Abstract
FOXO3Avariation has repeatedly been reported to associate with human longevity, yet only few studies have investigated whether FOXO3Avariation also associates with aging-related traits. Here, we investigate the association of 15 FOXO3Atagging single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 1088 oldest-old Danes (age 92–93) with 4 phenotypes known to predict their survival: cognitive function, hand grip strength, activity of daily living (ADL), and self-rated health. Based on previous studies in humans and foxo animal models, we also explore self-reported diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and bone (femur/spine/hip/wrist) fracture. Gene-based testing revealed significant associations of FOXO3Avariation with ADL (P = 0.044) and bone fracture (P = 0.006). The single-SNP statistics behind the gene-based analysis indicated increased ADL (decreased disability) and reduced bone fracture risk for carriers of the minor alleles of 8 and 10 SNPs, respectively. These positive directions of effects are in agreement with the positive effects on longevity previously reported for these SNPs. However, when correcting for the test of 9 phenotypes by Bonferroni correction, bone fracture showed borderline significance (P = 0.054), while ADL did not (P = 0.396). Although the single-SNP associations did not formally replicate in another study population of oldest-old Danes (n = 1279, age 94–100), the estimates were of similar direction of effect as observed in the Discovery sample. A pooled analysis of both study populations displayed similar or decreased sized P-values for most associations, hereby supporting the initial findings. Nevertheless, confirmation in additional study populations is needed.
Keywords: aging phenotypes, association study, Forkhead box O3, oldest-old, SNPs
Introduction
Genetic factors contribute to the variation in human lifespan as well as to aging-related traits such as physical and cognitive function (Frederiksen et al., 2002; McGue & Christensen, 2002; Hjelmborg et al., 2006). The forkhead box O3 gene (FOXO3A) may, due to the verification in several study populations (Willcox et al., 2008; Anselmi et al., 2009; Flachsbart et al., 2009; Li et al., 2009; Pawlikowska et al., 2009; Soerensen et al., 2010; Zeng et al., 2010; Di Bona et al., 2013; Bao et al., 2014; Broer et al., 2014), be considered a second consistently confirmed longevity-associated gene in addition to the apolipoprotein E gene (APOE). However, only few studies have investigated whether FOXO3Avariation might also associate with aging-related phenotypes in the oldest-old.
FOXO3Ais part of the insulin/insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling pathway, one of the key candidate pathways of longevity (Christensen et al., 2006). Together with FOXO1A,FOXO4,and FOXO6,FOXO3Aconstitutes the FoxO family of transcription factors, which regulates the expression of numerous downstream genes involved in a wide range of biological processes including apoptosis, cell cycle transition, DNA repair, oxidative stress, cell differentiation, and glucose metabolism (reviewed in (Huang & Tindall, 2007)).
Several animal studies have aimed to shed light on the physiological effects of loss-of-function or overexpression of foxo3a or its homologues. For example, lack of foxoin fruit flies (Drosophila Melanogaster) was, among other things, observed to increase the sensitivity to oxidative stress (Junger et al., 2003), while overexpression in the fat body was reported to reduce fecundity and increase lifespan in females (Giannakou et al., 2004). In zebra fish (Danio rerio), neural developmental defects were detected after knockdown of foxo3a, an effect likely mediated via increased apoptosis (Peng et al., 2010). In mice (Mus musculus) knockout of Foxo3has for instance been found to cause hematological abnormalities, decreased glucose uptake in glucose tolerance tests, and increased follicular activation, the latter leading to depletion of functional follicles, oocyte death, and infertility in female mice (Castrillon et al., 2003). In other mouse studies, Foxo3knockout induced incorrect immune responses, among others manifested as reduced numbers of B-cells (Hinman et al., 2009) and auto inflammation (Lin et al., 2004). Furthermore, Foxo3knockout has been reported to affect the maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells; for example, manifested as reduced autophagy after metabolic stress (Warr et al., 2013) and as reduced self-renewal in general, the latter likely impairing the maintenance of the stem cells during aging (Miyamoto et al., 2007). Tissue-specific mouse models have also been made, for instance cardiac-specific constitutive expression of foxo3was, among others, described to result in decreased heart weight (Schips et al., 2011), while constitutive expression in rat substantia nigra led to neuronal loss (Pino et al., 2014). Finally, as foxo1, foxo3, and foxo4 have overlapping functions, conditional triple knockout mice have been generated (reviewed in (Arden, 2008)). These mice were, among other things, reported to have decreased insulin levels in liver-specific knockouts (Haeusler et al., 2010), increased numbers of thymic lymphomas and hemangiomas (Paik et al., 2007), and reduced bone formation and bone mass (Ambrogini et al., 2010). In the latter study, osteoblast-specific overexpression of foxo3was found to increase bone formation (Ambrogini et al., 2010).
