Abstract
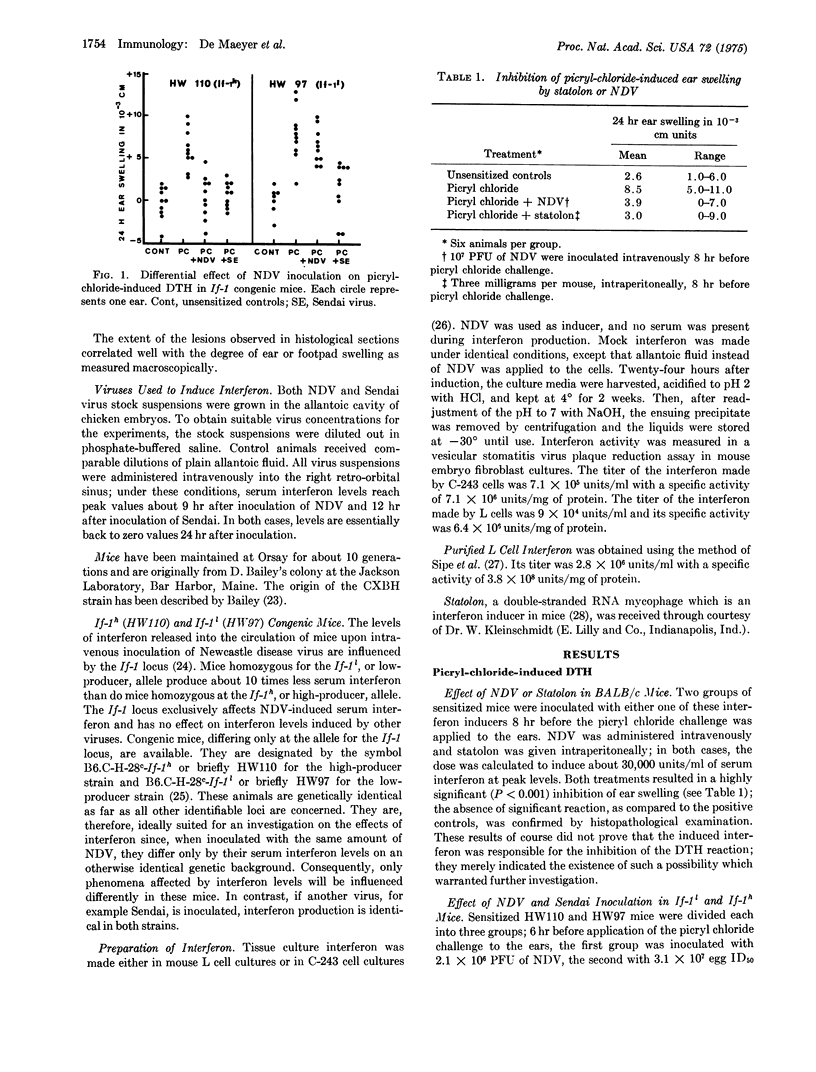
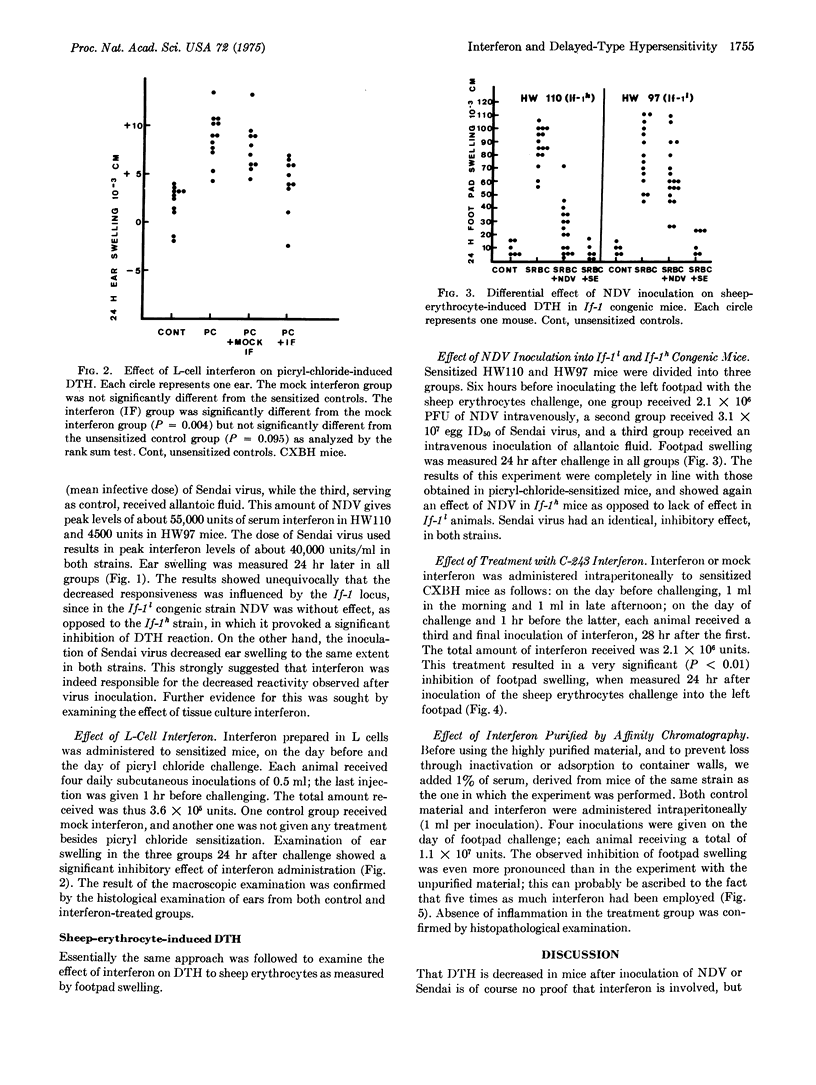
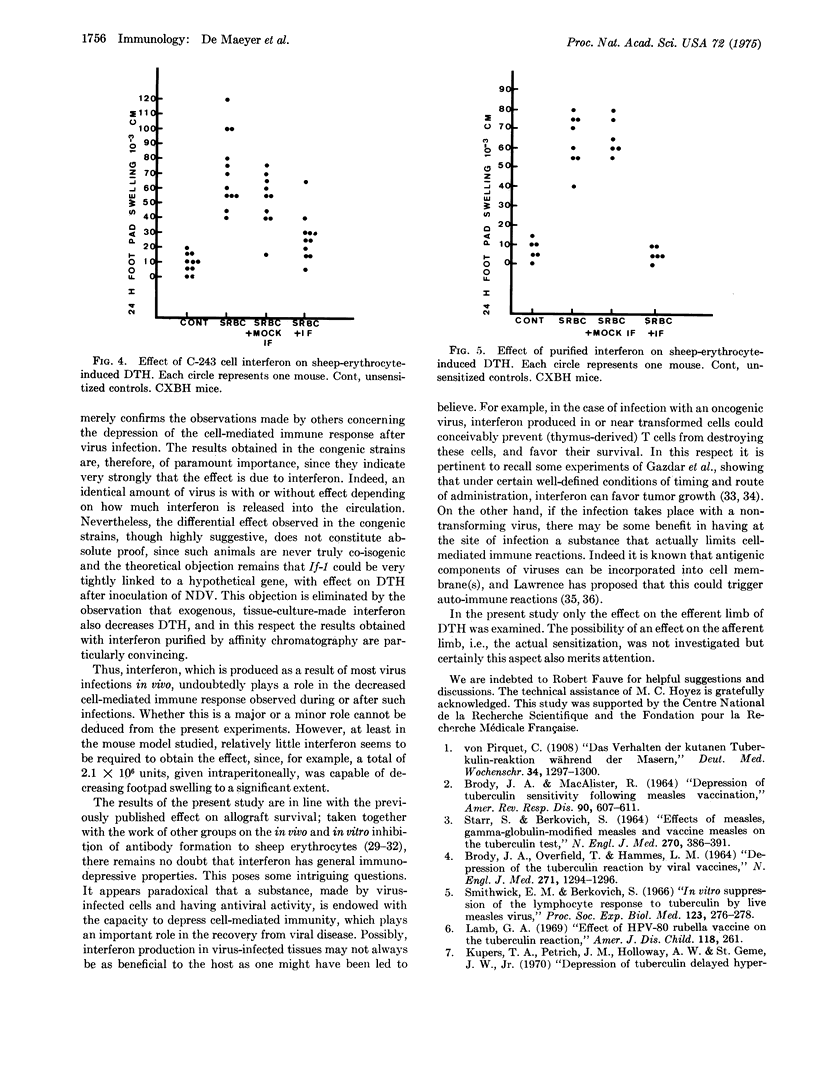
The effect of interferon on delayed-type by persensitivity to picryl chloride and sheep erythrocytes was examined in the mouse. When administered to sensitized animals on the day before or the day of challenge, tissue culture interferon inhibited both the ear swelling induced by pieryl chloride and footpad swelling induced by sheep erythrocytes. Newcastle disease virus, when injected into sensitized If-1l or If-1h congenic mice a few hours before challenge, caused an inhibition of delayed-type hypersensitivity which could be related to the amount of serum interferon induced by the virus. These results indicate that interferon production may represent one of the factors responsible for the depression of cell-mediated immune reactions during virus infection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C. The role of membranes in the replication of animal viruses. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1971;10:181–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Ptak W. Contact and delayed hypersensitivity in the mouse. I. Active sensitization and passive transfer. Immunology. 1968 Sep;15(3):405–416. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODY J. A., MCALISTER R. DEPRESSION OF TUBERCULIN SENSITIVITY FOLLOWING MEASLES VACCINATION. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Oct;90:607–611. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.90.4.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODY J. A., OVERFIELD T., HAMMES L. M. DEPRESSION OF THE TUBERCULIN REACTION BY VIRAL VACCINES. N Engl J Med. 1964 Dec 17;271:1294–1296. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196412172712505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey D. W. Recombinant-inbred strains. An aid to finding identity, linkage, and function of histocompatibility and other genes. Transplantation. 1971 Mar;11(3):325–327. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197103000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W., Levy H. B. Interferon preparations as modifiers of immune responses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Dec;141(3):769–773. doi: 10.3181/00379727-141-36868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur B. R., Merigan T. C. Suppressive effect of interferon on the humoral immune response to sheep red blood cells in mice. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1319–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester T. J., Paucker K., Merigan T. C. Suppression of mouse antibody producing spleen cells by various interferon preparations. Nature. 1973 Nov 9;246(5428):92–94. doi: 10.1038/246092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Cline M. J., Merigan T. C. The interaction of human macrophages and lymphocytes in the phytohemagglutinin-stimulated production of interferon. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):744–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI106545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Sims H., Spahn G. J., Baron S. Interferon mediates enhancement of tumour growth and virus-induced sarcomas in mice. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 19;245(142):77–78. doi: 10.1038/newbio245077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Steinberg A. D., Spahn G. F., Baron S. Interferon inducers: enhancement of viral oncogenesis in mice and rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Apr;139(4):1132–1137. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gisler R. H., Lindahl P., Gresser I. Effects of interferon on antibody synthesis in vitro. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):438–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Kantor F. S. Depression of established delayed hepersensitivity by mumps virus. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. S., Ellis D. A., Black P. H., Monaco A. P., Wood M. L. Immunosuppressive effects of an interferon preparation in vivo. Transplantation. 1974 Feb;17(2):234–236. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197402000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. J., Mergenhagen S. E., Notkins A. L., Dougherty S. F. Inhibition of cellular immunity and enhancement of humoral antibody formation in mice infected with lactic dehydrogenase virus. Transplant Proc. 1969 Mar;1(1):586–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT W. J., CLINE J. C., MURPHY E. B. INTERFERON PRODUCTION INDUCED BY STATOLON. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:741–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange P. H., Mackaness G. B., Miller T. E. Influence of dose and route of antigen injection on the immunological induction of T cells. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):528–542. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb G. A. Effect of HPV-80 rubella vaccine on the tuberculin reaction. Am J Dis Child. 1969 Aug;118(2):261–261. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1969.02100040263020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl-Magnusson P., Leary P., Gresser I. Interferon inhibits DNA synthesis induced in mouse lymphocyte suspensions by phytohaemagglutinin or by allogeneic cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 24;237(73):120–121. doi: 10.1038/newbio237120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz H., Person D. A., Gitnick G. L., Ritts R. E., Jr Immunosuppressive activity of concanavalin A. Science. 1969 Jan 31;163(3866):476–476. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3866.