Abstract
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by pathological deposits of β-amyloid (Aβ) in senile plaques, intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) comprising hyperphosphorylated aggregated tau, synaptic dysfunction and neuronal death. Substantial evidence indicates that disrupted neuronal calcium homeostasis is an early event in AD that could mediate synaptic dysfunction and neuronal toxicity. Sodium calcium exchangers (NCXs) play important roles in regulating intracellular calcium, and accumulating data suggests that reduced NCX function, following aberrant proteolytic cleavage of these exchangers, may contribute to neurodegeneration. Here, we show that elevated calpain, but not caspase-3, activity is a prominent feature of AD brain. In addition, we observe increased calpain-mediated cleavage of NCX3, but not a related family member NCX1, in AD brain relative to unaffected tissue and that from other neurodegenerative conditions. Moreover, the extent of NCX3 proteolysis correlated significantly with amounts of Aβ1–42. We also show that exposure of primary cortical neurons to oligomeric Aβ1–42 results in calpain-dependent cleavage of NCX3, and we demonstrate that loss of NCX3 function is associated with Aβ toxicity. Our findings suggest that Aβ mediates calpain cleavage of NCX3 in AD brain and therefore that reduced NCX3 activity could contribute to the sustained increases in intraneuronal calcium concentrations that are associated with synaptic and neuronal dysfunction in AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, beta-amyloid, calcium, calpain, sodium calcium exchanger, tau
Introduction
Degenerating brain regions in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) show deposits of β-amyloid (Aβ) in senile plaques and accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau aggregates in intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (Schellenberg & Montine, 2012). Substantial evidence indicates that disrupted neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis in these brain areas is likely an early event in AD pathogenesis that mediates synaptic dysfunction and neuronal toxicity (Small, 2009; Li et al., 2011). However, the mechanisms leading to prolonged elevations in intraneuronal Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) in AD have yet to be fully elucidated. Mutations in presenilin 1 (PS1) perturb [Ca2+]i, primarily by inducing release of excess Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum. Such Ca2+ release occurs through a number of different mechanisms, including alteration in ryanodine and inositol triphosphate receptor expression and gating, and modified sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase function (Verkhratsky & Toescu, 2003). These events may account for alterations in cellular Ca2+ homeostasis in familial AD. In cellular models of sporadic AD, application of Aβ has been shown to cause the formation of Ca2+-permeable pores in bilayer membranes (Arispe et al., 1993) or thinning of membranes resulting in increased ion permeability (Kayed et al., 2004). Many reports also demonstrate that Aβ stimulates neuronal Ca2+ influx through native ion channels and/or receptors (Small, 2009), and increased Ca2+ influx via these mechanisms leads to rapid increases in neuronal Ca2+ content. Recent evidence has suggested that inactivation of plasma membrane ion exchangers may also contribute to sustained neuronal Ca2+ overload in neurodegenerative conditions by preventing the extrusion of excess cytosolic Ca2+ (Bano et al., 2005, 2007).
In conditions of high [Ca2+]i, the sodium calcium exchanger (NCX) family members, NCX1, NCX2 and NCX3, activate high-capacity currents to extrude excess Ca2+ from the cytosol in exchange for Na+ ions (Lytton, 2007). NCX3 is subject to cleavage by the Ca2+-activated cysteine protease calpain-1 (Bano et al., 2005, 2007) and by caspase-3 (Bano et al., 2007).
Calpain-1-mediated cleavage of NCX3 diminishes NCX3 exchanger activity by preventing the binding of Ca2+ to the NCX Ca2+ regulatory domain, a process essential for NCX function (Bano et al., 2005, 2007). In a cell-based model of ischaemia, Bano et al. (2005) found that cleavage of NCX3 by calpain-1 caused the inactivation of NCX3 ionic exchange activity, retention of intracellular Ca2+, prolonged calpain activation and resultant neurotoxicity. These effects were reversed by over-expression of the calpain inhibitor, calpastatin. Similar outcomes have also been reported following the treatment of hippocampal neurons with excitotoxic concentrations of glutamate (Brustovetsky et al., 2010).
Increased calpain activity is a prominent feature of postmortem AD brain (Nixon, 2003), leading to speculation that NCX function may be altered during the development of AD. Application of Aβ1–42 to primary neuronal cultures results in the elevation of calpain-1 activity (Town et al., 2002; Noble et al., 2009), and transgenic mice over-expressing mutant human APP also exhibit increased calpain-1 activity (Vaisid et al., 2007). Thus, it is possible that Aβ-induced increases in calpain activity may modulate NCX3 function in AD. In support of this, Sokolow et al. (2011) demonstrated co-localization of NCX3 and Aβ in synaptosome preparations from AD brain and a loss of NCX3 holoprotein in homogenates of parietal cortex in AD.
In this study, we have investigated the possibility that NCX3 function is disrupted in AD as a result of NCX cleavage by calpain. Examination of postmortem human brain showed that elevated calpain-1 activity and reduced activity of the endogenous calpain inhibitor, calpastatin, are closely associated with increased fragmentation of NCX3 in AD brain. This appears to be relatively specific for AD as significantly altered NCX3 cleavage was not observed in brain from other neurodegenerative tauopathies. The other tauopathies examined were frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism associated with tau mutations on chromosome 17 (FTD), corticobasal degeneration (CBD) and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). It is worth noting that CBD and PSP also show significant tau pathology in the frontal cortex in end-stage disease, especially when assessed using biochemical methods (Zhukareva et al., 2006).
No changes were observed in either the total protein amounts or cleavage of NCX1, another NCX family member, in any neurodegenerative tauopathy brain. This suggests that related proteins do not compensate for NCX3 inactivation in AD. In addition, our data suggest that the over-production of Aβ in AD is likely to cause calpain-mediated NCX3 cleavage, because we found a significant positive correlation between Aβ amounts and calpain-mediated NCX3 cleavage in AD brain. In primary neural cell cultures, treatment with 10 μm Aβ1–42 induced calpain cleavage of NCX3, and this was prevented by treatment with the calpain inhibitor, calpeptin. In addition, suppression of NCX3 expression with antisense oligonucleotides sensitized neurons to normally subtoxic concentrations of Aβ1–42.
Results
NCX3 is cleaved by both calpain-1 and caspase-3 in cell models of neurological disease (Bano et al., 2005). Thus, we first determined the relative activities of these proteases in neurodegenerative disease brain on Western blots. To determine whether any changes detected were specific to AD, we also examined three other tauopathies, PSP, CBD and FTD caused by the intronic tau mutation 10 + 16.
Calpain-1 activity is increased in tauopathy brain
Calpain-1 is an approximately 80-kDa Ca2+-activated cysteine protease that is activated by its autolysis into 76- and 58-kDa fragments (Goll et al., 2003). Blots of postmortem human brain were probed with an antibody that specifically detects the active 76-kDa subunit of calpain-1 (Fig. S1, Supporting information), revealing a single prominent band of the expected size (Fig. 1A). Blots were also probed with an antibody to neuron-specific enolase (NSE) for normalization purposes and to control for any loss of neuronal proteins and/or gliosis. This analysis revealed that active calpain-1 is significantly increased in AD cortex (P < 0.001) when compared to controls (Fig. 1B). In addition, significantly increased amounts of active calpain-1 were also detected in cortex from PSP, CBD and FTD brain (P < 0.05 for all). Blots were also probed with an antibody against calpain-2 that detects calpain-2 holoprotein at 76–80 kDa and active calpain-2 at 58 kDa (Huang et al., 2010). When standardized against NSE, somewhat elevated amounts of active calpain-2 were detected in AD and FTD brain; however, these differences were not statistically significant (Fig. 1A,C). Nevertheless, these findings confirm previous data showing that calpain-1 activity is increased in AD brain (Saito et al., 1993) and indicate that increased calpain-1 cleavage to its active form is observed not only in conditions characterized by elevated Aβ deposition, but also in a number of other neurodegenerative tauopathies.