A few studies in humans have explored the association between FOXO3Avariation and aging-related phenotypes in the oldest-old. Kuningas et al. (2007) observed an increased risk of stroke, but not of diabetes or cardiovascular disease (CVD), in elderly carriers of two specific FOXO3Ahaplotypes. A borderline significant association was seen for cardiovascular mortality risk, yet not for cancer mortality risk. Willcox et al. (2008) found no significant association of rs2802292 with stroke, diabetes, coronary heart disease, or cancer when long-lived individuals were investigated separately. However, when average-lived individuals from the same birth cohorts were included, the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) displayed association with coronary heart disease and health status. Also, a borderline significant association with cancer was noted. Pawlikowska et al. (2009) examined rs1935949 and rs4946935 in long-lived individuals and participants of their prospective cohort, who died from specific causes. rs4946935 showed association with death caused by cancer, while both SNPs showed association with death caused by atherosclerosis. Although a replication sample did not reveal significance, meta-analyses did support the associations.
To further explore whether FOXO3Avariation associates with aging-related traits likely influencing longevity, we investigated the association of 15 FOXO3Atagging SNPs with phenotypes previously shown to predict survival in the oldest-old studied here (Nybo et al., 2003): cognitive function, physical function (as measured by hand grip strength), activity of daily living (ADL), and self-rated health. In addition, we also explored the prevalence of self-reported diabetes, cancer, CVD, osteoporosis, and bone (femur/spine/hip/wrist) fracture (bone fracture).
Results
The characteristics of the study populations are shown in Table S1 (Supporting information), while the 15 FOXO3ASNPs are given in Fig.1.
Figure 1.
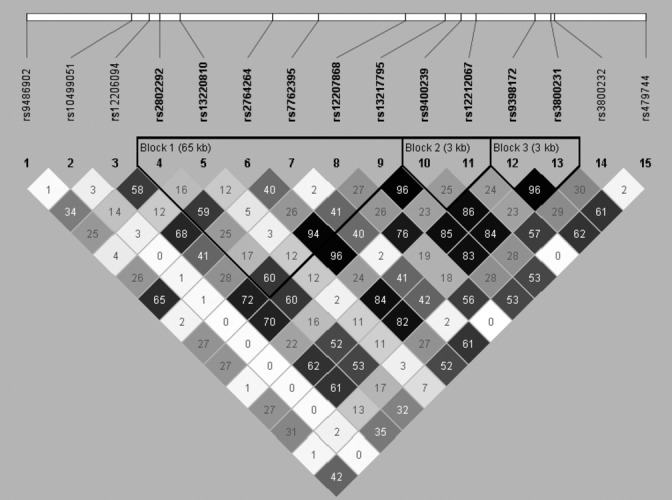
Linkage disequilibrium plot of the 15 FOXO3ASNPs under study. Notes: The values are R2 (a value of 100 reflects complete dependency between SNPs), and the colors reflect R2 (the darker color the higher the R2). kb: kilobases.
Gene-based association study in the Discovery sample
To investigate the overall association of FOXO3Avariation with the nine phenotypes, a gene-based analysis was performed. The data are summarized in Table1. Only ADL and self-reported bone fracture displayed p-gene values below 0.05: p-gene (ADL) = 0.044 and p-gene (bone fracture) = 0.006. These p-gene values are corrected for the test of 15 SNPs, but not for the test of nine phenotypes. When conducting a strict Bonferroni correction, the association of FOXO3Avariation with bone fracture was borderline significant (p-gene = 0.054), while the association of FOXO3Avariation with ADL was not (p-gene = 0.396).
Table 1.
Gene-based association of FOXO3Avariation and the nine phenotypes in the Discovery sample
| Phenotype | n | p-gene |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive composite score | 1026 | 0.851 |
| Self-reported CVD | 1086 | 0.777 |
| Hand grip strength | 980 | 0.281 |
| Self-reported diabetes | 1087 | 0.228 |
| Self-reported cancer | 1085 | 0.226 |
| Self-reported osteoporosis | 1061 | 0.221 |
| Self-rated health | 1040 | 0.163 |
| Activity of daily living | 1086 | 0.044 |
| Self-reported bone fracture | 1063 | 0.006 |
n, number of individuals with data (in total 1088 individuals were genotyped); p-gene, set-based value obtained after 10000 permutations; CVD, cardiovascular disease. p-gene values < 0.05 are shown in bold.
Effects at the single-SNP level for ADL and bone fracture
The gene-based analysis gives no overall effect estimate. Hence, the direction of effect of the associations observed at the gene-level must be represented by the size and direction of effect of the coefficients of the single-SNP tests, which were the basis of the gene-based analysis. These data are summarized in Table2. Five of the 15 SNPs showed p-SNP values below 0.05 for ADL, while 3 SNPs showed nonsignificant borderline association (p-SNPs: 0.055–0.074). For the minor alleles of all of these SNPs the direction of effect on ADL was positive, corresponding to a decreased disability (see Table2A). With respect to bone fracture, 10 of the 15 SNPs showed P-values below 0.05. Again, the direction of effect was positive for all minor alleles of these SNPs, corresponding to a decreased risk of bone fracture (see Table2B).
Table 2.