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mobraaten L. E., De Maeyer E., De Maeyer-Guignard J. Prolongation of allograft survival in mice by inducers of interferon. Transplantation. 1973 Nov;16(5):415–420. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197311000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Ceglowski W. S., Friedman H. Leukemia virus-induced immunosuppression. IX. Depression of delayed hypersensitivity and MIF production after infection of mice with Friend leukemia virus. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1810–1819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Mergenhagen S. E., Howard R. J. Effect of virus infections on the function of the immune system. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:525–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.002521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F., Buckler C. E., Baron S. High interferon producing line of transformed murine cells. J Gen Virol. 1972 Oct;17(1):107–109. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-17-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenau W., Habler J., Goldberg M. Prolongation of skin graft survival by administration of purified phytohemagglutinin. Transplantation. 1972 Jun;13(6):624–626. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197206000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARR S., BERKOVICH S. EFFECTS OF MEASLES, GAMMA-GLOBULIN-MODIFIED MEASLES AND VACCINE MEASLES ON THE TUBERCULIN TEST. N Engl J Med. 1964 Feb 20;270:386–391. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196402202700802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipe J. D., de Maeyer-Guignard J., Fauconnier B., de Maeyer E. Purification of mouse interferon by affinity chromatography on a solid-phase immunoadsorbent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1037–1040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithwick E. M., Berkovich S. In vitro suppression of the lymphocyte response to tuberculin by live measles virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Oct;123(1):276–278. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani S. S., Moore C. D. Effect of phytohemagglutinin on skin allograft survival in mice. J Immunol. 1970 Apr;104(4):780–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer E., Mobraaten L., de Maeyer-Guignard J. Prolongation par l'interféron de la survie des greffes de peau chez la souris. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1973 Nov 12;277(19):2101–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maeyer E., de Maeyer-Guignard J. Gene with quantitative effect on circulating interferon induced by Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1969 May;3(5):506–512. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.5.506-512.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