Figure 1.
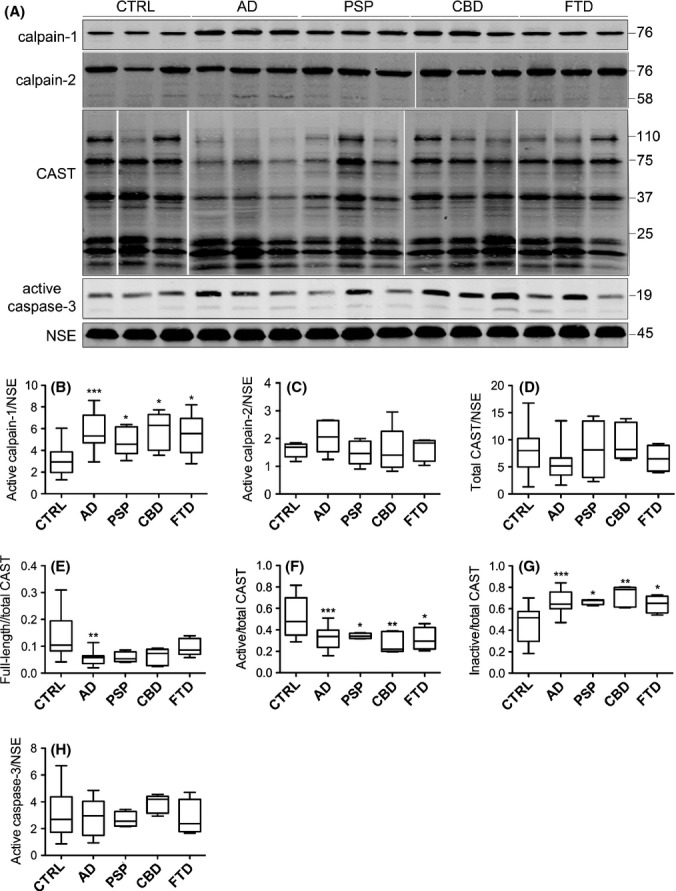
Calpain-1 active subunit amounts are elevated in neurodegenerative disease brain. (A) Representative immunoblots of cortical lysates from postmortem brain. Blots were probed with antibodies that detect active fragments of calpain-1 at 76 kDa, calpain-2 holoprotein and cleaved fragments at 76 and 58 kDa, respectively, and active caspase-3 at 17 and 19 kDa. An antibody against calpastatin (CAST) was used that detects active CAST holoprotein at 110 kDa, active fragments of > 25 kDa and inactive fragments of < 25 kDa. Blots were also probed with an antibody- to neuron-specific enolase (NSE), 45 kDa. Box plots show amounts of (B) active calpain-1, (C) active calpain-2 and (D) total CAST, all as a proportion of NSE. (E) Full length (FL) CAST, (F) active CAST and (G) inactive CAST, all as a proportion of total CAST, and (H) active caspase-3 following standardization to NSE content in each sample. CTRL: control (n = 20), AD: Alzheimer’s disease (n = 20), PSP: progressive supranuclear palsy (n = 5), CBD: corticobasal degeneration (n = 5), FTD: frontotemporal dementia with tau mutations (n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001.
Active calpastatin is decreased in neurodegenerative disease brain
An important cellular regulator of calpain activity in the brain is the endogenous calpain-1 and calpain-2 inhibitor, calpastatin (CAST) (Rao et al., 2008). It has been suggested that reduced CAST amounts and/or activities might contribute to the increased activation of calpain observed in AD brain (Rao et al., 2008). To examine CAST activity in tauopathy brain, cortical lysates were immunoblotted with a polyclonal antibody directed against human CAST. This antibody detects CAST holoprotein at 110–120 kDa, as well as a number of calpain-cleaved CAST fragments of 37–75 kDa, which, together with the full-length protein, have calpain inhibitory activity. Several inactive CAST fragments (< 25 kDa), generated by the action of caspase-1 and caspase-3 on CAST (Rao et al., 2008), were also detected by this antibody (Fig. 1A).
Following normalization to NSE, we found no differences in the total amount (intact plus fragments) of CAST between any groups (Fig. 1D). In contrast, there was a significant decrease in the amount of full-length CAST as a proportion of total CAST in AD brain relative to controls (P < 0.05, Fig. 1E), with samples from other tauopathies showing a trend towards decreased CAST holoprotein. The amounts of active CAST (holoprotein plus 37–75 kDa fragments) and inactive CAST (fragments < 25 kDa) were then quantified as a proportion of total CAST. We found significant decreases in the amounts of active CAST fragments and corresponding increases in inactive CAST protein, in AD, PSP, CBD and FTD in comparison with control brain (Fig. 1F,G). These findings support previous results showing reduced CAST activity in AD brain (Nilsson et al., 1990; Nixon, 2003; Rao et al., 2008) and extend this data with the novel finding that CAST activity is decreased in brain from ‘pure’ tauopathies.
Active caspase-3 is not increased in postmortem neurodegenerative disease brain
As caspase-3 can also cleave and inactivate NCX3 (Bano et al., 2007), we next assessed the activity of this protease in the control and diseased brain samples. Caspase-3 exists as a holoprotein (pro-caspase-3, approximately 32 kDa) with limited enzymatic activity. Caspase-3 is cleaved by caspase-8 and caspase-9 to generate active fragments of approximately 17 and 19 kDa. Western blotting with an antibody that detects active caspase-3 revealed a prominent band of 19 kDa and a relatively weak band at 17 kDa, corresponding to active caspase-3 fragments (Fig. 1A). Relative to NSE, we found no significant increases in the amounts of cleaved caspase-3 fragments in any of the neurodegenerative conditions investigated when compared to control brain (Fig. 1H). This finding suggests that caspase-3 activity is not globally increased in neurodegenerative disease cortex, at least not to an extent detectable by immunoblotting. This is consistent with previous reports showing that only ‘exceptional’ neurons label with antibodies against active caspase-3 in AD brain (Jellinger & Stadelmann, 2000).
Altered proteolysis of the calpain and caspase-3 substrate, α-spectrin, in neurodegenerative disease brain
To further assess calpain-1 and caspase-3 activities in neurodegenerative disease brain, calpain-1- and caspase-3-mediated cleavage of the cytoskeletal protein α-spectrin was examined. Calpains cleave 240 kDa α-spectrin holoprotein to generate 145- and 150-kDa products, whereas cleavage by caspase-3 results in the production of 120- and 150-kDa fragments (Martin et al., 1995). When standardized to NSE, there were no significant differences in total α-spectrin amounts (holoprotein and all fragments) between groups (Fig. 2A,B). In contrast, when the amount of full-length α-spectrin was quantified as a proportion of total α-spectrin, analysis revealed a loss of the holoprotein in AD (P < 0.05) and CBD (P < 0.005) brain (Fig. 2A,C). We also observed a significant increase in the amount of 140–50 kDa calpain- and caspase-cleaved fragments as a proportion of total α-spectrin in AD (P < 0.01) brain when compared to controls (Fig. 2A,D). In contrast, when the 110- to 125-kDa caspase-cleaved α-spectrin products were analysed as a proportion of total α-spectrin, a significant increase in the amount of these fragments was found only in CBD brain (P < 0.01) (Fig. 2A,E). As there were no significant increases in the amount of the caspase-3-cleaved 110- to 125-kDa fragments in AD brain, this suggests that the accumulation of the 140- to 150-kDa fragments detected in these brains occurs as a result of calpain, rather than caspase, activity. Therefore, these findings appear to support the notion of increased calpain-mediated proteolysis in AD.
Figure 2.