Single-SNP analysis in the Discovery sample of FOXO3Avariation and (A) activity of daily living and (B) bone (femur/spine/hip/wrist) fracture
| (A) Activity of daily living (n = 1086) |
(B) Bone fracture (n = 1063) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | β-coef. | p-SNP | 95% CI | SNP | OR | p-SNP | 95% CI |
| rs9400239 | 0.07 | 0.020 | 0.01; 0.14 | rs9486902 | 0.60 | 0.001 | 0.45; 0.81 |
| rs9398172 | 0.07 | 0.021 | 0.01; 0.14 | rs7762395 | 0.57 | 0.001 | 0.42; 0.78 |
| rs13217795 | 0.07 | 0.024 | 0.01; 0.14 | rs479744 | 0.69 | 0.007 | 0.52; 0.90 |
| rs2802292 | 0.07 | 0.026 | 0.01; 0.13 | rs3800231 | 0.72 | 0.008 | 0.57; 0.92 |
| rs2764264 | 0.07 | 0.042 | 0.01; 0.13 | rs9398172 | 0.74 | 0.012 | 0.58; 0.94 |
| rs479744 | 0.07 | 0.055 | −0.01; 0.14 | rs9400239 | 0.75 | 0.017 | 0.59; 0.95 |
| rs3800231 | 0.06 | 0.063 | −0.01; 0.12 | rs2764264 | 0.75 | 0.020 | 0.59; 0.96 |
| rs7762395 | 0.07 | 0.074 | −0.01; 0.15 | rs13217795 | 0.76 | 0.028 | 0.60; 0.97 |
| rs10499051 | 0.08 | 0.133 | −0.02; 0.18 | rs12206094 | 0.77 | 0.035 | 0.61; 0.98 |
| rs12206094 | 0.05 | 0.149 | −0.02; 0.11 | rs2802292 | 0.80 | 0.049 | 0.64; 0.99 |
| rs9486902 | 0.05 | 0.171 | −0.02; 0.13 | rs13220810 | 0.88 | 0.303 | 0.70; 1.12 |
| rs3800232 | 0.04 | 0.392 | −0.05; 0.13 | rs12207868 | 1.17 | 0.362 | 0.83; 1.65 |
| rs12207868 | 0.01 | 0.828 | −0.09; 0.11 | rs10499051 | 1.12 | 0.549 | 0.78; 1.61 |
| rs12212067 | 0.01 | 0.869 | −0.09; 0.10 | rs3800232 | 0.94 | 0.711 | 0.68; 1.30 |
| rs13220810 | -0.01 | 0.905 | −0.07; 0.06 | rs12212067 | 1.03 | 0.874 | 0.73; 1.45 |
The single-SNP tests were the basis of the gene-set analysis in the Discovery sample. n, number of individuals with data; β-coef., beta coefficient; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; p-SNP values < 0.05 are shown in bold, while p-SNP values > 0.05 < 0.10 are shown in bold and italics.
Replication study of the ADL and bone fracture findings
Five SNPs were investigated in the Replication sample: rs12206094, rs2802292, rs3800231, rs479744, and rs7762395 (see Experimental procedures). None of the initial findings could be formally replicated. However, all of the effect estimates observed in the Replication sample were in the same direction, although generally attenuated, as compared to the Discovery sample (compare Table3A to B, and Table3D to E).
Table 3.
Replication study of activity of daily living and bone fracture findings
| Activity of daily living | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) ADL in Discovery sample (n = 1086) |
(B) ADL in Replication sample (n = 1279) |
(C) ADL Pooled analysis |
|||||||
| SNP | β-coef. | p-SNP | 95% CI | β-coef. | p-SNP | 95% CI | β-coef. | p-SNP | 95% CI |
| rs2802292 | 0.07 | 0.026 | 0.01; 0.13 | 0.04 | 0.183 | −0.02; 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.017* | 0.01; 0.09 |
| rs479744 | 0.07 | 0.055 | −0.01; 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.582 | −0.05; 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.112 | −0.01; 0.09 |
| rs3800231 | 0.06 | 0.063 | −0.01; 0.12 | 0.03 | 0.331 | −0.03; 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.054* | −0.01; 0.09 |
| rs7762395 | 0.07 | 0.074 | −0.01; 0.15 | 0.03 | 0.514 | −0.05; 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.114 | −0.01: 0.10 |
| rs12206094 | 0.05 | 0.149 | −0.02; 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.202 | −0.02; 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.069* | −0.01; 0.08 |
| Bone fracture | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (D) BF in Discovery sample (n = 1063) |
(E) BF in replication sample (n = 691) |
(F) BF Pooled analysis |
|||||||
| SNP | OR | p-SNP | 95% CI | OR | p-SNP | 95% CI | OR | p-SNP | 95% CI |
| rs7762395 | 0.57 | 0.001 | 0.42; 0.78 | 0.90 | 0.542 | 0.64; 1.26 | 0.71 | 0.003 | 0.56; 0.89 |
| rs479744 | 0.69 | 0.007 | 0.52; 0.90 | 0.86 | 0.311 | 0.63; 1.16 | 0.76 | 0.006* | 0.62; 0.92 |
| rs3800231 | 0.72 | 0.008 | 0.57; 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.361 | 0.68; 1.15 | 0.80 | 0.012 | 0.67; 0.95 |
| rs12206094 | 0.77 | 0.035 | 0.61; 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.817 | 0.73; 1.28 | 0.85 | 0.085 | 0.71; 1.02 |
| rs2802292 | 0.80 | 0.049 | 0.64; 0.99 | 0.87 | 0.287 | 0.67; 1.12 | 0.83 | 0.033* | 0.70; 0.99 |
ADL, activity of daily living; n, number of individuals with data; β-coef., beta coefficient; CI, confidence interval; BF, bone fracture; OR, odds ratio;
SNPs for which the pooled analysis showed lower p-SNPs as compared to the analysis of the Discovery sample alone.
