Abstract
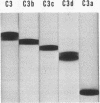
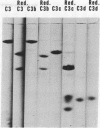
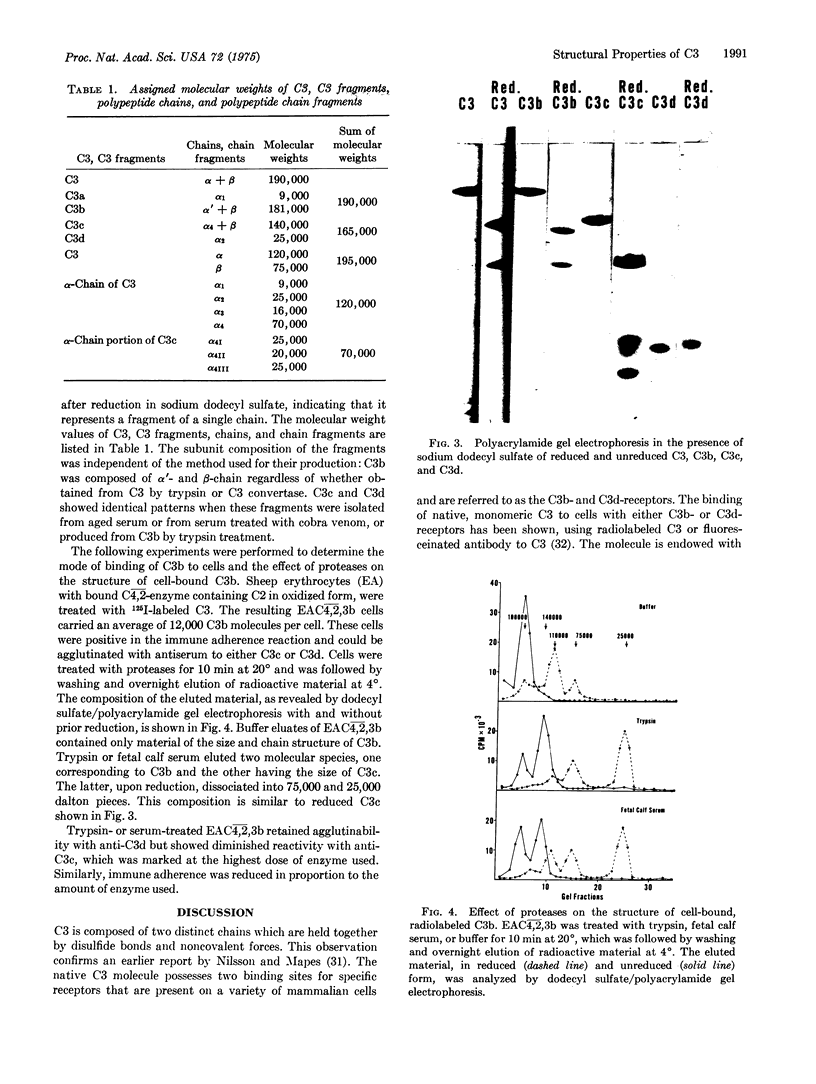
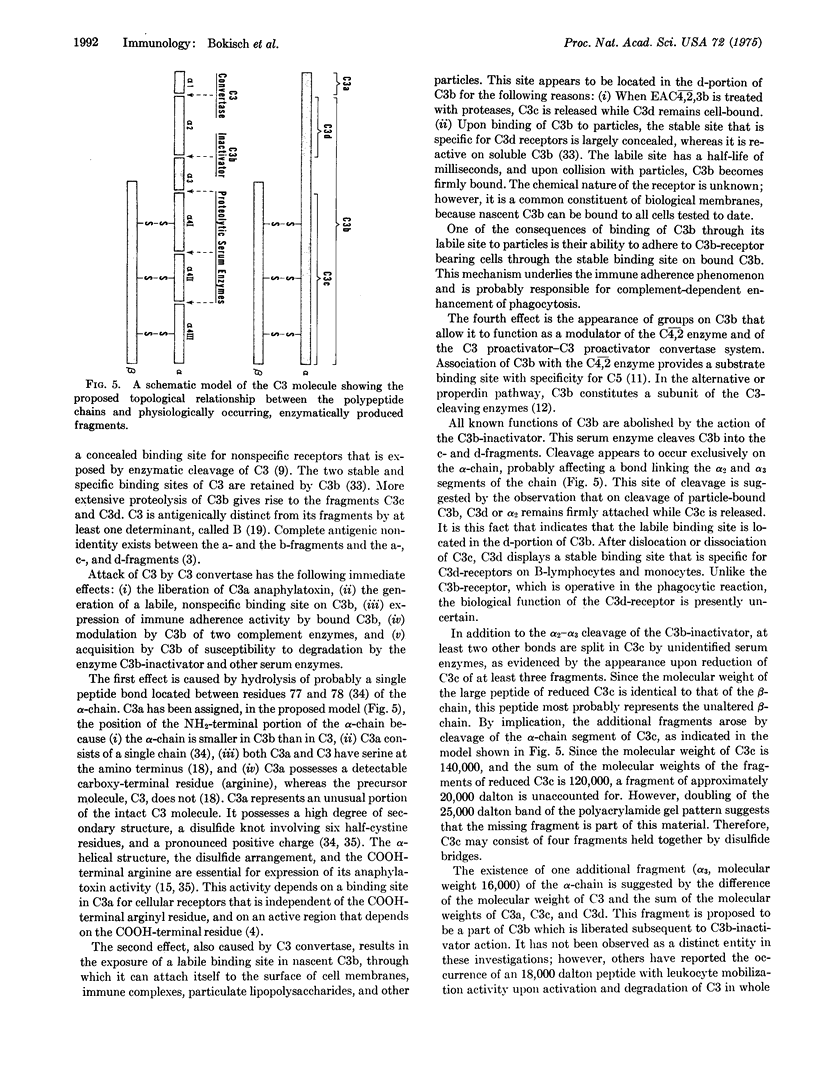
The third component of complement (C3) fulfills a pivotal role in the functions of the complement system. We have investigated the topological relationships among its polypeptide chains, physiologic fragments, enzyme attack regions, and functional sites. C3 consists of two chains (alpha and beta) which are linked by disulfide bonds and noncovalent forces and which have molecular weights of, respectively, 120,000 and 75,000. C3 is activated by action of C3 convertase on the alpha-chain. With hydrolysis of one polypeptide bonds, C3a, the 9000 dalton activation peptide is dislocated from the NH2-terminal portion of the alpha-chain. A previously concealed binding region is thereby transiently revealed in the C3b-fragment (181,000 dalton) which displays affinity for apparently nonspecific acceptors present on biological membranes. Binding of nascent C3b membranes occurs through the C3d portion of the fragment because subsequent action of the C3b-inactivator or trypsin on bound C3b causes release of C3c, but not of C3d. Bound C3b and C3d possess stable sites that are capable of binding to specific receptors present on a limited variety of cells. We propose that all known physiologically occurring fragments of C3 arise by enzymatic cleavage of the alpha-chain: C3a, C3b, C3c, and C3d. Whereas C3a (alpha1) and C3e (alpha2) consist of a single chain and C3b consists of two chains (alpha' and beta), C3c is composed of the entire beta-chain and multiple fragments of the alpha-chain, each of which is linked by disulfide bonds to the beta-chain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson N., Alper C. A., Lachmann P. J., Rosen F. S., Jandl J. H. Deficiency of C3 inactivator in man. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Colten H. R., Rosen F. S., Rabson A. R., Macnab G. M., Gear J. S. Homozygous deficiency of C3 in a patient with repeated infections. Lancet. 1972 Dec 2;2(7788):1179–1181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92598-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxin inactivator of human plasma: its isolation and characterization as a carboxypeptidase. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2427–2436. doi: 10.1172/JCI106462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Cochrane C. G. Isolation of a fragment (C3a) of the third component of human complement containing anaphylatoxin and chemotactic activity and description of an anaphylatoxin inactivator of human serum. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):1109–1130. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzko D. B., Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. A fragment of the third component of human complement with anaphylatoxin activity. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1166–1172. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The derivation of two distinct anaphylatoxin activities from the third and fifth components of human complement. J Exp Med. 1968 Feb 1;127(2):371–386. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukor P., Hartmann K. U. Hypothesis. Bound C3 as the second signal for B-cell activation. Cell Immunol. 1973 Jun;7(3):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukor P., Schumann G., Gisler R. H., Dierich M., König W., Hadding U., Bitter-Suermann D. Complement-dependent B-cell activation by cobra venom factor and other mitogens? J Exp Med. 1974 Feb 1;139(2):337–354. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Mosesson M. W. Degradation of human fibrinogen by plasms alpha2-macroglobulin-enzyme complexes. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2175–2184. doi: 10.1172/JCI107402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Morgan W. T., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Circular dichroism of C3a anaphylatoxin. Effects of pH, heat, guanidinium chloride, and mercaptoethanol on conformation and function. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1479–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Vallota E. H., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Purification and partial characterization of human and porcine C3a anaphylatoxin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1472–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The demonstration in human serum of "conglutinogen-activating factor" and its effect on the third component of complement. J Immunol. 1968 Apr;100(4):691–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Fjellström K. E. Isolation of the anticomplementary protein from cobra venom and its mode of action on C3. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1666–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Götze O. C3 proactivator convertase and its mode of action. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.1003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllerèberhard H. J., Dalmasso A. P., Calcott M. A. The reaction mechanism of beta-1C-globulin (C'3) in immune hemolysis. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):33–54. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polley M. J., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Enharncement of the hemolytic activity of the second component of human complement by oxidation. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1013–1025. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rother K. Leucocyte mobilizing factor: a new biological activity derived from the third component of complement. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Dec;2(6):550–558. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. C3b inactivator of man. II. Fragments produced by C3b inactivator cleavage of cell-bound or fluid phase C3b. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):742–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura N., Nelson R. A., Jr Three naturally-occurring inhibitors of components of complement in guinea pig and rabbit serum. J Immunol. 1967 Sep;99(3):582–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Bokisch V. A., Dixon F. J. Receptor for soluble C3 and C3b on human lymphoblastoid (RAJI) cells. Properties and biologocal significance. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):696–711. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C., Davis N. C., Forristal J., Herbst J., Spitzer R. Antigenic determinants of human beta-1c and beta-1g-globulins. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):650–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Stoughton R. B. Cutaneous responses to human C 3 anaphylatoxin in man. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 May;11(1):13–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva W. D., Eisele J. W., Lepow I. H. Complement as a mediator of inflammation. 3. Purification of the activity with anaphylatoxin properties generated by interaction of the first four components of complement and its identification as a cleavage product of C'3. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1027–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]