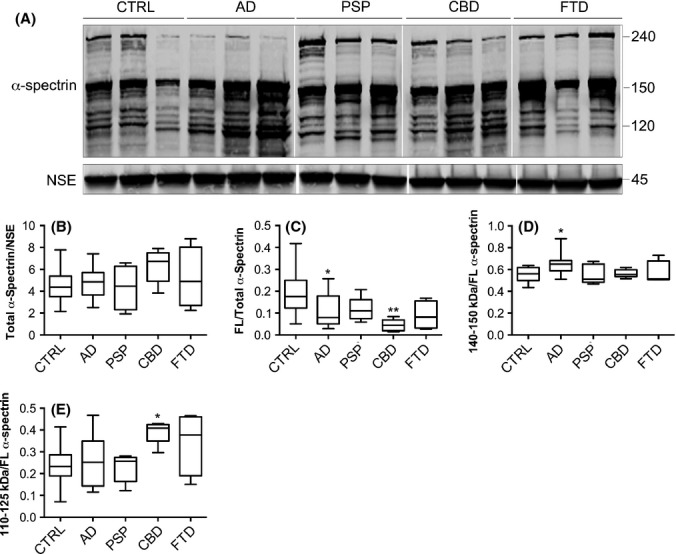
Calpain- and caspase-mediated proteolysis of α-spectrin in neurodegenerative disease brain. (A) Representative immunoblot of cortical lysates from postmortem brain. Blots were probed with an antibody that detects α-spectrin holoprotein at approximately 240 kDa, calpain- and caspase-cleaved fragments at approximately 140–150 kDa and caspase-cleaved fragments at approximately 110–125 kDa. Blots were also probed with an antibody to neuron-specific enolase (NSE), 45 kDa. Box plots show quantification of (B) total α-spectrin following standardization to NSE amounts. (C) α-spectrin holoprotein, (D) 140- to 150-kDa α-spectrin fragments and (E) 110- to 125-kDa α-spectrin fragments, all quantified as a proportion of total α-spectrin. Mean ± standard error is shown. CTRL: control (n = 20), AD: Alzheimer’s disease (n = 20), PSP: progressive supranuclear palsy (n = 5), CBD: corticobasal degeneration (n = 5), FTD: frontotemporal dementia with tau mutations (n = 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005.
NCX3 cleavage by calpain is elevated in AD brain
We next determined the amount of full-length and cleaved NCX3 in postmortem human brain. Western blotting with an antibody previously shown to detect full-length and cleaved NCX3 in cultured neurons (Bano et al., 2005) revealed a band of approximately 110 kDa, which corresponds to the predicted molecular weight of full-length NCX3 (Fig. 3A). In addition, a single band of approximately 66 kDa was observed, which corresponds to caspase-cleaved NCX3, and a cluster of bands of approximately 60 kDa are calpain-cleaved NCX3 (Bano et al., 2005, 2007). Blots were normalized by probing with an antibody against NSE.
Figure 3.
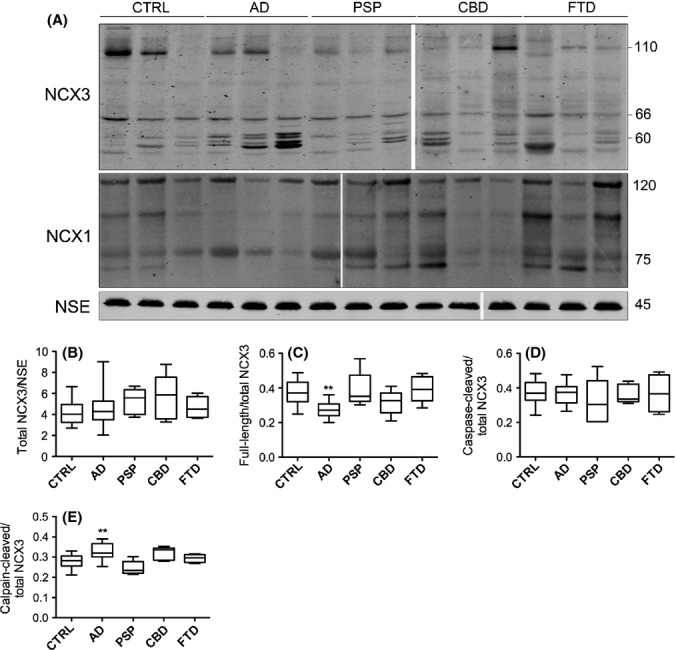
Calpain-mediated cleavage of NCX3, but not NCX1, is increased in AD brain. (A) Representative immunoblots of cortical lysates from postmortem brain. Blots were probed with an antibody that detects NCX3 holoprotein at approximately 110 kDa, a caspase-3-cleaved fragment at approximately 66 kDa, calpain-cleaved fragments at approximately 60 kDa and an antibody against NCX1, which detects full-length NCX1 at 120 kDa and proteolytic fragments at approximately 70–80 kDa. Blots were also probed with an antibody to neuron-specific enolase (NSE), 45 kDa. Plots show quantification of (B) total NCX3 amounts when standardized to NSE, and (C) full-length NCX3, (D) caspase-3-cleaved NCX3 and (E) calpain-cleaved NCX3, all as a proportion of total NCX3. CTRL: control (n = 20), AD: Alzheimer’s disease (n = 20), PSP: progressive supranuclear palsy (n = 5), CBD: corticobasal degeneration (n = 5), FTD: frontotemporal dementia with tau mutations (n = 4). **P < 0.005.
Quantification of the total amount of NCX3 (intact plus fragmented) showed that there were no significant differences between any tauopathy and control brain following normalization to NSE (Fig. 3B). There was, however, a significant decrease in the amount of NCX3 holoprotein in AD brain relative to control (Fig. 3C, P < 0.005) in agreement with previous studies (Sokolow et al., 2011). This reduction in intact NCX3 appeared to be specific to AD brain because full-length NCX3 was not significantly altered in PSP, CBD or FTD brain. In addition, no significant differences in the amount of caspase-3-cleaved NCX3 fragments were detected in any tauopathy tissue (Fig. 3D), supporting our earlier findings that there is no global increase in caspase-3 activity in these brains. However, we found a significant increase in the amount of calpain-cleaved NCX3 in AD, but not in any other disease group, when compared to control brain (Fig. 3E). This is consistent with our finding of decreased intact NCX3 in these samples and our demonstration of elevated calpain-1 activity in AD brain. It is possible that NCX3 cleavage is increased in AD as a result of altered neuronal distribution of active calpain and/or NCX3, as suggested by previous studies (Sokolow et al., 2011). These results indicate that calpain-mediated cleavage of the NCX3 exchanger is a prominent feature of AD brain. Because NCX3 cleavage disrupts the ion exchanger activity of this channel (Bano et al., 2005, 2007), this finding suggests that altered NCX3 function may contribute to the abnormal neuronal regulation of Ca2+ in AD.
We also assessed the amount of NCX1 in these brain samples to determine whether there are alterations in the amounts or activity of this related ion exchanger in neurodegenerative disease brain, which may indicate compensation for loss of NCX3 function. When Western blots were probed with an antibody that detects NCX1, an immunoreactive band was observed at approximately 120 kDa, corresponding to the predicted molecular weight of full-length NCX1 (Shaikh et al., 2010) as well as cleaved species at 70–80 kDa (Fig. 3A). Quantification of total NCX1 protein as a proportion of NSE revealed no significant alterations in NCX1 in any of the neurodegenerative disease brains when compared to controls. Moreover, no changes in the amount of full-length NCX1, or calpain-cleaved NCX1 species, were detected in any experimental group in relation to control brain (data not shown). These results indicate that loss of NCX3 function does not result in an upregulation of the related family member, NCX1.
