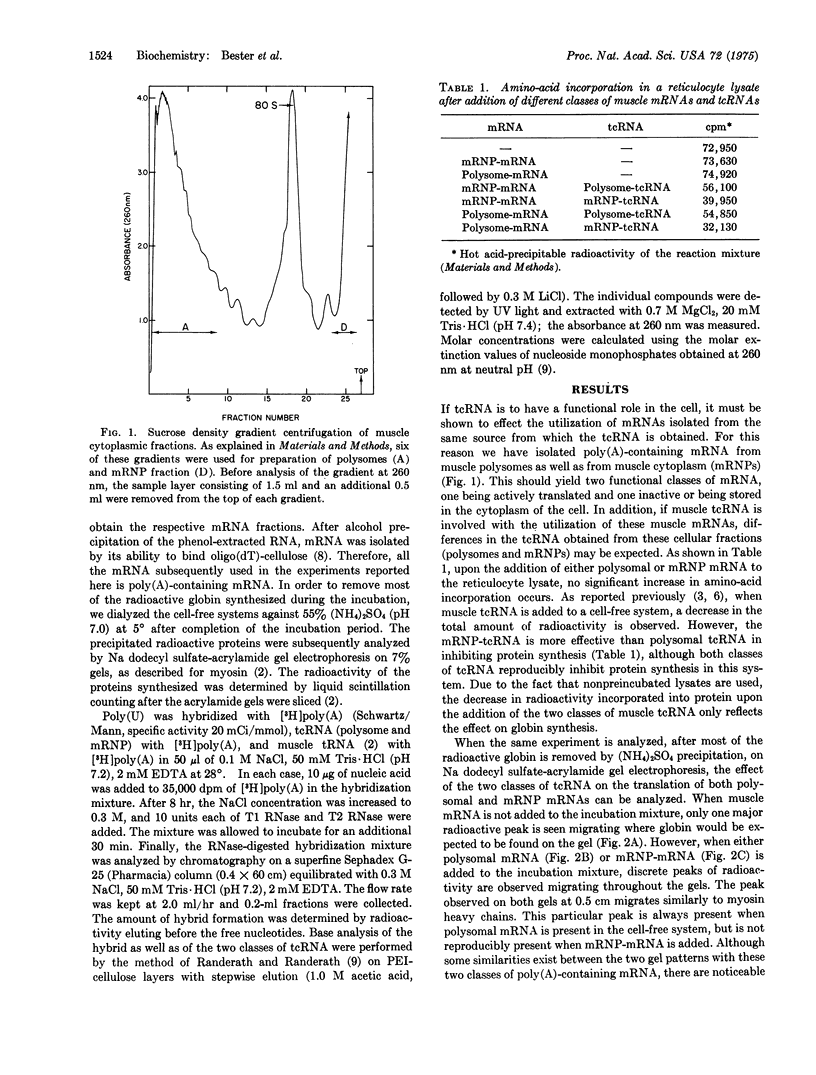
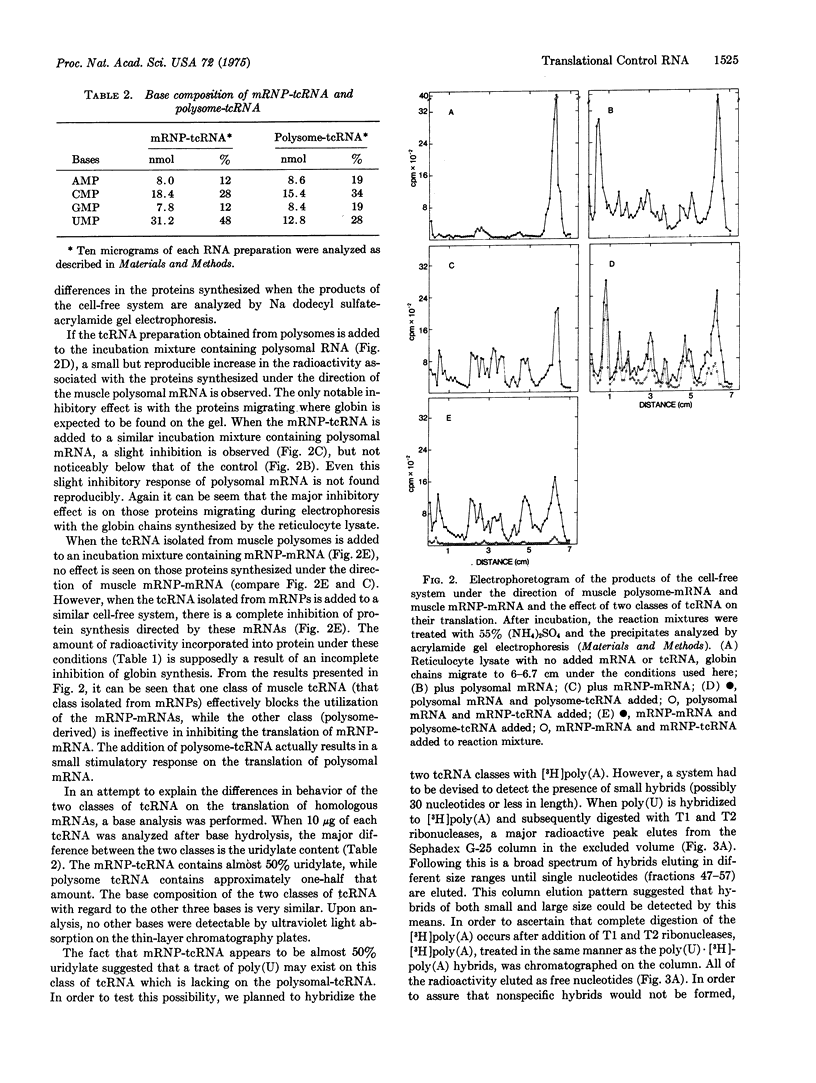
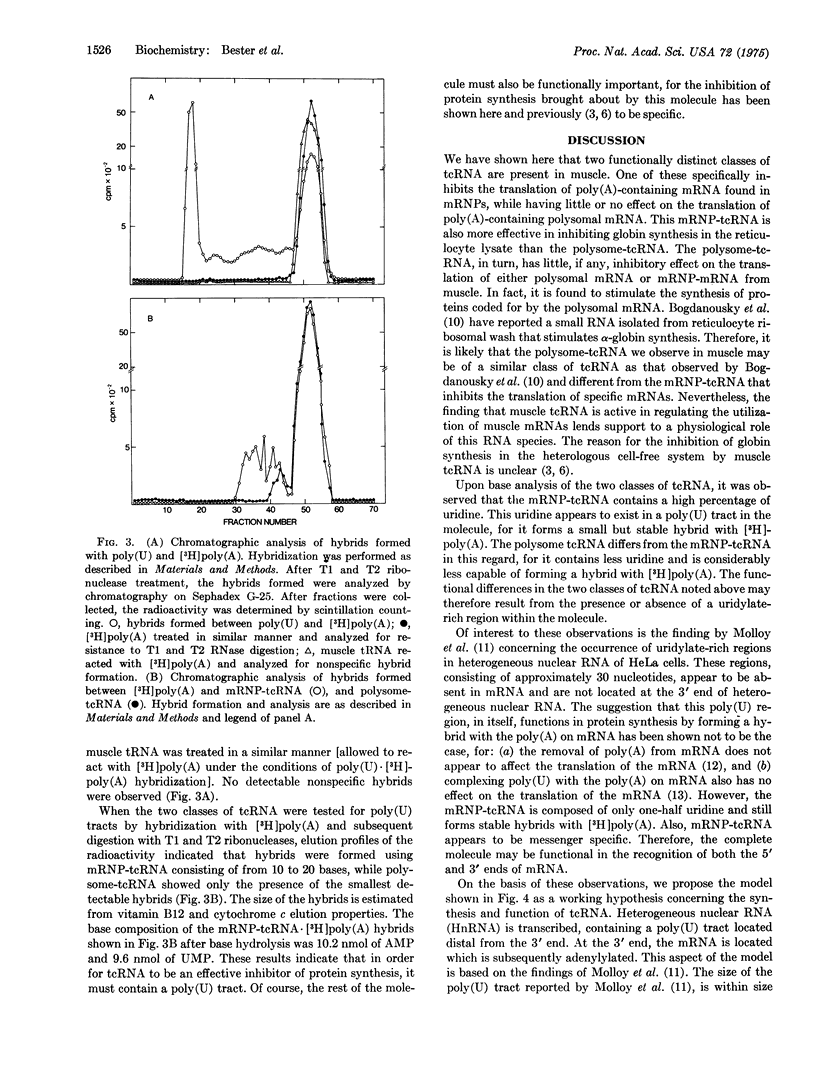
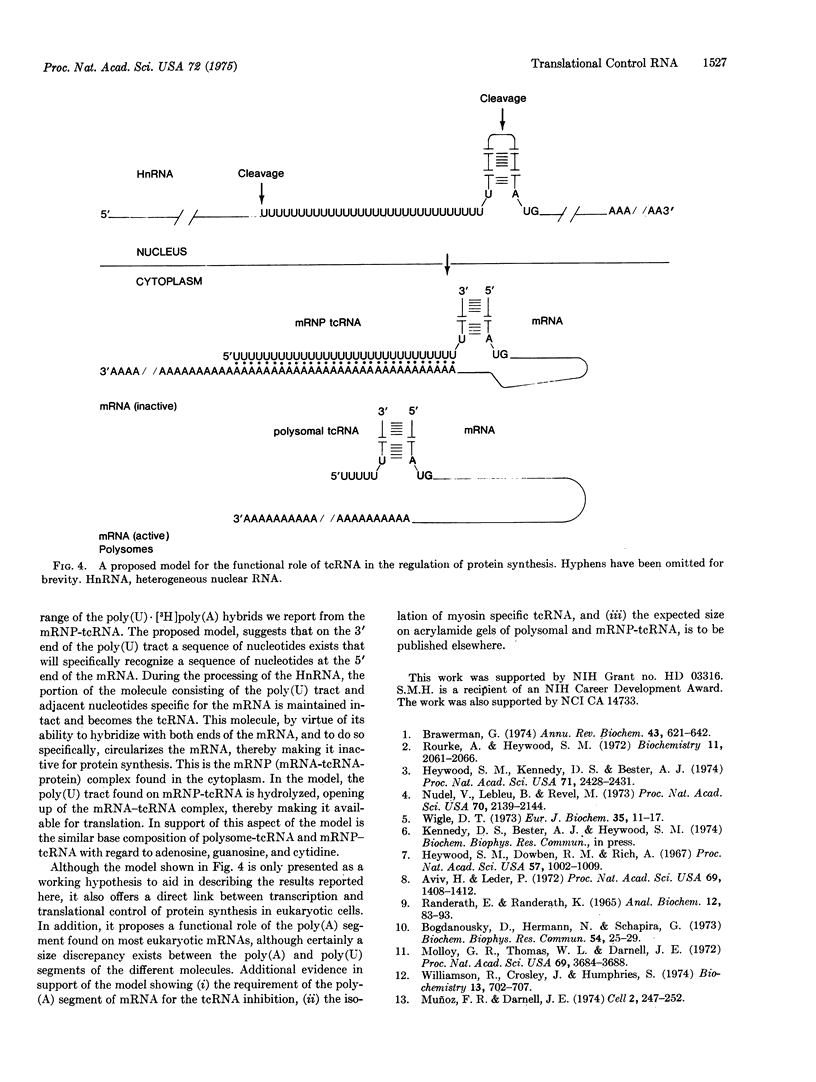
Two classes of translation control RNA (tcRNA) have been isolated from embryonic chick muscle. One of these classes, the tcRNA isolated from messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNP-tcRNA), is effective in inhibiting the translation of mRNP-mRNA while having little if any effect on polysomal mRNA. The other class, polysome-tcRNA, has no effect on mRNP-mRNA while it stimulates the translation of polysomal mRNA. The mRNP tcRNA contains approximately 50 percent uridylate residues and forms small but stable hybrids with poly (A), while polysome-tcRNA contains fewer uridylate residues and is much less effective in forming a hybrid with poly (A). A proposed model concerning the role of these two classes of tcRNA in the regulation of protein synthesis is presented.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanovsky D., Hermann W., Schapira G. Presence of a new RNA species among the initiation protein factors active in eukaryotes translation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 