In a pooled analysis of the data from both study populations, all five SNPs showed nominal or borderline significant (p-SNP>0.05 < 0.10) association with bone fracture, and the significance was increased for rs2802292 and rs479744 as compared to the Discovery sample (compare Table3D to F). With respect to ADL, rs12206094, rs2802292, and rs3800231 showed nominal or borderline significant association in the pooled analysis and furthermore showed lower sized p-SNP values as compared to the Discovery sample (compare Table3A to C). The effect estimates of the pooled analysis were of the same direction, as compared to the analyses in the Discovery sample alone and in the Replication sample alone.
Discussion
In this study, we investigated the association of variation in the second consistently confirmed longevity-associated gene, FOXO3A, with aging-related phenotypes in the oldest-old. In the Discovery sample, we explored four phenotypes known to predict their survival, that is, cognitive function, self-reported health, hand grip strength, and ADL. Moreover, we included data on five self-reported diseases: diabetes, cancer, CVD, osteoporosis, and bone fracture, as these are either investigated in genetic association studies and/or are supported by foxo animal models.
We found FOXO3Avariation to show nominal significant association with two of the investigated phenotypes; ADL and bone fracture (see Table1). This does, however, not exclude relevance of FOXO3Avariation for the remaining seven phenotypes or for the physiological processes behind these phenotypes; it is possible that more statistical power is needed to detect such associations, especially if these are of small effect size (see Experimental procedures). Furthermore, as the foxo3a protein has a wide array of downstream targets, which themselves affect a wide range of cellular and physiological processes, it may simply be difficult to pinpoint the candidate phenotypes, which FOXO3Apotentially affects.
Contrary to our results, two previous studies (Willcox et al., 2008; Pawlikowska et al., 2009) described association of single FOXO3ASNPs with cancer and health status, respectively. In a retrospective lookup, none of these associations could, however, be replicated in our data (data not shown). The lack of concordance could be due to differences in phenotypes or study designs, for example the present study investigates oldest-old only, while early dying controls were included in the other studies. Hence, it might be speculated that FOXO3Ainfluences health status and cancer prevalence only at younger ages. That associations can change with age has been described previously (Jacobsen et al., 2010). Similarly, due to the study by Kuningas et al. (2007), we performed a retrospective analysis of CVD data restricting to stroke and found no association (data not shown). This is, however, in accordance with the previous study, as they only found haplotype specific and not single variant specific associations (Kuningas et al., 2007). A few additional studies have indicated association of FOXO3Avariation with insulin sensitivity, for example fasting insulin levels, in young and/or elderly individuals (Willcox et al., 2008; and Banasik et al., 2011). As we did not have data on insulin sensitivity, we could not test this. However, we did not find any association with self-reported diabetes. One explanation could be that such an association is most relevant at younger ages and not among the oldest-old.
The single-SNP statistics behind the gene-based analyses of ADL and bone fracture indicated positive effects of the minor alleles of the majority of the 15 FOXO3ASNPs; that is, increased ADL (decreased disability) and reduced risk of bone fracture. The associations were, however, not statistically significant for all SNPs (see Tables2A,B). Further supporting an effect of variation in FOXO3Aon ADL and bone fracture, it can be noticed that the 15 SNPs were distributed over the entire gene region and that, at least for some of the SNPs, there was rather modest linkage disequilibrium (LD) (see Fig.1). Hence, it seems that the estimates, obtained for either ADL or bone fracture, are not completely redundant. Furthermore, it might also suggest that the findings are not chance findings.
Our findings are strengthened by the fact that for all of the 8 SNPs suggested to associate with ADL and the 10 SNPs associated with bone fracture, the minor alleles (or the minor alleles of their proxies (R2 > 0.8)) have previously been reported to pose a positive effect on human longevity in between 1 and 5 studies (Willcox et al., 2008; Anselmi et al., 2009; Flachsbart et al., 2009; Li et al., 2009; Pawlikowska et al., 2009; Soerensen et al., 2010; Zeng et al., 2010; Broer et al., 2014). This convincing overlap in SNP associations could indicate an influence of FOXO3Avariation directly on both the aging phenotypes and on longevity or it might alternatively suggest that an effect on the aging phenotypes could affect longevity.
Interestingly, 8 of the 15 FOXO3ASNPs showed borderline or nominal significant association with both ADL and bone fracture, and the coefficients for both phenotypes showed the same direction of effect. In retrospective regression analyses of ADL and each of these SNPs additionally adjusting for bone fracture, significance was observed between ADL and bone fracture, and the associations between ADL and the SNPs were slightly attenuated (data not shown). The SNP associations were, however, still found to be significant or borderline significant (data not shown). The same was found when additionally adjusting the regression analyses of bone fracture and each SNP for ADL (data not shown). The associations observed between ADL and bone fracture imply that the associations between the FOXO3ASNPs and the two phenotypes could partly be due to shared underlying factors, while the preservation of (borderline) significance for the SNPs implies that the associations with the two phenotypes must also be explained by nonshared underlying factors. Considering that FOXO3Aaffects a wide range of target genes, which in turn influence various biological processes, the potential shared and nonshared factors are numerous.
