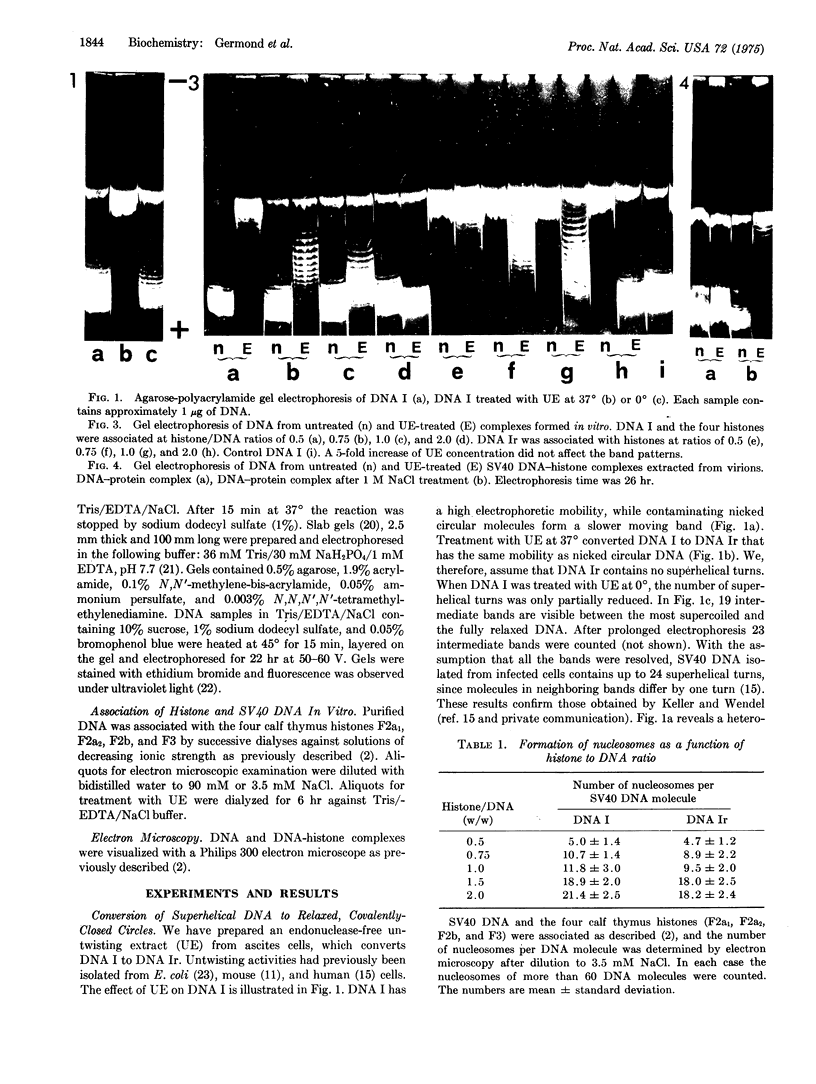
Abstract
Relaxed circular, covalently closed simian virus 40 DNA molecules were associated with the four histones that are present in virions. In electron micrographs the resulting complexes appear twisted, with globular structures (nucleosomes) along the DNA. Incubation with an untwisting extract converts the twisted complexes to relaxed structures. Extraction of the DNA from the relaxed complexes yields supercoiled molecules. The number of superhelical turns in these molecules corresponds to the number of nucleosomes per DNA molecule in the complexes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. P., Boseley P. G., Bradbury E. M., Ibel K. The subunit structure of the eukaryotic chromosome. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):245–249. doi: 10.1038/253245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgaux P., Bourgaux-Ramoisy D. Is a specific protein responsible for the supercoiling of polyoma DNA? Nature. 1972 Jan 14;235(5333):105–107. doi: 10.1038/235105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne L. A., Hewish D. R., Mobbs J. Mammalian chromatin substructure studies with the calcium-magnesium endonuclease and two-dimensional polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1974 Oct;143(1):67–72. doi: 10.1042/bj1430067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., Dulbecco R. An activity from mammalian cells that untwists superhelical DNA--a possible swivel for DNA replication (polyoma-ethidium bromide-mouse-embryo cells-dye binding assay). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. General model for the chromosomes of higher organisms. Nature. 1971 Nov 5;234(5323):25–27. doi: 10.1038/234025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. Effect of DNA length on the free energy of binding of an unwinding ligand to a supercoiled DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 14;66(2):307–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey G., Hirt B. Fingerprints of polyoma virus proteins and mouse histones. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):235–241. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Vogt V. M., Hirt B. Characterization of the single-strand-specific nuclease S1 activity on double-stranded supercoiled polyoma DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):591–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. Interphase chromosomal deoxyribonucleoprotein isolated as a discrete structure from cultured cells. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 5;86(3):649–663. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S. Gel electrophoretic separation of the complementary strands of bacteriophage DNA. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):342–344. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Estes M. K., Pagano J. S. Structure and function of the polypeptides in simian virus 40. I. Existence of subviral deoxynucleoprotein complexes. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):923–929. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.923-929.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W., Wendel I. Stepwise relaxation of supercoiled SV40 DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):199–208. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Thomas J. O. Chromatin structure; oligomers of the histones. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):865–868. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. F., Berg P. Cleavage of Simian virus 40 DNA at a unique site by a bacterial restriction enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1573–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Subunit structure of chromatin. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):249–251. doi: 10.1038/251249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Molecular weight estimation and separation of ribonucleic acid by electrophoresis in agarose-acrylamide composite gels. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):668–674. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmir M., Révet B. M., Vinograd J. Dependence of the sedimentation coefficient of denatured closed circular DNA in alkali on the degree of strand interwinding. The absolute sense of supercoils. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 15;83(1):35–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebring E. D., Garon C. F., Salzman N. P. Superhelix density of replicating simian virus 40 DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seebeck T., Weil R. Polyoma viral DNA replicated as a nucleoprotein complex in close association with the host cell chromatin. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):567–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.567-576.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior M. B., Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Chromatin fragments resembling v bodies. Science. 1975 Jan 17;187(4172):173–175. doi: 10.1126/science.1111096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Sugden B., Sambrook J. Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in Haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose--ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3055–3063. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Holde K. E., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Shaw B. R. A model for particulate structure in chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1579–1586. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J., Watson R. Early and late helix-coil transitions in closed circular DNA. The number of superhelical turns in polyoma DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):173–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and an Escherichia coli protein omega. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M., Eason R. Supercoiling of SV40 DNA can occur independently of replication. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 10;241(106):46–49. doi: 10.1038/newbio241046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bruggen E. F., Arnberg A. C., van Holde K. E., Sahasrabuddhe C. G., Shaw B. R. Electron microscopy of chromatin subunit particles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1365–1370. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]