Aβ1-42 burden correlates with NCX3 cleavage in AD brain
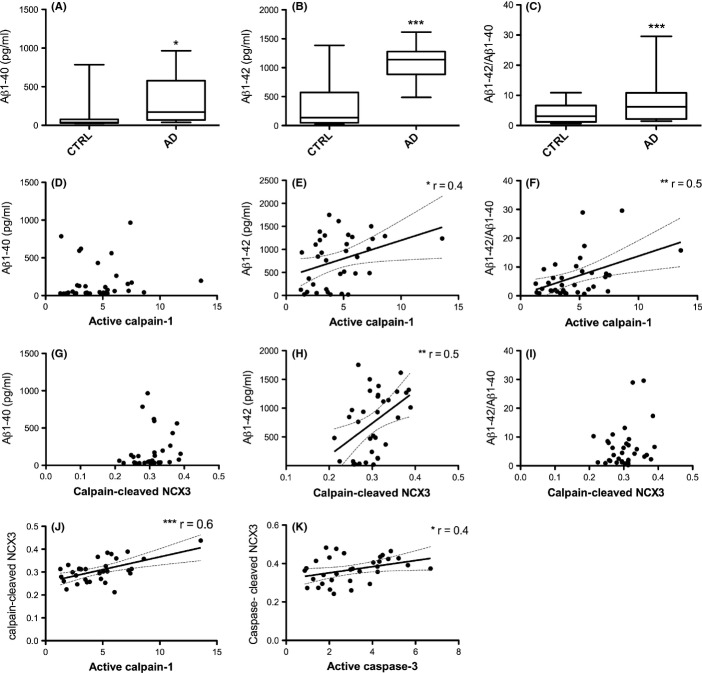
Because Aβ is known to activate calpain-1 in neurons, we sought to determine whether increased calpain-mediated NCX3 cleavage is associated with elevated Aβ amounts in postmortem AD brain. Aβ ELISAs were used to determine total amounts of Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42, and the ratio of Aβ1–42/Aβ1–40 in control and AD brain (Fig. 4A–C). These data were then correlated with the amounts of active calpain-1 proteins and calpain-cleaved NCX3 fragments (Fig. 4D–I). These analyses revealed that Aβ1–42 amounts significantly correlate with calpain activity (Fig. 3E, P < 0.05) and the presence of calpain-cleaved NCX3 protein fragments (Fig. 3H, P < 0.005) in control and AD brain. We also found a strong correlation between calpain-1 activity and the amounts of calpain-cleaved NCX3 fragments, as would be expected (Fig. 4J). These data support the hypothesis that calpain-mediated NCX3 cleavage is driven by altered Aβ production in AD brain. Unfortunately, due to the small number of samples available, it was not possible to correlate calpain-1 activity and NCX3 cleavage in brain from other tauopathies.
Figure 4.
NCX3 cleavage correlates with calpain-1 activity and Aβ burden. Aβ ELISAs were used to measure Aβ amounts in frontal cortex samples from AD and control (CTRL) brain. Box plots show (A) Aβ1–40, and (B) Aβ1–42amounts in pg mL−1, (C) shows the ratio of Aβ1–42 to Aβ1–40. Scatter plots show the correlation between amounts of active calpain-1 and (D) Aβ1–40, (E) Aβ1–42 and (F) Aβ1–42/Aβ1–40, and between calpain-cleaved NCX3 fragments and (G) Aβ1–40, (H) Aβ1–42, (I) Aβ1–42/Aβ1–40, and (J) active calpain-1, and (K) caspase-cleaved NCX-3 fragments with active caspase-3. Parametric Pearson correlation analysis was used to generate r values since all data were normally distributed, and statistical statistical significance is shown for each analysis. CTRL: control (n = 16), AD: Alzheimer’s disease (n = 16).
Aβ induces calpain-dependent NCX3 cleavage
To determine whether calpain-mediated cleavage of NCX3 is causally related to elevated Aβ amounts in AD, we measured NCX3 cleavage following application of 10 μm soluble oligomeric Aβ1–42 to primary cortical neuronal cultures for 48 h. We have previously shown that this treatment results in neurotoxicity (Noble et al., 2009; Garwood et al., 2011). Western blots of cell lysates revealed increased amounts of active calpain-1 (76 kDa) and caspase-3 (19 kDa) in neurons exposed to Aβ relative to vehicle-treated cells (Fig. 5A–C). Total NCX3 protein amounts were unchanged by Aβ treatment (Fig. 5A), although there was a small, but nonsignificant reduction in the amount of full-length NCX3 present in Aβ-treated cells following standardization to β-actin amounts (data not shown). In contrast, Aβ treatment increased the generation of calpain-cleaved (66 kDa) fragments of NCX3 (Fig. 5D, P < 0.05), and this was prevented when neurons were pretreated for 3 h with the calpain inhibitor, calpeptin (5 μm, Fig. 5A,D), which also lowered Aβ-induced increases in calpain activity (Fig. 5B). The generation of caspase-cleaved NCX3 fragments were not affected by Aβ treatment (Fig. 5A,E). These findings show that Aβ1–42 induces calpain-dependent cleavage of NCX3 in primary cortical neurons, and therefore, elevated Aβ content may account for the increased NCX3 cleavage we observed in AD brain relative to controls.
Figure 5.
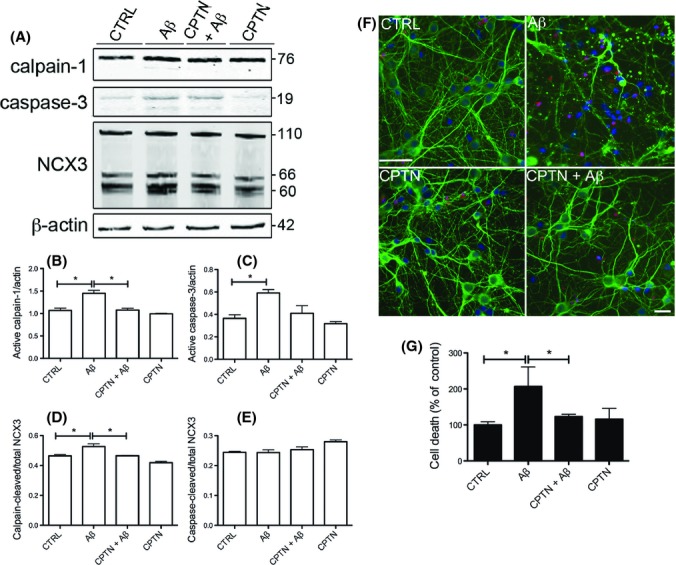
Aβ-induced calpain-mediated NCX3 cleavage is associated with neurotoxicity in primary cortical cultures. Rat primary cortical cultures were exposed to 10 μm Aβ1–42 (Aβ) for 48 h with and without pretreatment with 5 μm calpeptin (CPTN) for 1 h. (A) Representative Western blots probed with antibodies against active calpain-1 (76 kDa) and that pick up full-length (110 kDa), caspase-cleaved (66 kDa) and calpain-cleaved (60 kDa) NCX3 are shown. Blots were also probed with β-actin (42 kDa) as a loading control. Molecular weight markers are indicated (kDa). Bar charts show amounts of (B) active calpain-1 and (C) active caspase-3 as a proportion of β-actin in each sample. The amounts of (D) calpain-cleaved and (E) caspase-cleaved NCX3, both as a proportion of total NCX3, are also shown. (F) Representative images from cortical cultures incubated with live/dead cell dye (red), fixed and immunostained with an antibody against βIII-tubulin (green). Hoechst 33352 was used to stain nuclei (blue). Scale bar: 25 μm. (G) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release from control and treated primary cortical cultures. Values represent LDH release from cells into the medium as a percentage of total LDH, presented as % control. Data are mean ± SEM. Experiments were performed in triplicate (n = 3). *P < 0.05.