The association between FOXO3Avariation and bone fracture was not accompanied by a concurrent association with osteoporosis. However, these two phenotypes cannot be expected to be completely interchangeable, as osteoporosis is often underdiagnosed and undertreated in Denmark (Eiken & Abrahamsen, 2010). This aspect appears to be reflected in the prevalence of bone fracture and osteoporosis in the Discovery sample; despite some concordance between the two phenotypes (P-value (χ2 test) < 0.001), only 9.2% of the individuals reported an osteoporosis diagnosis, while 25% reported a bone fracture. Furthermore, due to the nature of the survey data, we cannot affirm that all fractures are osteoporotic; for this end, information on high- or low-energy fractures and the age at the time of fracture would be needed, that is, low-energy fractures occurring at higher ages would be more likely to be osteoporotic. Nevertheless, when retrospectively inspecting the coefficients of the single-SNP analysis of osteoporosis, 9 of the 10 SNPs, which showed a nominal significant positive effect on bone fracture, also indicated a positive effect on osteoporosis, although it was not statistically significant (data not shown).
We could not formally replicate the associations of FOXO3Avariation with ADL and bone fracture in another sample of Danish oldest-olds. There are a number of possible reasons for this. First of all, it may indicate that these were merely chance findings or that the Replication sample could be underpowered with respect to small effect sizes. However, another explanation could be that the individuals of the Replication sample were slightly older (94.7–100.9 years) than the individuals of the Discovery sample (92.2–93.8 years). This could potentially be of importance if the associations are not constant with age. As mentioned earlier, such changes in association with age have been reported previously (Jacobsen et al., 2010). Still, the Replication sample was the best obtainable study population, as the Replication sample was surveyed using the exact same questionnaire and assessment instrument as the Discovery sample. Finally, the effect estimates are of critical importance (Olsen et al., 2010) and for the majority of the SNPs, the effect estimates [β-coefficients and odds ratios (ORs)] of the Replication sample had similar direction as those observed in the Discovery sample (Table3). In the pooled analysis (Table3), this was further supported by comparable direction of the effect estimates and by a lowering of p-SNP values for some of the SNPs. In general, we believe that these findings lend suggestive support to the associations seen in the Discovery sample, although additional studies are needed to enable conclusion.
In this study, we for the first time suggest the association of variation in the second consistently confirmed longevity-associated gene, FOXO3A, with ADL and bone fracture. Such effects could mediate the influence of FOXO3Avariation on longevity; however, further explorations in additional study populations are needed before conclusions can be drawn.
Experimental procedures
Subjects
The Discovery sample was 1200 participants randomly drawn from 1651 eligible members of the Danish 1905 Birth Cohort Study (Nybo et al., 2001), a nationwide survey of an entire birth cohort. The FOXO3Agenotype data set is described in (Soerensen et al., 2010, 2012). After data cleaning, data were available for 1088 individuals with an age range of 92.2–93.8 years (mean: 93.1 years) and a gender distribution of 29% males and 71% females.
For replication of the findings observed in the Discovery sample, we used data on 1279 individuals from two additional population-based surveys of oldest-old Danes: the Danish 1910 and 1915 Birth Cohort Studies (unpublished data and (Christensen et al., 2013)). These surveys were conducted similar to the Danish 1905 Birth Cohort Study. The age range was 94.7–100.9 years (mean: 96.0 years), and the gender distribution was 27% males and 73% females.
Permission to collect blood samples and to use survey information was granted by The Danish Regional Committees on Biomedical Research Ethics.
Genotype data
The 15 FOXO3ASNPs investigated in the Discovery sample are located in position 108982719–109113664 of chromosome 6, which corresponds to FOXO3Aand 5000 base pairs (bp) upstream and 1000 bp downstream (NCBI assemble 36). Details on how these FOXO3ASNPs were chosen and the generation of Illumina GoldenGate (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) genotype data were previously described (Soerensen et al., 2010, 2012). The LD plot in Fig.1 is based on the genotype data of the Discovery sample, and the plot was generated in the Haploview software (http://www.broadinstitute.org/scientific-community/science/programs/medical-and-population-genetics/haploview/haploview, (Barrett et al., 2005)).
To perform a replication study of the initial findings, the LD pattern of the 10 SNPs, which showed significance in the Discovery sample, was investigated in the SNAP Proxy database (http://www.broadinstitute.org/mpg/snap/ldsearch.php). The r2 > 0.8 criterion was used with data from the 1000 Genomes project (Abecasis et al., 2010). Consequently, five SNPs, rs12206094, rs2802292, rs3800231, rs479744 and rs7762395, were selected, which in general cover the same genetic variation as the 10 SNPs found to be significant in the Discovery sample. The DNA of the Replication sample was purified from blood spot cards using the Extract-N-AmpTM Blood PCR Kit (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and genotyping was performed by standard TaqMan procedures, using predesigned TaqMan® SNP Genotyping Assays (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).