5;54(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90883-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Eukaryotic messenger RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):621–642. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez Muñoz R., Darnell J. E. Poly(A) in mRNA does not contribute to secondary structure necessary for protein synthesis. Cell. 1974 Aug;2(4):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M., Dowben R. M., Rich A. The identification of polyribosomes synthesizing myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1002–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heywood S. M., Kennedy D. S., Bester A. J. Separation of specific initiation factors involved in the translation of myosin and myoglobin messenger RNAs and the isolation of a new RNA involved in translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2428–2431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy G. R., Thomas W. L., Darnell J. E. Occurrence of uridylate-rich oligonucleotide regions in heterogeneous nuclear RNA of HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3684–3688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Lebleu B., Revel M. Discrimination between messenger ribonucleic acids by a mammalian translation initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2139–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath E., Randerath K. Ion-exchange thin-layer chromatography. XII. Quantitative elution and microdetermination of nucleoside monophosphates, ATP, and other nucleotide coenzymes. Anal Biochem. 1965 Jul;12(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rourke A. W., Heywood S. M. Myosin synthesis and specificity of eukaryotic initiation factors. Biochemistry. 1972 May 23;11(11):2061–2066. doi: 10.1021/bi00761a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigle D. T. Purification of a messenger-specific initiation factor from ascites-cell supernatant. Eur J Biochem. 1973 May;35(1):11–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Crossley J., Humphries S. Translation of mouse globin messenger ribonucleic acid from which the poly(adenylic acid) sequence has been removed. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):703–707. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