To determine whether calpain-mediated NCX3 cleavage is associated with Aβ-induced neurotoxicity, primary cortical cultures were pretreated with 5 μm calpeptin prior to application of 10 μm soluble oligomeric Aβ, and cell death was assessed by live/dead assay (Fig. 5F) and LDH release (Fig. 5G). Aβ treatment for 48 h resulted in a statistically significant increase in neuronal cell death, as observed by the degeneration of βIII-tubulin-labelled primary neurons (green), increased incorporation of dead cell dye (red) and the appearance of fragmented, condensed nuclei (blue). The extent of cell death was reduced upon pretreatment of cultures with calpeptin (Fig. 5F). These results were confirmed by the measurement of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release (Fig. 5G). These findings show that elevated calpain activity is closely associated with Aβ-induced neurotoxicity and suggest that Aβ-induced calpain-mediated NCX3 cleavage may contribute to neuronal loss in AD, perhaps by preventing the extrusion of excess intraneuronal Ca2+.
NCX3 expression mediates Aβ-induced neurotoxicity
To further investigate the role of NCX3 in Aβ-mediated neurotoxicity, rat primary cortical cultures were treated with phosphorothioated sense or antisense oligonucleotides specific for rat NCX3, as previously described (Iwamoto & Kita, 2006). Western blotting confirms that treatment of cultured neurons with antisense NCX3 oligonucleotides for 24 h resulted in an approximately 38.5 ± 12.6% reduction in NCX3 protein amounts (Fig. 6A), in line with previous observations in primary neurons (Ranciat-McComb et al., 2000). The amounts of NCX3 fragments were less affected by exposure to antisense oligonucleotides, suggesting that the turnover rate of cleaved NCX3 may be slower than that of the full-length protein. Sense oligonucleotides to NCX3 had no effect on NCX3 levels (Fig. 6A). Cultures were also treated with 1 μm Aβ for a further 16 h. This treatment alone had no significant effect on cell death in comparison with vehicle-treated cells (Fig. 6B). In contrast, application of 1 μm Aβ for 16 h caused a significant increase in cell death in cells treated with antisense NCX3 oligonucleotides in comparison with cells treated with vehicle or sense NCX3 oligonucleotides (P < 0.05, Fig. 6B). The relatively modest extent of the enhanced sensitivity to Aβ toxicity may be indicative of compensation for NCX3 loss of function in these cells, as has been previously demonstrated in rat cerebellar granule cells (Bano et al., 2007). Nevertheless, these results indicate that reduced expression of functional NCX3 exchangers can sensitize cultured neurons to Aβ.
Figure 6.
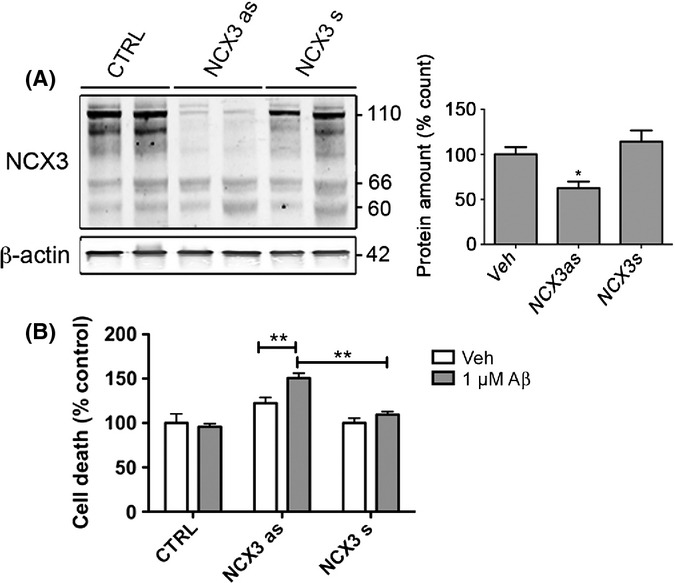
Antisense knockdown of NCX3 sensitizes cortical neurons to Aβ. Rat primary cortical cultures were treated with sense (s) or antisense (as) oligonucleotides against rat NCX3 for 24 h and then treated with a subtoxic concentration (1 μm) of Aβ1–42 (Aβ) for a further 16 h. (A) Representative Western blots probed with antibodies that detect full-length (110 kDa) and cleaved (66, 60 kDa) NCX3. Blots were also probed with β-actin (42 kDa) as a loading control. Molecular weight markers are indicated. Bar charts show (A) total NCX3 expression following standardization to the β-actin loading control and (B) cell death as measured by live/dead cell assay in cells treated with 1 μm Aβ as a proportion of death in control cultures and antisense oligonucleotides 1 μm Aβ standardized to cells treated with sense NCX3 oligonucleotides only. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005.
Discussion
Altered cellular Ca2+ homeostasis is an early and prominent feature of AD that likely accelerates disease progression (Small, 2009). In cell models of AD, Aβ-induced neuronal Ca2+ influx through native ion channels and/or plasma membrane pores leads to synaptic deficits, altered long term potentiation, learning and memory impairments, and neurotoxicity (Smith et al., 2005). Similarly, altered cellular Ca2+ regulation is apparent in the vicinity of amyloid plaques in transgenic mice expressing mutant human APP (Kuchibhotla et al., 2008).
Many downstream effects of increased [Ca2+]i have been reported that may modify the progression of AD, including Ca2+-dependent activation of the calpain family of proteases. Calpains mediate an array of disease-associated events including aberrant amyloid precursor protein processing (Mathews et al., 2002), generation of potentially toxic tau fragments (Nicholson et al., 2011), activation of key tau protein kinases including cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (Town et al., 2002; Goni-Oliver et al., 2007), processing of dynamin 1, a protein critically involved in memory formation (Kelly et al., 2005), Aβ-induced synaptic dysfunction (Trinchese et al., 2008) and LTP impairment (Li et al., 2011). These data thus suggest a key role for calpains as mediators of the synaptotoxic and neurotoxic events that occur downstream of Aβ-induced increases in AD.
In addition, calpain activation has also been demonstrated to influence the cellular mechanisms that regulate Ca2+ efflux. Several studies have shown that calpain cleaves and inactivates NCX3 ion exchangers, preventing the extrusion of excess neuronal Ca2+ (Bano et al., 2005, 2007; Brustovetsky et al., 2010). Here, we have demonstrated that Aβ induces calpain-mediated NCX3 cleavage in primary cortical cultures, suggesting that NCX3 cleavage may perhaps contribute to sustained and neurotoxic increases in cellular Ca2+ in AD. In support of this idea, we show that inhibition of calpain activity ameliorates Aβ-induced neuronal loss and that suppressing NCX3 expression with antisense oligonucleotides sensitizes neurons to normally subtoxic doses of Aβ.
We also observe elevated calpain activity and NCX3 cleavage in postmortem AD brain. Whilst the total amount of NCX3 protein is unchanged, NCX3 truncation was associated with loss of NCX3 holoprotein, supporting previous findings of decreased full-length NCX3, but not NCX1 or NCX2, in parietal cortex or synaptosome preparations from a relatively small number of AD cases (Sokolow et al., 2011). Moreover, the increased proteolysis of NCX3 that we observed showed significant positive correlation with amounts of Aβ1–42 in frontal cortex. Because significantly increased NCX3 cleavage was detected only in AD, but not other tauopathy brain, this raises the possibility that analysis of NCX3 fragments may have utility as a biomarker for AD. It is of interest that increased abundance of NCX3 fragments was only observed in AD brain despite other tauopathies also showing elevated calpain activity. It has previously been shown that tau can bind to EF hand domain-containing proteins (Vega et al., 2008). It is therefore possible that NCX3 fragments may bind PHF tau, a conformation of tau that is found in AD and not other tauopathy brain, and thereby become sequestered into insoluble tau aggregates that are not easily degraded, thereby leading to an accumulation of these fragments in postmortem AD brain. A similar mechanism may explain the increase in calpain-cleaved α-spectrin fragments that were found to accumulate in AD tissue. Indeed, cleaved α-spectrin fragments have previously been identified in affected neurons in AD brain (Ayala-Grosso et al., 2006).