Phenotype data
The phenotype data for all surveys were collected as part of a comprehensive home-based interview focusing on health and disease issues. Cognitive function was assessed by a cognitive composite score, which investigates verbal fluency, forward and backward digit span, and immediate and delayed recall (McGue & Christensen, 2002). Handgrip strength was determined using a handheld dynamometer (SMEDLEY'S dynamometer, Scandidact, Kvistgaard, Denmark); the maximum of three measurements with the strongest hand was used. Self-rated health was assessed by the question ‘How do you consider your health in general?’ with five response categories: very poor, poor, acceptable, good, and excellent. ADL was inspected by a five-item ADL disability score (based on the Katz ADL index (Katz et al., 1970)) about bathing, dressing, toileting, transfer and feeding; the score was categorized into ‘disabled = could do maximum two items’, ‘moderately disabled = could do three or four items, ‘ or ‘not disabled = could do all five items. ‘ Self-reported status on cancer, osteoporosis, and diabetes was evaluated by asking: ‘Did a doctor ever tell you that you have/had any of the following diseases? ‘ with the response categories ‘has now or has had‘ and ‘no. ‘ Self-reported CVD was obtained in the same way, yet with six diseases combined in one group; stroke, heart attack, angina pectoris, irregular heart rhythm, other heart problems, and treatment for hypertension with prescription medicine/drop. Self-reported fracture of the femur, spine, hip, and/or wrist was investigated, as these types of fractures are considered typical osteoporotic frailty fractures and likely indicate low bone density (Nguyen et al., 2001; Bathum et al., 2004; Broderick et al., 2013). Status on bone fracture was evaluated by asking ‘Did you fracture a bone after the age of 40? ‘, and if the answer was ‘yes‘ subsequently asking: ‘Where did you have the fracture? ‘ with five response categories ‘femur, ‘spine (also collapse), ‘hip, ‘wrist, ‘ and ‘other places. ‘ The individuals, whom reported at least 1 fracture of the femur, spine, hip, and/or wrist after age 40, were compared to the rest of the study population.
The phenotype data used for the Replication sample were based on data from the respective surveys, and the questions were identical to the questions in the Danish 1905 Birth Cohort Study.
Statistical analyses
Set(gene)-based analyses of the 15 FOXO3ASNPs and each of the nine phenotypes were performed in Plink (Purcell et al., 2007); applying the most inclusive settings, that is set-max 99999, set-r2 1, and set-p 1. In the set-based test, linear regression was applied for analysis of the cognitive composite score, hand grip strength, ADL, and self-rated health, while logistic regression was used for analysis of status on cancer, diabetes, CVD, osteoporosis, and bone fracture. All set-based analyses were adjusted for age and sex, while the set-based analysis of the cognitive composite score was additionally adjusted for level of education (<7th grade, 7th–8th grade, 9th–10th grade or >11th grade), the set-based analysis of self-reported cancer was additionally adjusted for smoking status (current, former, or never smoker), the set-based analyses of hand grip strength and self-reported diabetes were additionally adjusted for body mass index (bmi), the set-based analysis of self-reported CVD was additionally adjusted for bmi and smoking status, and the set-based analyses of self-reported bone fracture and osteoporosis were additionally adjusted for bmi, smoking status, and hormone use after menopause (hormone therapy or no hormone therapy). In the set-based analysis, the single-SNP P-values are summarized by their overall mean, while considering LD; hence, the analysis estimates the average association of the FOXO3ASNPs with a given phenotype. The significance (p-gene) was determined by repeating this for 10000 permutations of the phenotype, consequently correcting for the test of 15 SNPs.
Analysis of the genotype and phenotype data from the Replication sample was performed by single-SNP analysis using the same single-SNP statistics as described above as part of the set-based test conducted for the Discovery sample. The analysis of bone fracture was restricted to the 691 individuals of the Replication sample for whom data on bmi were available. All replication analyses were done in the STATA 11.0 software (Stata Corporation, College Station, TX, USA).
Power calculations
The set(gene)-based method applied in the present study is a power-full approach as it tests a group of SNPs in a gene and hereby increases power as compared to testing the individual SNPs separately. However, power calculations for set(gene)-based approaches are unfortunately not yet available. To inspect the effect sizes obtainable with good certainty (power>0.8) in the single-SNP analysis in the Discovery sample, we performed power calculations in the Quanto software (version Quanto1_2_4a, http://biostats.usc.edu/cgi-bin/DownloadQuanto.pl) assuming an additive model. For SNPs with a minor allele frequency (MAF) of 0.4, ORs of moderate size (OR < 0.60–0.78) should be obtainable for the binary phenotypes, while for a MAF of 0.1 sizeable ORs (ORs < 0.36–0.66) should be attainable. For the cognitive composite score, hand grip strength, ADL, and self-rated health, rather small beta-coefficients should be obtainable for a MAF of 0.4: >0.43, >0.86, >0.09 and >0.12, respectively (≈0.13 of a standard deviation for all four phenotypes). The same was true for the less frequent variants (MAF 0.1), where the values were >0.70, >1.42, >0.14, and >0.19, respectively (≈0.21of a standard deviation for all four phenotypes).
