Abstract
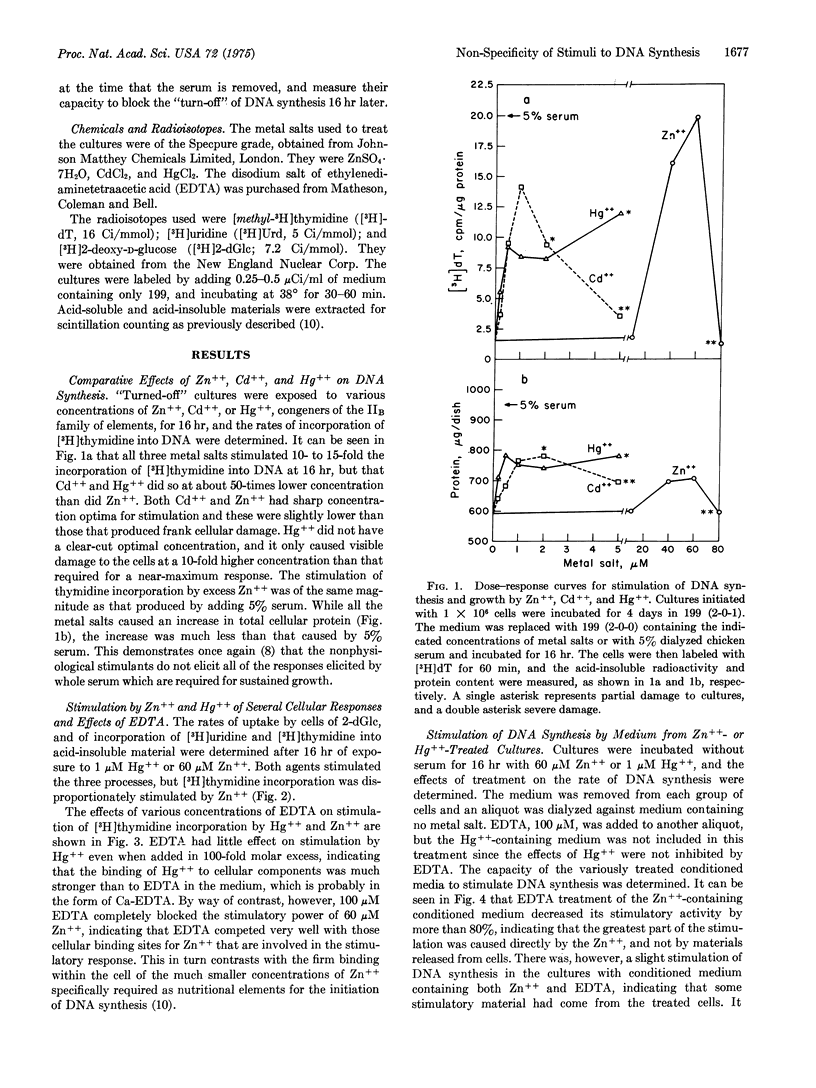
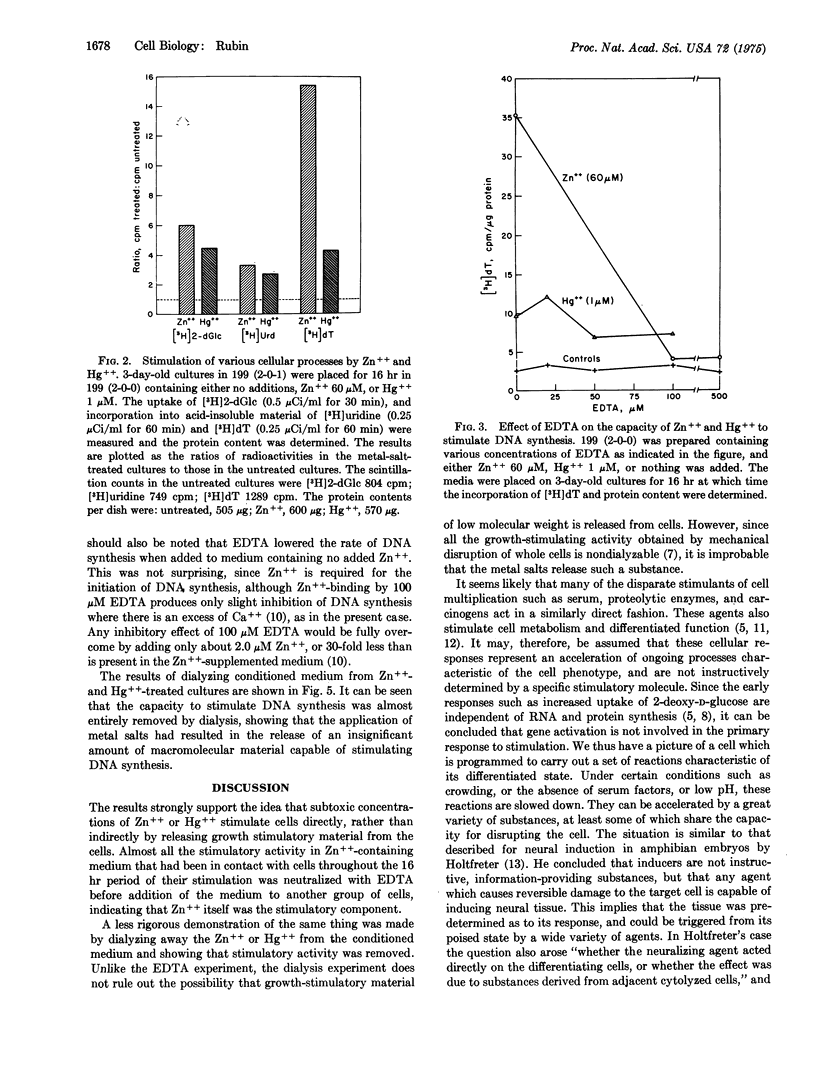
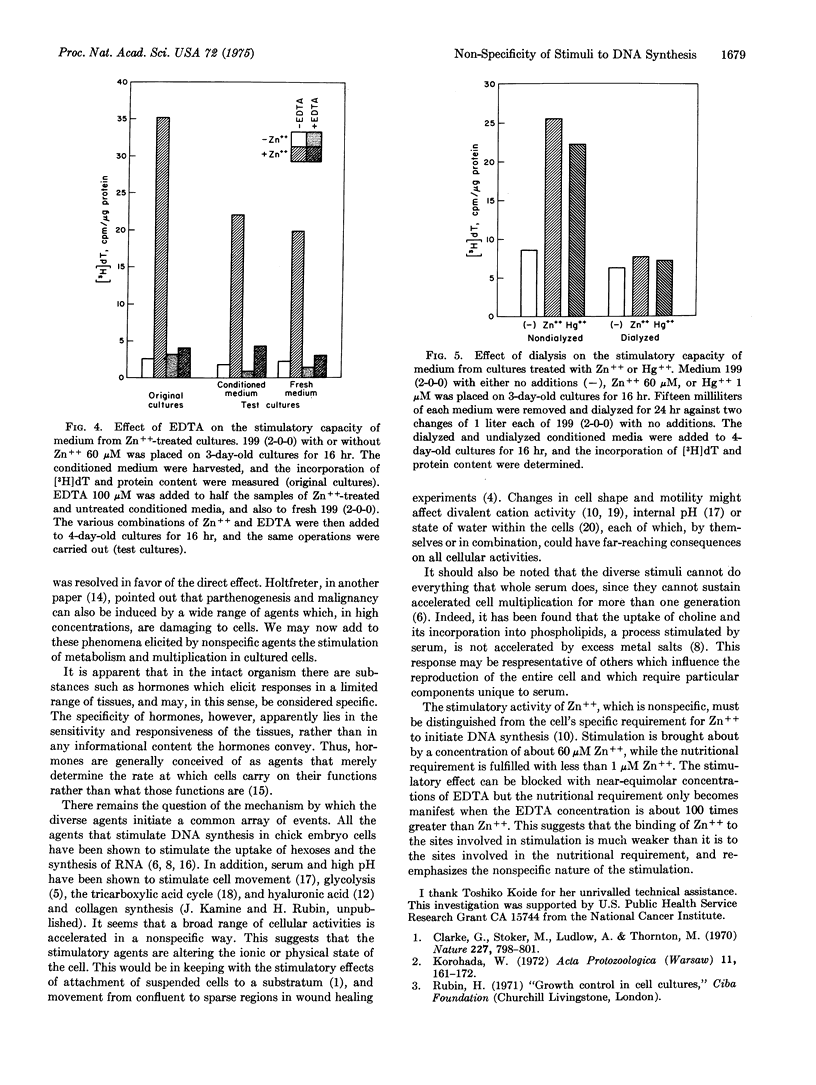
The rate of DNA synthesis in chick embryo cultures deprived of serum is stimulated 5- to 20-fold by a large variety of substances, including subtoxic concentrations of certain metal ions such as Zn++, Cd++, and Hg++. The stimulatory concentrations of Zn++ and Cd++ have sharp optima, which are just below the concentrations that produce frank morphological damage in each case. A much wider gap exists between stimulatory and morphologically damaging concentrations of Hg++. These metal ions also stimulate RNA synthesis, and the uptake of 2-deoxy-D-glucose. The stimulatory effects of Zn++, but not those of Hg++, are prevented by treatment with EDTA. Although medium from cultures stimulated by Zn++ or Hg++ retains its stimulatory capacity for a new set of cultures, the capacity in the case of Zn++-treated cultures is almost entirely lost upon addition of EDTA. It is also lost upon dialysis of conditioned medium from cultures treated with either Zn++ or Hg++. It is concluded that the stimulatory effect is the direct result of interaction between metal ions and cells, and not to the release of growth-stimulatory materials from the cells. The stimulation is thus seen as a non-specific event resulting in an integrated, metabolic response by the cells.