Abstract
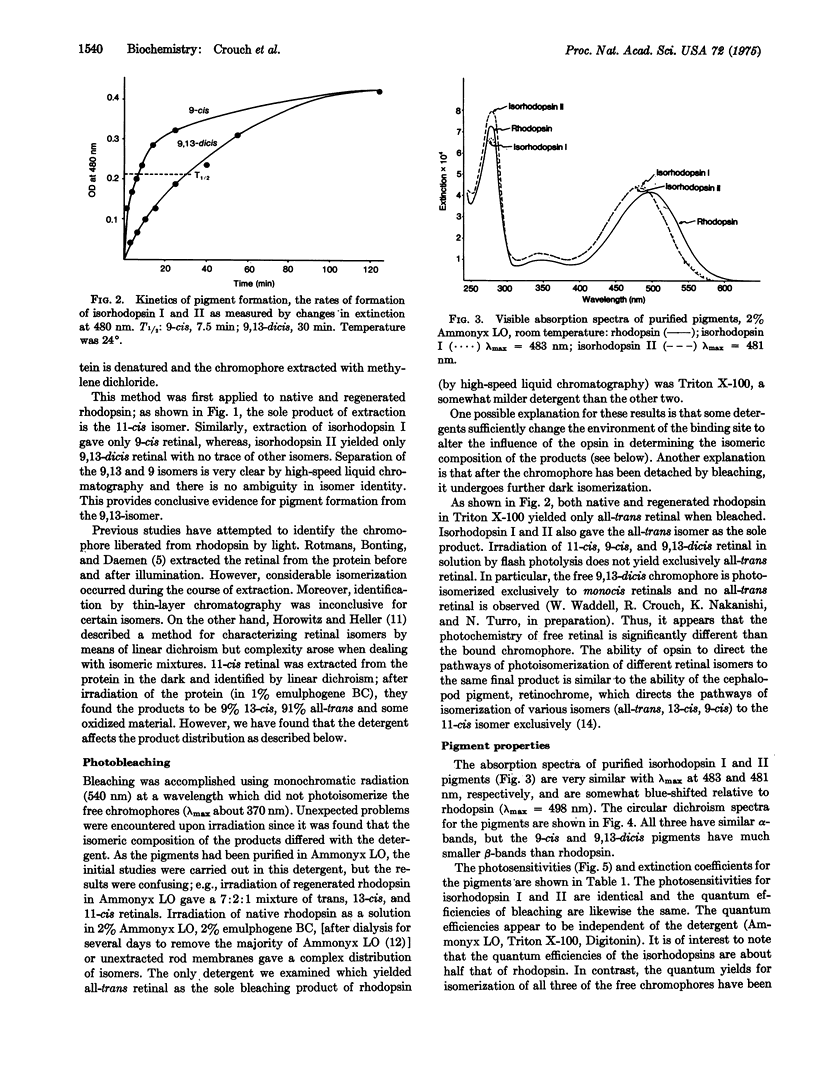
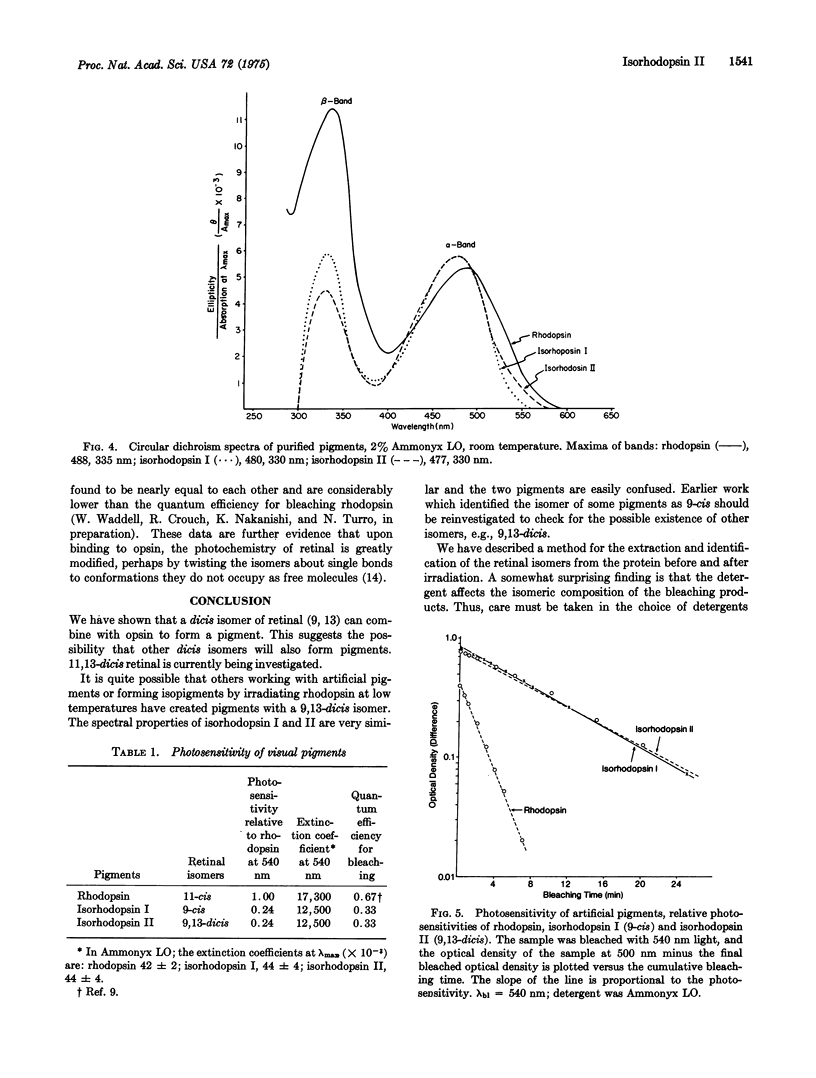
We have found that in addition to the 11-cis and 9-cis isomers of retinal which are known to couple with the visual pigment apoprotein opsin to form pigments, a third isomer 9,13-dicis retinal also will form a pigment. That this isomer is indeed bound to opsin has been shown unequivocally by removing the chromophore without isomerization and subsequent identification by high-speed liquid chromatography. Using similar techniques, we have shown that the product of bleaching by light of all three pigments in Trition X-100 is the all-trans isomer. This specificity in the product of bleaching, as with many other properties of visual pigments, is not shared by the free chromophore. Of particular interest is that when 9,13-dicis retinal is combined with opsin to form a pigment, a single photon can isomerize it about two double bonds, to the all-trans isomer.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Applebury M. L., Zuckerman D. M., Lamola A. A., Jovin T. M. Rhodopsin. Purification and recombination with phospholipids assayed by the metarhodopsin I leads to metarhodopsin II transition. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3448–3458. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Nakanishi K., Ebrey T. G., Honig B. Letter: Properties of 14-methylretinal, 13-desmethyl-14-methylretinal, and visual pigments formed therefrom. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 May 29;96(11):3642–3644. doi: 10.1021/ja00818a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebrey T. G. The use of Ammonyx LO in the purification of rhodopsin and rod outer segments. Vision Res. 1971 Sep;11(9):1007–1009. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD R., WALD G. Cis-trans isomers of vitamin A and retinene in the rhodopsin system. J Gen Physiol. 1952 Nov;36(2):269–315. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Ebrey T. G. The structure and spectra of the chromophore of the visual pigments. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1974;3(0):151–177. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.03.060174.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz J., Heller J. Photoselection and linear dichroism of retinals. A method for identification and measurement of various geometrical isomers. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 10;248(3):1051–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irreverre F., Stone A. L., Shichi H., Lewis M. S. Biochemistry of visual pigments. I. Purification and properties of bovine rhodopsin. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 25;244(4):529–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropf A., Hubbard R. The photoisomerization of retinal. Photochem Photobiol. 1970 Oct;12(4):249–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1970.tb06057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J. 220 MHz proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of retinals. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):825–828. doi: 10.1038/221825a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotmans J. P., Bonting S. L., Daemen F. J. On the chromophoric group of rhodopsin. Vision Res. 1972 Feb;12(2):337–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(72)90123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALD G., BROWN P. K. The molar extinction of rhodopsin. J Gen Physiol. 1953 Nov 20;37(2):189–200. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorn M., Futterman S. Properties of rhodopsin dependent on associated phospholipid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):881–886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