Accumulating evidence shows that Aβ induces disruptions in cellular Ca2+ homeostasis that are particularly detrimental to synaptic function in AD (Wu et al., 2010). NCX3 is expressed in subpopulations of neurons, where it localizes predominantly to dendrites and distal astrocyte processes that contact excitatory synapses (Minelli et al., 2007). This positioning suggests that NCX3 may play a key role in regulating Ca2+ currents during synaptic activity. Furthermore, NCX3 buffering of astrocytic Na+ could further impact on synaptic function by regulating the activity of Na+-dependent glutamate transporters that are critical for the clearance of extracellular glutamate during synaptic activity (Minelli et al., 2007). Because healthy synaptic transmission is essential for normal learning and memory (DeKosky & Scheff, 1990; Sze et al., 1997), this implies that NCX3-mediated sustained elevations in neuronal Ca2+ may contribute to the synaptic dysfunction and cognitive deficits associated with Aβ in AD. Indeed, NCX3 has been shown to play a crucial role in regulating LTP, spatial learning and memory. Higher basal [Ca2+]i, due to delayed Ca2+ clearance after stimulation of neuronal activity, impaired synaptic transmission and reduced performance in spatial learning and memory tasks have all been observed in NCX3 knockout mice (Molinaro et al., 2011), a situation analogous to proteolytic inactivation of NCX3. These findings suggest therefore that targeting aberrant NCX3 cleavage by calpain may have therapeutic potential for the treatment for Alzheimer’s disease.
Experimental procedures
Postmortem human brain
Frozen postmortem human frontal cortex (Table 1) from control brain (N = 20) and pathologically confirmed cases of AD (N = 20), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) (N = 5), corticobasal degeneration (CBD) (N = 5) and frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism associated with tau mutations on chromosome 17 (FTD) (n = 4) were obtained from the MRC London Brain Bank for Neurodegenerative Diseases, Kings College London, Institute of Psychiatry. Frozen tissue was homogenized (200 mg mL−1) in ice-cold lysis buffer, 50 mm Tris-buffered saline, 0.1% (w/v) Triton X-100, 10 mm sodium fluoride, 1 mm sodium orthovanadate, 2 mm ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid, 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride and Complete™ protease inhibitor (Roche), pH 7.4, using a mechanical homogenizer. Following centrifugation of homogenates at 25 000 g(av) for 20 min at 4 °C, the supernatants were collected, and protein concentrations were measured using a BCA protein assay kit (Pierce Endogen, Rockford, IL, USA). Samples were standardized to equal protein concentration before being analysed by Western blotting.
Table 1.
Characteristics of postmortem brain samples. Frontal cortex was obtained from postmortem control brains (CTRL), those with Braak stage IV–VI Alzheimer’s disease (AD), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD) and frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism associated with the 10 + 16 tau mutation on chromosome 17 (FTD). Postmortem delay (PMD), age and sex were balanced between groups as far as possible
| Diagnosis | Case number | Sex | Age (years) | PMD (h) | Case notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL* | A042/01 | F | 52 | 44 | Carcinoma of the lung |
| CTRL* | A278/96 | F | 77 | 29 | Pulmonary embolism |
| CTRL* | A239/95 | F | 79 | 38 | Chronic obstructive airway disease |
| CTRL* | A155/95 | F | 63 | 34 | Myocardial infarction |
| CTRL* | A094/95 | F | 80 | 31 | Bronchopneumonia/liver failure |
| CTRL* | A047/02 | F | 87 | 22 | Carcinoma of the breast |
| CTRL* | A170/00 | F | 68 | 9 | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| CTRL* | A322/94 | F | 62 | 81 | Haemothorax |
| CTRL* | A346/95 | M | 85 | 16 | Ruptured aortic aneurysm |
| CTRL* | A135/95 | M | 65 | 24 | Coronary artery occlusion |
| CTRL* | A134/00 | M | 86 | 6 | Myocardial infarction |
| CTRL* | A401/97 | M | 85 | 42 | Gastrointestinal haemorrhage |
| CTRL* | A223/96 | M | 80 | 11 | Carcinoma of the prostate |
| CTRL* | A133/95 | M | 85 | 48 | Left ventricular failure |
| CTRL* | A149/01 | M | 95 | 44 | Gastrointestinal bleed |
| CTRL | A077/00 | M | 68 | 53 | Ischaemic heart disease |
| CTRL | A066/00 | M | 61 | 53 | Cardiac arrest |
| CTRL* | A330/94 | M | 69 | 52 | Aortic aneurysm |
| CTRL | A261/94 | M | 75 | 85 | Unknown. Diabetic. |
| CTRL | A320/94 | M | 77 | 96 | Myocardial infarction |
| AD* | A157/00 | F | 75 | 9 | Braak stage IV |
| AD* | A240/06 | F | 97 | 12 | Braak stage V |
| AD* | A010/06 | F | 67 | 56 | Braak stage VI |
| AD* | A210/05 | F | 84 | 18 | Braak stage V |
| AD* | A169/05 | F | 82 | 43 | Braak stage V–VI |
| AD* | A168/05 | F | 84 | 36 | Braak stage V–VI |
| AD* | A074/05 | F | 89 | 29 | Braak stage V–VI |
| AD* | A203/04 | F | 84 | 37 | Braak stage V–VI |
| AD* | A221/03 | F | 81 | 37 | Braak stage V |
| AD* | A188/00 | F | 64 | 10 | Braak stage V |
| AD* | A232/00 | F | 79 | 8 | Braak stage V |
| AD* | A074/06 | F | 69 | 25 | Braak stage VI, diffuse neocortical Lewy body disease |
| AD | A309/07 | F | 83 | 7 | Braak stage VI, mild neocortical Lewy body disease |
| AD | A219/07 | F | 82 | 5 | Braak stage VI, mild amyloid angiopathy |
| AD* | A206/07 | M | 81 | 47 | Braak stage V |
| AD* | A186/04 | M | 71 | 5 | Braak stage V–VI |
| AD* | A122/04 | M | 86 | 26 | Braak stage V, moderate amyloid angiopathy |
| AD* | A176/01 | M | 71 | 41 | Braak stage V–VI |
| AD | A249/07 | M | 74 | 69 | Braak stage V–VI with amyloid angiopathy |
| AD | A270/06 | M | 82 | 41 | Braak stage VI with amyloid angiopathy |
| PSP | A196/98 | F | 68 | 9 | |
| PSP | A202/98 | F | 75 | 48 | |
| PSP | A142/07 | M | 93 | 20 | |
| PSP | A391/97 | M | 71 | 16 | |
| PSP | A180/04 | M | 71 | 21 | |
| CBD | A140/01 | F | 65 | 72 | |
| CBD | A037/98 | M | 64 | 66 | |
| CBD | A197/98 | M | 51 | 34 | |
| CBD | A302/99 | M | 67 | 89 | |
| CBD | A008/00 | M | 74 | 9 | |
| FTD | A099/08 | M | 70 | 7 | Tau mutation 10 + 16 |
| FTD | A171/02 | M | 71 | 5 | Tau mutation 10 + 16 |
| FTD | A176/00 | M | 48 | 65 | Tau mutation 10 + 16 |
| FTD | A074/00 | M | 67 | 35 | Tau mutation 10 + 16 |
Indicates samples from which tissue was available for the analysis of Aβ content by ELISA (N = 16).