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bissell M. J., Hatié C., Rubin H. Patterns of glucose metabolism in normal and virus-transformed chick cells in tissue culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Aug;49(2):555–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G. D., Stoker M. G., Ludlow A., Thornton M. Requirement of serum for DNA synthesis in BHK 21 cells: effects of density, suspension and virus transformation. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):798–801. doi: 10.1038/227798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodge D. W., Rubin H. Activation of phosphofructokinase by stimulants of cell multiplication. Nat New Biol. 1973 Dec 12;246(154):181–183. doi: 10.1038/newbio246181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney T., Jr Local stimulation of growth in primary cultures of chick embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):906–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelwood C. F., Chang D. C., Medina D., Cleveland G., Nichols B. L. Distinction between the preneoplastic and neoplastic state of murine mammary glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1478–1480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscatelli D., Rubin H. Increased hyaluronic acid production on stimulation of DNA synthesis in chick embryo fibroblasts. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):65–66. doi: 10.1038/254065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Rubin H. On the survival of chick embryo cells at low concentrations in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Mar;65(1):209–214. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in animal cells by ethylene diamine tetraacetate, and its reversal by zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H., Koide T. Stimulation of DNA synthesis and 2-deoxy-D-glucose transport in chick embryo cultures by excessive metal concentrations and by a carcinogenic hydrocarbon. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Jun;81(3):387–396. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040810311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. Overgrowth-stimulating activity of disrupted chick embryo cells and cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1256–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. pH and population density in the regulation of animal cell multiplication. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):686–702. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Rubin H. Stimulation of glucose transport in cultures of density-inhibited chick embryo cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3154–3157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


