Abstract
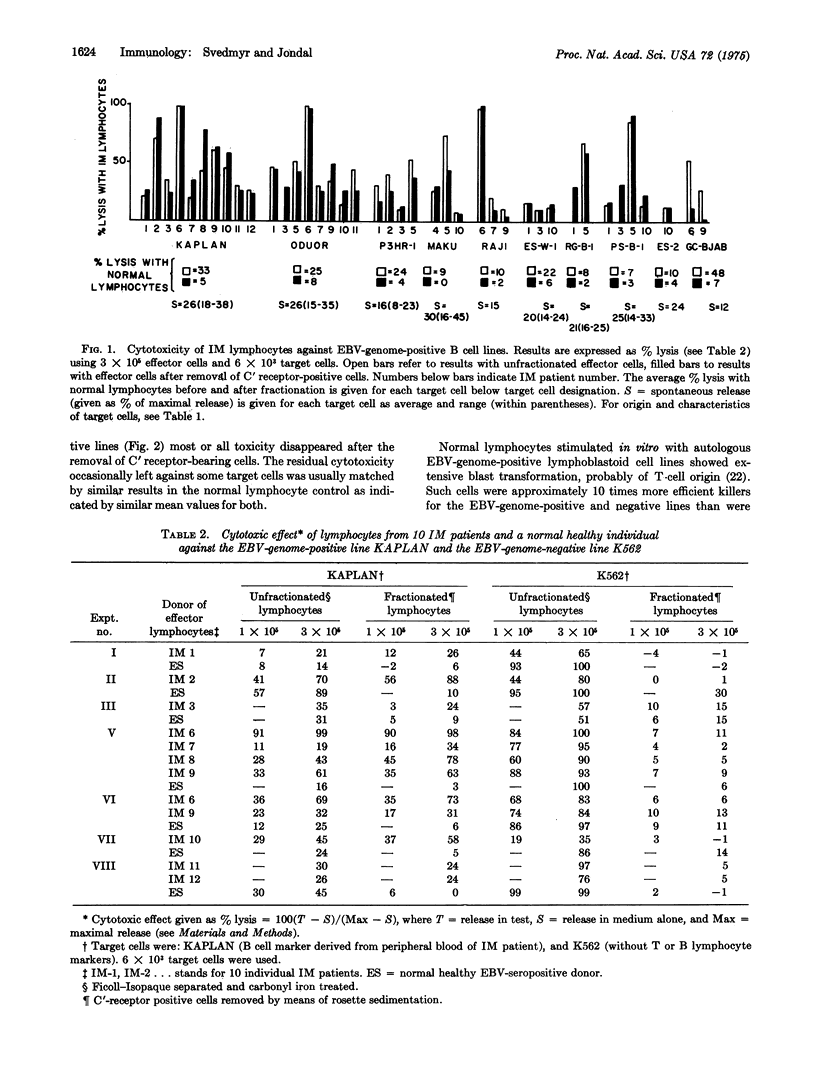
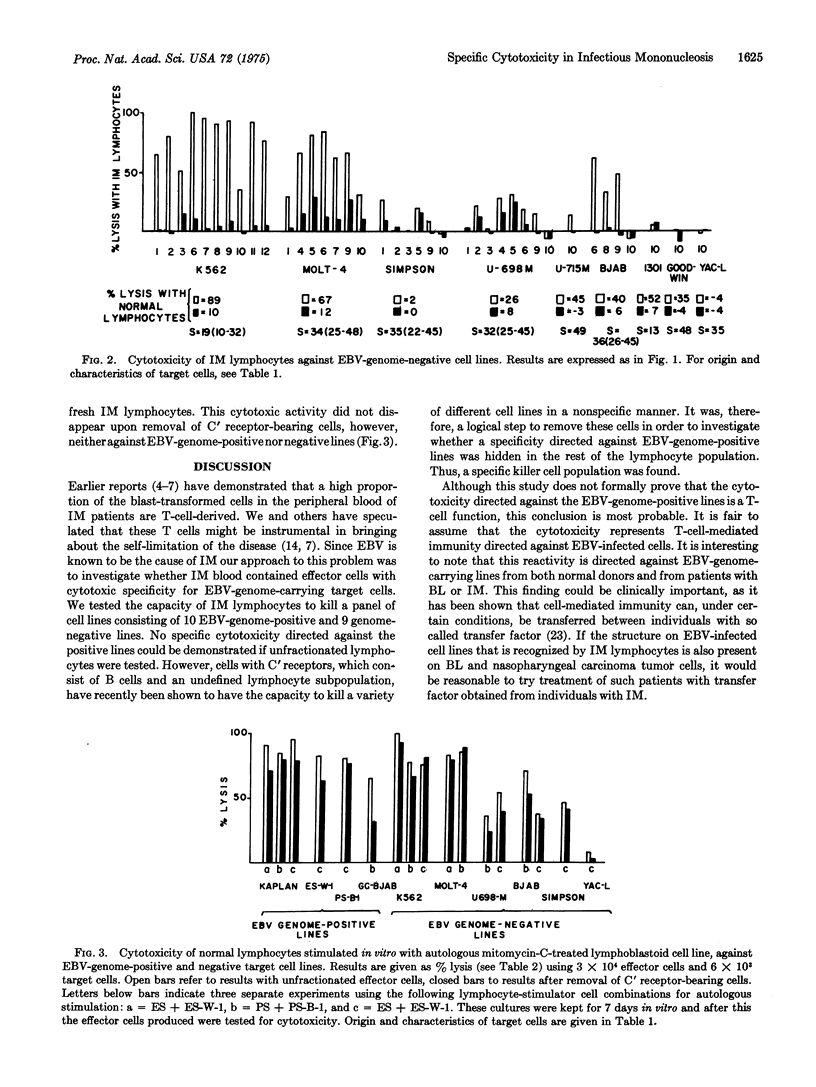
Peripheral lymphoid cells, from 12 cases of acute infectious mononucleosis (IM), were tested in a micro chromium-51 release assay for cytotoxic activity against a variety of cell lines that did or did not carry the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome. Unfractionated lymphocytes from these patients were cytotoxic to both types of cell lines, as were lymphocytes from healthy individuals. If, however, lymphocytes bearing complement receptors were removed, the residual IM lymphocyte fraction was specifically cytotoxic for EBV-genome-carrying cell lines. The residual lymphocyte fraction in normal donors had no such effect. Heterophile-positive IM is caused by EBV, and these results indicate that, during the acute phase of this disease, patients harbor killer cells, probably T cells, which specifically kill EBV-genome-carrying B cells in vitro. No such specificity for EBV-genome-psitive target cells was found in normal lymphocytes stimulated in vitro with autologous EBV-genome-positive lymphoblastoid cells. Such stimulated cells were highly cytotoxic to both genome-positive and negative lines after removal of complement receptor-positive lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanden R. V. T cell response to viral and bacterial infection. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):56–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. A one-stage procedure for isolation of granulocytes and lymphocytes from human blood. General sedimentation properties of white blood cells in a 1g gravity field. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:51–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cikes M. Antigenic expression of a murine lymphoma during growth in vitro. Nature. 1970 Feb 14;225(5233):645–647. doi: 10.1038/225645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denman A. M., Pelton B. K. Control mechanisms in infectious mononucleosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):13–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY G. E., LAZARUS H., FARBER S., UZMAN B. G., BOONE B. A., MCCARTHY R. E. CONTINUOUS CULTURE OF HUMAN LYMPHOBLASTS FROM PERIPHERAL BLOOD OF A CHILD WITH ACUTE LEUKEMIA. Cancer. 1965 Apr;18:522–529. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196504)18:4<522::aid-cncr2820180418>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. IV. Distribution of surface markers on resting and blast-transformed lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(6):739–747. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Lindahl T., Jondal M., Leibold W., Menézes J., Nilsson K., Sundström C. Continuous lymphoid cell lines with characteristics of B cells (bone-marrow-derived), lacking the Epstein-Barr virus genome and derived from three human lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3283–3286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence H. S. Transfer factor. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:195–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. L., Davidsohn I., Panczyszyn O. Horse agglutinins in infectious mononucleosis. II. The spot test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;49(1):12–18. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/49.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Cytotoxicity of a factor isolated from human spleen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):535–538. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Sundström C. Establishment and characteristics of two unique cell lines from patients with lymphosarcoma. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):808–823. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson A. S., Rosen S. W., Tashijan A. H., Jr, Weintraub B. D. Production of human chorionic gonadotropin in vitro by a cell line derived from a carcinoma of the lung. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Mar;50(3):669–674. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.3.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr E. A., Deinhardt F., Klein G. Sensitivity of different target cells to the killing action of peripheral lymphocytes stimulated by autologous lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jun 15;13(6):891–903. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910130617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr E., Wigzell H., Jondal M. Sensitization of human lymphocytes against autologous or allogeneic lymphoblastoid cell lines: characteristics of the reactive cells. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(4):499–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1974.tb01283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virolainen M., Andersson L. C., Lalla M., von Essen R. T-lymphocyte proliferation in mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1973 Nov;2(1):114–120. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(73)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B. Diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis by the monospot test. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;52(3):303–308. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/52.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yata J., Desgranges C., de Thé G., Tachibana T. Lymphocytes in infectious mononucleosis. Properties of atypical cells and origin on the lymphoblastoid lines. Biomedicine. 1973 Nov 20;19(11):479–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


