Abstract
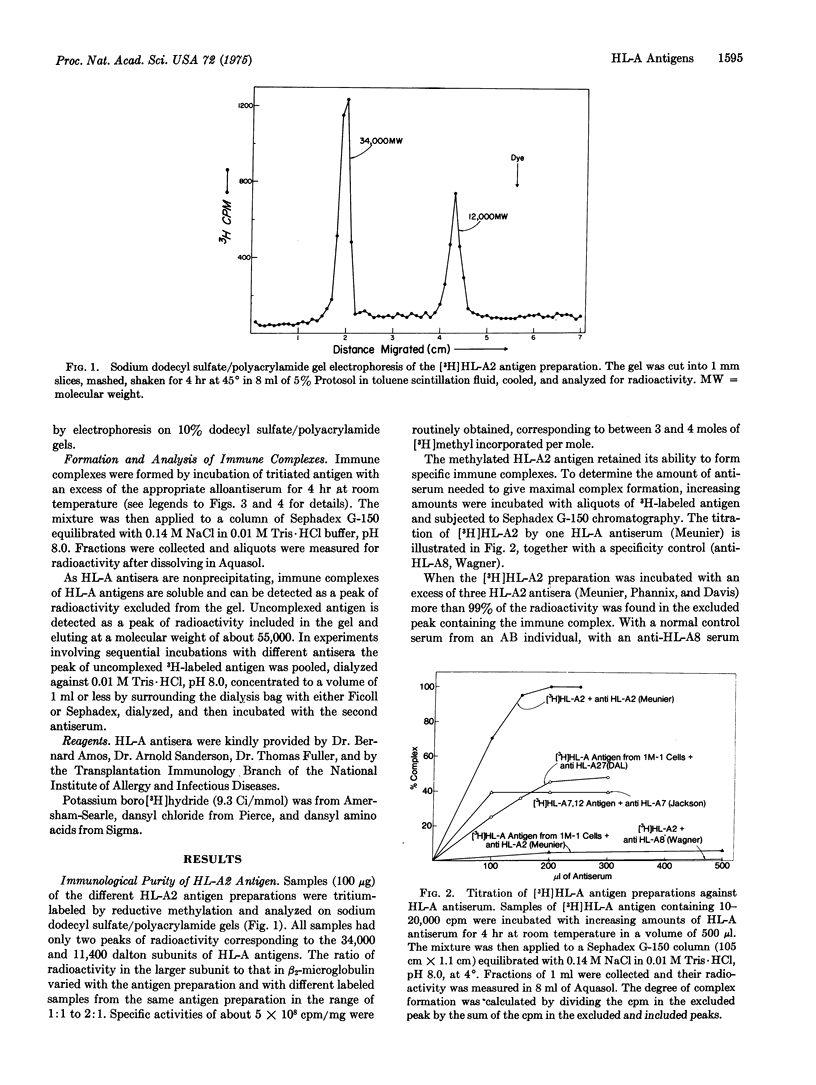
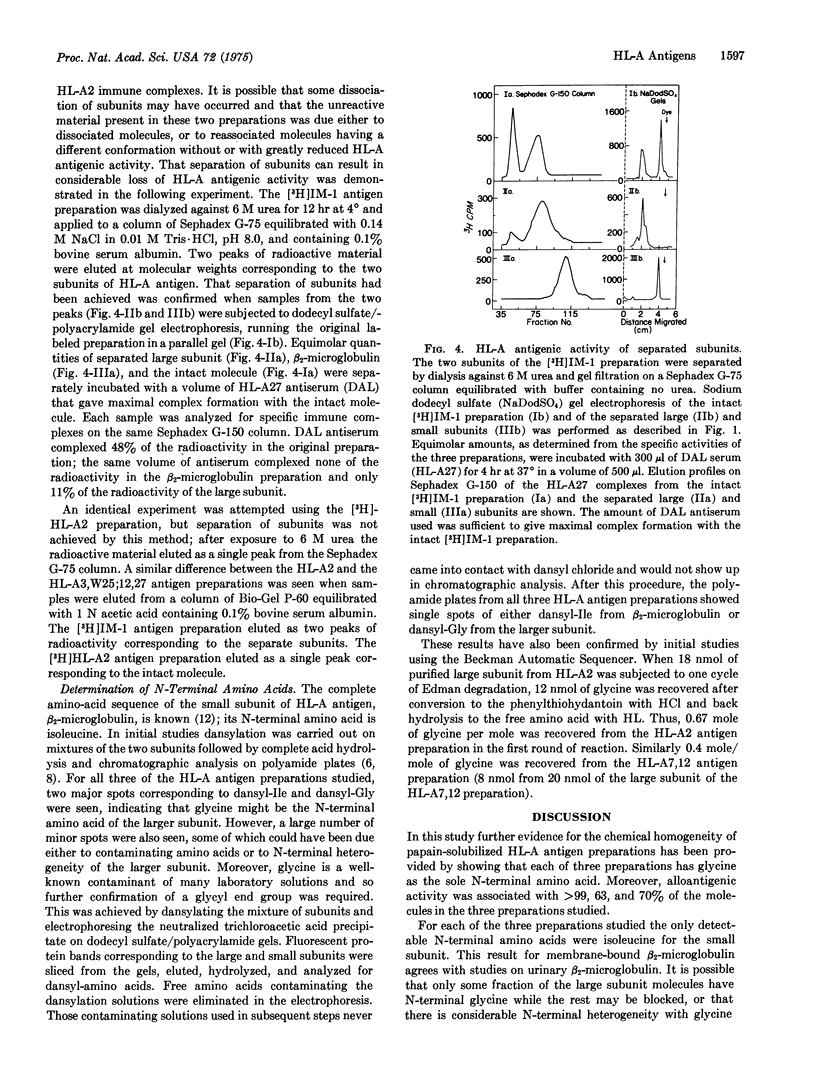
Three preparations of purified papain-solublized HL-A antigens have been radiolabeled by reductive methylation using formaldehyde and potassium boro[3H]hydride, and their reaction with specific HL-A antisera has been investigated. Greater than 99 percent of the radioactivity in the [3H]HL-A2 preparation could be complexed with several HL-A2 antisera, but not with specificity controls. The other two preparations, which contained mixtures of HL-A antigenic specificities (HL-A7,12 an HL-A3,W25;12,27), showed 63 per cent and 70 per cent complex formation with mixtures of the appropriate HL-A antisera. The N-terminal amino acid of both subunits has been determined for the three HL-A antigen preparations. In all cases the only detectable N-terminal amino acids were isoleucine for the small subunits, beta-2-microblogulin, and glycine for the larger subunit.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cresswell P., Turner M. J., Strominger J. L. Papain-solubilized HL-A antigens from cultured human lymphocytes contain two peptide fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Wang J. L., Berggård I., Peterson P. A. The complete amino acid sequence of beta 2-microglobulin. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 20;12(24):4811–4822. doi: 10.1021/bi00748a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Strategy and tactics in protein chemistry. Biochem J. 1970 Oct;119(5):805–822. doi: 10.1042/bj1190805f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neauport-Sautes C., Bismuth A., Kourilsky F. M., Manuel Y. Relationship between HL-A antigens and beta-2-microglobulin as studied by immunofluorescence on the lymphocyte membrane. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):957–968. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancake S. J., Nathenson S. G. Selective loss of H-2 antigenic reactivity after chemical modification. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1086–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Humphreys R. E., Turner M. J., Strominger J. L. Heterogeneity of HL-A antigen preparations is due to variable sialic acid content. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3998–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rask L., Ostberg L., Lindblom B., Fernstedt Y., Peterson P. A. The subunit structure of transplantation antigens. Transplant Rev. 1974;21(0):85–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb01547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Means G. E. Radioactive labeling of proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):831–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solheim B. G., Bratlie A., Sandberg L., Staub-Nielsen L., Thorsby E. Further evidence of a third HL-A locus. Tissue Antigens. 1973;3(6):439–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1973.tb00514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solheim B. G., Thorsby E. Beta-2-microglobulin is part of the HL-A molecule in the lymphocyte membrane. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):36–38. doi: 10.1038/249036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigaki N., Katagiri M., Nakamuro K., Kreiter V. P., Pressman D. Common antigenic structures of HL-A antigens. II. Small fragments derived from papain-solubilized HL-A antigen molecules. Immunology. 1974 Jan;26(1):155–168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigaki N., Miyakawa Y., Yagi Y., Kreiter V. P., Pressman D. Radioiodinated soluble HL-A antigens: HL-A alloantigenic characterization and use in radioimmunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1973 Oct;3(2):109–125. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(73)90027-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thieme T. R., Raley R. A., Fahey J. L. Demonstration of molecular individuality of HL-A antigens. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):323–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Platt T., Weber K. Amino-terminal sequence analysis of proteins purified on a nanomole scale by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 25;247(10):3242–3251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