Primary cortical cell culture
Primary cortical neuronal cultures were prepared from embryonic day 18 (E18) rat embryos as described previously (Pooler et al., 2013). Cultures are primarily neuronal with approximately 4% astrocytes and negligible numbers of oligodendrocytes and microglia (Garwood et al., 2011). Cultures were treated with 10 μm soluble oligomeric Aβ1–42 (California Peptide Co., Napa, CA, USA). To inhibit calpain activity, cells were treated with 5 μm calpeptin (EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) or vehicle for 24 h prior to addition of Aβ. Aβ1–42 was prepared according to the method described in Garwood et al. (2011), which generates predominantly soluble oligomeric species of Aβ. After treatment, culture medium was removed and cells were washed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), lysed in ice-cold lysis buffer and centrifuged at 16 000 g(av) for 20 min at 4 °C. The protein concentration of supernatants was measured using a BCA protein assay kit, as described above, and protein concentrations were standardized prior to analysis.
Treatment of primary cortical cultures with oligodeoxynucleotides
Primary cortical cultures (4 DIV) were treated with antisense and sense phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides, specific for rat NCX3 (Iwamoto & Kita, 2006). The 5′–3′ sequences are as follows: NCX3 antisense: GCCATACACAAGAG; NCX3 sense: CTCTTGTGTATGGC. Cells were incubated with oligodeoxynucleotides (5 μm) and Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Paisley, UK), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Twenty-four hours after the application of oligonucleotides, neurons were treated with vehicle or subtoxic (1 μm) concentrations of oligomeric Aβ1–42 for a further 16 h.
Gel electrophoresis and Western blotting
Five to ten microgram protein was loaded onto 10% (w/v) SDS–polyacrylamide gels. Separated proteins were blotted onto nitrocellulose membranes (Whatman, Maidstone, UK) and blocked with 5% (w/v) nonfat milk/0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 in PBS for 1 h. After blocking, membranes were incubated overnight at 4 °C in blocking solution containing primary antibody. Blots were washed and incubated with the appropriate fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 h at ambient temperature. Proteins were visualized and quantified using an Odyssey Infrared Imaging system (Li-Cor Biosciences, Cambridge, UK).
Human postmortem brain samples were run on multiple gels, each of which contained a standard control sample to enable comparison of samples across gels. Statistical analysis was performed following standardization of specific protein amounts in each sample against NSE, used as a loading control. White lines separating lanes in some immunoblots indicate removal of portions of the blots for clarity and/or splicing together of distinct blots.
Antibodies
The following primary antibodies were used for Western blotting: calpain-1 large active subunit (No. 2556, rabbit IgG; Cell Signalling Ltd, Beverly, MA, USA); calpain-2 (AB81023, rabbit IgG; EMD Millipore, MA, USA); calpastatin (CAST, #4146, rabbit IgG; Cell Signalling Ltd.); cleaved (active) caspase-3 (Asp175, rabbit IgG; Cell Signaling Ltd.); neuron-specific enolase (BBS/NC/VI-H14, mouse IgF; DAKO Ltd, Ely, UK); β-actin (clone AC-15, mouse IgG; Abcam, Cambridge, UK). NCX3 and NCX1 antibodies were kindly provided by Professor Kenneth Phillipson (UCLA) (Porzig et al., 1993; Thurneysen et al., 2002).
Cell death assays
Cytotoxicity was evaluated by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in culture medium using Cytotox 96 assay kits (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) according to the manufacturer’s directions. After collection of medium, the remaining cells were lysed in 0.9% (w/v) Triton X-100, and LDH content in medium and lysed cells was measured to determine total LDH content. Optical density was measured at 492 nm (Wallac 1420 Victor3 plate reader; Perkin-Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). LDH release from cells was calculated as a percentage of total LDH in each sample.
Cell death was confirmed using a live/dead fixable cell stain (Invitrogen, Paisley, UK), performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Following uptake of the amine-reactive fluorescent dye, cells were washed, immunolabelled with an antibody against βIII-tubulin, and nuclei were labelled with 1 μg mL−1 Hoechst-33342 as described previously (Garwood et al., 2011).
Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 ELISA
Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 in human brain samples were quantified using ELISA kits from Invitrogen (Aβ40 ELISA KHB3481; Aβ1–42 ELISA KHB3442) as we have previously described (Vagnoni et al., 2012).
Statistical analysis
Normalcy of data was first established using D’Agostino and Pearson omnibus normality tests and was then analysed by parametric one-way analysis of variance followed by Newman–Keuls post hoc tests (Graphpad Prism v5.0; La Jolla, CA, USA). Differences were considered statistically significant when P < 0.05. Differences in the amount of Aβ in control and AD human brain were assessed using two-tailed student t-tests. These data were correlated with active calpain-1- and calpain-cleaved NCX3 protein amounts using parametric two-tailed Pearson tests.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Medical Research Council (G0700355 to WN), the NIHR BRC for Mental Health at the South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust, the National Council for Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research, and the Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP) Association. Human post-mortem brain tissues were obtained from the MRC London Brain Bank for Neurodegenerative Diseases/Brains for Dementia Research. We would like to thank Professor Kenneth Philipson and Dr Deborah Nicoll (University of California Los Angeles) for their kind gift of NCX1 and NCX3 antibodies.
Author contributions
JA, KK, CLC, MB, CJG, RC, SW, AJ and WN performed the experiments and analysed the data. JA, KK, DPH and WN designed the research and wrote the paper.
Supporting Information
Additional Supporting Information may be found in the online version of this article at the publisher’s web-site.
Fig. S1 Detection of active calpain-1 in human postmortem brain.
References
- Arispe N, Pollard HB, Rojas E. Giant multilevel cation channels formed by Alzheimer disease amyloid beta-protein [A beta P-(1-40)] in bilayer membranes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1993;90:10573–10577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayala-Grosso C, Tam J, Roy S, Xanthoudakis S, Da Costa D, Nicholson DW, Robertson GS. Caspase-3 cleaved spectrin colocalizes with neurofilament- immunoreactive neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience. 2006;141:863–874. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bano D, Young KW, Guerin CJ, Lefeuvre R, Rothwell NJ, Naldini L, Rizzuto R, Carafoli E, Nicotera P. Cleavage of the plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in excitotoxicity. Cell. 2005;120:275–285. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.11.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bano D, Munarriz E, Chen HL, Ziviani E, Lippi G, Young KW, Nicotera P. The plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+ exchanger is cleaved by distinct protease families in neuronal cell death. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007;1099:451–455. doi: 10.1196/annals.1387.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brustovetsky T, Bolshakov A, Brustovetsky N. Calpain activation and Na+/Ca2+ exchanger degradation occur downstream of calcium deregulation in hippocampal neurons exposed to excitotoxic glutamate. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010;88:1317–1328. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeKosky ST, Scheff SW. Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer’s disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann. Neurol. 1990;27:457–464. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garwood CJ, Pooler AM, Atherton J, Hanger DP, Noble W. Astrocytes are important mediators of Abeta-induced neurotoxicity and tau phosphorylation in primary culture. Cell Death Dis. 2011;2:e167. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2011.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J. The calpain system. Physiol. Rev. 2003;83:731–801. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00029.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goni-Oliver P, Lucas JJ, Avila J, Hernandez F. N-terminal cleavage of GSK-3 by calpain: a new form of GSK-3 regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:22406–22413. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702793200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang CJ, Gurlo T, Haataja L, Costes S, Daval M, Ryazantsev S, Wu X, Butler AE, Butler PC. Calcium-activated calpain-2 is a mediator of beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:339–348. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.024190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto T, Kita S. YM-244769, a novel Na+/Ca2+ exchange inhibitor that preferentially inhibits NCX3, efficiently protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation- induced SH-SY5Y neuronal cell damage. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006;70:2075–2083. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.028464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger KA, Stadelmann C. Mechanisms of cell death in neurodegenerative disorders. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2000;59:95–114. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6781-6_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayed R, Sokolov Y, Edmonds B, McIntire TM, Milton SC, Hall JE, Glabe CG. Permeabilization of lipid bilayers is a common conformation-dependent activity of soluble amyloid oligomers in protein misfolding diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:46363–46366. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C400260200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly BL, Vassar R, Ferreira A. Beta-amyloid-induced dynamin 1 depletion in hippocampal neurons. A potential mechanism for early cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:31746–31753. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M503259200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchibhotla KV, Goldman ST, Lattarulo CR, Wu HY, Hyman BT, Bacskai BJ. Abeta plaques lead to aberrant regulation of calcium homeostasis in vivo resulting in structural and functional disruption of neuronal networks. Neuron. 2008;59:214–225. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S, Jin M, Koeglsperger T, Shepardson NE, Shankar GM, Selkoe DJ. Soluble Abeta oligomers inhibit long-term potentiation through a mechanism involving excessive activation of extrasynaptic NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. J. Neurosci. 2011;31:6627–6638. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0203-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lytton J. Na+/Ca2+ exchangers: three mammalian gene families control Ca2+ transport. Biochem. J. 2007;406:365–382. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin SJ, O’Brien GA, Nishioka WK, McGahon AJ, Mahboubi A, Saido TC, Green DR. Proteolysis of fodrin (non-erythroid spectrin) during apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:6425–6428. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.12.6425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews PM, Jiang Y, Schmidt SD, Grbovic OM, Mercken M, Nixon RA. Calpain activity regulates the cell surface distribution of amyloid precursor protein. Inhibition of calpains enhances endosomal generation of beta-cleaved C-terminal APP fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:36415–36424. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M205208200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minelli A, Castaldo P, Gobbi P, Salucci S, Magi S, Amoroso S. Cellular and subcellular localization of Na+-Ca2+ exchanger protein isoforms, NCX1, NCX2, and NCX3 in cerebral cortex and hippocampus of adult rat. Cell Calcium. 2007;41:221–234. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2006.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinaro P, Viggiano D, Nistico R, Sirabella R, Secondo A, Boscia F, Pannaccione A, Scorziello A, Mehdawy B, Sokolow S, Herchuelz A, Di Renzo GF, Annunziato L. Na+ -Ca2+ exchanger (NCX3) knock-out mice display an impairment in hippocampal long-term potentiation and spatial learning and memory. J. Neurosci. 2011;31:7312–7321. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6296-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson AM, Methner DN, Ferreira A. Membrane cholesterol modulates beta- amyloid-dependent tau cleavage by inducing changes in the membrane content and localization of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:976–986. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.154138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson E, Alafuzoff I, Blennow K, Blomgren K, Hall CM, Janson I, Karlsson I, Wallin A, Gottfries CG, Karlsson JO. Calpain and calpastatin in normal and Alzheimer-degenerated human brain tissue. Neurobiol. Aging. 1990;11:425–431. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(90)90009-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon RA. The calpains in aging and aging-related diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2003;2:407–418. doi: 10.1016/s1568-1637(03)00029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble W, Garwood C, Stephenson J, Kinsey AM, Hanger DP, Anderton BH. Minocycline reduces the development of abnormal tau species in models of Alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2009;23:739–750. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-113795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooler AM, Phillips EC, Lau DH, Noble W, Hanger DP. Physiological release of endogenous tau is stimulated by neuronal activity. EMBO Rep. 2013;14:389–394. doi: 10.1038/embor.2013.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porzig H, Li Z, Nicoll DA, Philipson KD. Mapping of the cardiac sodium-calcium exchanger with monoclonal antibodies. Am. J. Physiol. 1993;265(3 Pt 1):C748–C756. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranciat-McComb NS, Bland KS, Huschenbett J, Ramonda L, Bechtel M, Zaidi A, Michaelis ML. Antisense oligonucleotide suppression of Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger activity in primary neurons from rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2000;294:13–16. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01524-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao MV, Mohan PS, Peterhoff CM, Yang DS, Schmidt SD, Stavrides PH, Campbell J, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Paskevich PA, Cataldo AM, Haroutunian V, Nixon RA. Marked calpastatin (CAST) depletion in Alzheimer’s disease accelerates cytoskeleton disruption and neurodegeneration: neuroprotection by CAST overexpression. J. Neurosci. 2008;28:12241–12254. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4119-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K, Elce JS, Hamos JE, Nixon RA. Widespread activation of calcium-activated neutral proteinase (calpain) in the brain in Alzheimer disease: a potential molecular basis for neuronal degeneration. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1993;90:2628–2632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellenberg GD, Montine TJ. The genetics and neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;124:305–323. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-0996-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh S, Samanta K, Kar P, Roy S, Chakraborti T, Chakraborti S. m-Calpain- mediated cleavage of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger-1 in caveolae vesicles isolated from pulmonary artery smooth muscle. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2010;341:167–180. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0448-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small DH. Dysregulation of calcium homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Res. 2009;34:1824–1829. doi: 10.1007/s11064-009-9960-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith IF, Green KN, LaFerla FM. Calcium dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease: recent advances gained from genetically modified animals. Cell Calcium. 2005;38:427–437. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2005.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokolow S, Luu SH, Headley AJ, Hanson AY, Kim T, Miller CA, Vinters HV, Gylys KH. High levels of synaptosomal Na(+)-Ca(2 + ) exchangers (NCX1, NCX2, NCX3) co-localized with amyloid-beta in human cerebral cortex affected by Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Calcium. 2011;49:208–216. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2010.12.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sze CI, Troncoso JC, Kawas C, Mouton P, Price DL, Martin LJ. Loss of the presynaptic vesicle protein synaptophysin in hippocampus correlates with cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1997;56:933–944. doi: 10.1097/00005072-199708000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurneysen T, Nicoll DA, Philipson KD, Porzig H. Sodium/calcium exchanger subtypes NCX1, NCX2 and NCX3 show cell-specific expression in rat hippocampus cultures. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2002;107:145–156. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(02)00461-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town T, Zolton J, Shaffner R, Schnell B, Crescentini R, Wu Y, Zeng J, DelleDonne A, Obregon D, Tan J, Mullan M. p35/Cdk5 pathway mediates soluble amyloid- beta peptide-induced tau phosphorylation in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002;69:362–372. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchese F, Fa M, Liu S, Zhang H, Hidalgo A, Schmidt SD, Yamaguchi H, Yoshii N, Mathews PM, Nixon RA, Arancio O. Inhibition of calpains improves memory and synaptic transmission in a mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2008;118:2796–2807. doi: 10.1172/JCI34254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vagnoni A, Perkinton MS, Gray EH, Francis PT, Noble W, Miller CC. Calsyntenin-1 mediates axonal transport of the amyloid precursor protein and regulates Abeta production. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012;21:2845–2854. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaisid T, Kosower NS, Katzav A, Chapman J, Barnoy S. Calpastatin levels affect calpain activation and calpain proteolytic activity in APP transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2007;51:391–397. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2007.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega IE, Traverso EE, Ferrer-Acosta Y, Matos E, Colon M, Gonzalez J, Dickson D, Hutton M, Lewis J, Yen SH. A novel calcium-binding protein is associated with tau proteins in tauopathy. J. Neurochem. 2008;106:96–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkhratsky A, Toescu EC. Endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2 + ) homeostasis and neuronal death. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2003;7:351–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2003.tb00238.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu HY, Hudry E, Hashimoto T, Kuchibhotla K, Rozkalne A, Fan Z, Spires-Jones T, Xie H, Arbel-Ornath M, Grosskreutz CL, Bacskai BJ, Hyman BT. Amyloid beta induces the morphological neurodegenerative triad of spine loss, dendritic simplification, and neuritic dystrophies through calcineurin activation. J. Neurosci. 2010;30:2636–2649. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4456-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhukareva V, Joyce S, Schuck T, Van Deerlin V, Hurtig H, Albin R, Gilman S, Chin S, Miller B, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Unexpected abundance of pathological tau in progressive supranuclear palsy white matter. Ann. Neurol. 2006;60:335–345. doi: 10.1002/ana.20916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Fig. S1 Detection of active calpain-1 in human postmortem brain.