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr Karen Andersen-Ranberg and Dr Anders Jørgen Svendsen for helpful input and discussion during the conduction of this study.
Funding
The study was financially supported by the Max-Planck Institute for Demographic Research (Rostock, Germany), the European Union's Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2011) under grant agreement no 259679, the INTERREG 4 A programme Syddanmark-Schleswig-K.E.R.N. (by EU funds from the European Regional Development Fund), the National Institute on Aging (P01 AG08761), the Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Aase and Ejnar Danielsen Foundation, the Brødrene Hartmann Foundation, the King Christian the 10th Foundation, and the Einer Willumsens Mindelegat Foundation. The Danish Aging Research Center is supported by a grant from the VELUX Foundation, while Mette Soerensen is supported by an individual postdoctoral grant from The Danish Council for Independent Research – Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author contributions
Mette Soerensen participated in generating the conception of the study and the study design, acquisition of data, conduction of data analysis, interpretation of data, and drafting the manuscript. Marianne Nygaard participated in acquisition of data and interpretation of data. Serena Dato participated in acquisition of data and interpretation of data. Tinna Stevnsner participated in interpretation of data. Vilhelm A. Bohr participated in interpretation of data. Kaare Christensen participated in acquisition of data and interpretation of data. Lene Christiansen participated in generating the conception of the study and the study design, acquisition of data, and interpretation of data. All authors have revised the manuscript and given their final approval.
Supporting Information
Additional Supporting Information may be found in the online version of this article at the publisher's web-site.
Table S1. Characteristics of the Discovery and Replication samples with respect to the phenotypes investigated.
References
- Abecasis GR, Altshuler D, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Gibbs RA, Hurles ME, McVean GA. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature. 2010;467:1061–1073. doi: 10.1038/nature09534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrogini E, Almeida M, Martin-Millan M, Paik JH, Depinho RA, Han L, Goellner J, Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, O'Brien CA, Manolagas SC. FoxO-mediated defense against oxidative stress in osteoblasts is indispensable for skeletal homeostasis in mice. Cell Metab. 2010;11:136–146. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anselmi CV, Malovini A, Roncarati R, Novelli V, Villa F, Condorelli G, Bellazzi R, Puca AA. Association of the FOXO3A locus with extreme longevity in a southern Italian centenarian study. Rejuvenation. Res. 2009;12:95–104. doi: 10.1089/rej.2008.0827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arden KC. FOXO animal models reveal a variety of diverse roles for FOXO transcription factors. Oncogene. 2008;27:2345–2350. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banasik K, Ribel-Madsen R, Gjesing AP, Wegner L, Andersson A, Poulsen P, Borglykke A, Witte DR, Pedersen O, Hansen T, Vaag A. The FOXO3A rs2802292 G-allele associates with improved peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity and increased skeletal muscle-FOXO3A mRNA expression in twins. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011;96:E119–E124. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bao JM, Song XL, Hong YQ, Zhu HL, Li C, Zhang T, Chen W, Zhao SC, Chen Q. Association between FOXO3A gene polymorphisms and human longevity: a meta-analysis. Asian J Androl. 2014;16(5):769. doi: 10.4103/1008-682X.123673. Sep-Oct; [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:263–265. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bathum L, Hjelmborg J, Christiansen L, Madsen JS, Skytthe A, Christensen K. Evidence for an association of methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphism C677T and an increased risk of fractures: results from a population-based Danish twin study. Osteoporos. Int. 2004;15:659–664. doi: 10.1007/s00198-003-1584-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broderick JM, Bruce-Brand R, Stanley E, Mulhall KJ. Osteoporotic hip fractures: the burden of fixation failure. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013;2013:515197. doi: 10.1155/2013/515197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broer L, Buchman AS, Deelen J, Evans DS, Faul JD, Lunetta KL, Sebastiani P, Smith JA, Smith AV, Tanaka T, Yu L, Arnold AM, Aspelund T, Benjamin EJ, De Jager PL, Eirkisdottir G, Evans DA, Garcia ME, Hofman A, Kaplan RC, Kardia SL, Kiel DP, Oostra BA, Orwoll ES, Parimi N, Psaty BM, Rivadeneira F, Rotter JI, Seshadri S, Singleton A, Tiemeier H, Uitterlinden AG, Zhao W, Bandinelli S, Bennett DA, Ferrucci L, Gudnason V, Harris TB, Karasik D, Launer LJ, Perls TT, Slagboom PE, Tranah GJ, Weir DR, Newman AB, van DC, Murabito JM. GWAS of Longevity in CHARGE Consortium Confirms APOE and FOXO3 Candidacy. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014 doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu166. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castrillon DH, Miao L, Kollipara R, Horner JW, Depinho RA. Suppression of ovarian follicle activation in mice by the transcription factor Foxo3a. Science. 2003;301:215–218. doi: 10.1126/science.1086336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen K, Johnson TE, Vaupel JW. The quest for genetic determinants of human longevity: challenges and insights. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:436–448. doi: 10.1038/nrg1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen K, Thinggaard M, Oksuzyan A, Steenstrup T, Andersen-Ranberg K, Jeune B, McGue M, Vaupel JW. Physical and cognitive functioning of people older than 90 years: a comparison of two Danish cohorts born 10 years apart. Lancet. 2013;382:1507–1513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60777-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Bona D, Accardi G, Virruso C, Candore G, Caruso C. Association between genetic variations in the insulin/insulin-like growth factor (Igf-1) signaling pathway and longevity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014;12(5):674–681. doi: 10.2174/1570161111666131218152807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiken PA, Abrahamsen B. Assessment and treatment of osteoporotic hip fractures (paper in Danish) Ugeskr. Laeger. 2010;172:700–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flachsbart F, Caliebe A, Kleindorp R, Blanche H, von Eller-Eberstein H, Nikolaus S, Schreiber S, Nebel A. Association of FOXO3A variation with human longevity confirmed in German centenarians. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:2700–2705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809594106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederiksen H, Gaist D, Petersen HC, Hjelmborg J, McGue M, Vaupel JW, Christensen K. Hand grip strength: a phenotype suitable for identifying genetic variants affecting mid- and late-life physical functioning. Genet. Epidemiol. 2002;23:110–122. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannakou ME, Goss M, Junger MA, Hafen E, Leevers SJ, Partridge L. Long-lived Drosophila with overexpressed dFOXO in adult fat body. Science. 2004;305:361. doi: 10.1126/science.1098219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeusler RA, Kaestner KH, Accili D. FoxOs function synergistically to promote glucose production. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:35245–35248. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C110.175851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinman RM, Nichols WA, Diaz TM, Gallardo TD, Castrillon DH, Satterthwaite AB. Foxo3-/- mice demonstrate reduced numbers of pre-B and recirculating B cells but normal splenic B cell sub-population distribution. Int. Immunol. 2009;21:831–842. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmborg JV, Iachine I, Skytthe A, Vaupel JW, McGue M, Koskenvuo M, Kaprio J, Pedersen NL, Christensen K. Genetic influence on human lifespan and longevity. Hum. Genet. 2006;119:312–321. doi: 10.1007/s00439-006-0144-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H, Tindall DJ. Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J. Cell Sci. 2007;120:2479–2487. doi: 10.1242/jcs.001222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen R, Martinussen T, Christiansen L, Jeune B, Andersen-Ranberg K, Vaupel JW, Christensen K. Increased effect of the ApoE gene on survival at advanced age in healthy and long-lived Danes: two nationwide cohort studies. Aging Cell. 2010;9:1004–1009. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junger MA, Rintelen F, Stocker H, Wasserman JD, Vegh M, Radimerski T, Greenberg ME, Hafen E. The Drosophila forkhead transcription factor FOXO mediates the reduction in cell number associated with reduced insulin signaling. J. Biol. 2003;2:20. doi: 10.1186/1475-4924-2-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S, Downs TD, Cash HR, Grotz RC. Progress in development of the index of ADL. Gerontologist. 1970;10:20–30. doi: 10.1093/geront/10.1_part_1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuningas M, Mägi R, Westendorp RG, Slagboom PE, Remm M, van Heemst D. Haplotypes in the human Foxo1a and Foxo3a genes; impact on disease and mortality at old age. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2007;15:294–301. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Wang WJ, Cao H, Lu J, Wu C, Hu FY, Guo J, Zhao L, Yang F, Zhang YX, Li W, Zheng GY, Cui H, Chen X, Zhu Z, He H, Dong B, Mo X, Zeng Y, Tian XL. Genetic association of FOXO1A and FOXO3A with longevity trait in Han Chinese populations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009;18:4897–4904. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L, Hron JD, Peng SL. Regulation of NF-kappaB, Th activation, and autoinflammation by the forkhead transcription factor Foxo3a. Immunity. 2004;21:203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.06.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGue M, Christensen K. The heritability of level and rate-of-change in cognitive functioning in Danish twins aged 70 years and older. Exp. Aging Res. 2002;28:435–451. doi: 10.1080/03610730290080416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K, Araki KY, Naka K, Arai F, Takubo K, Yamazaki S, Matsuoka S, Miyamoto T, Ito K, Ohmura M, Chen C, Hosokawa K, Nakauchi H, Nakayama K, Nakayama KI, Harada M, Motoyama N, Suda T, Hirao A. Foxo3a is essential for maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:101–112. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen TV, Center JR, Sambrook PN, Eisman JA. Risk factors for proximal humerus, forearm, and wrist fractures in elderly men and women: the Dubbo Osteoporosis Epidemiology Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001;153:587–595. doi: 10.1093/aje/153.6.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nybo H, Gaist D, Jeune B, Bathum L, McGue M, Vaupel JW, Christensen K. The Danish 1905 cohort: a genetic-epidemiological nationwide survey. J. Aging Health. 2001;13:32–46. doi: 10.1177/089826430101300102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nybo H, Petersen HC, Gaist D, Jeune B, Andersen K, McGue M, Vaupel JW, Christensen K. Predictors of mortality in 2,249 nonagenarians-the Danish 1905-Cohort Survey. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2003;51:1365–1373. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen J, Christensen K, Murray J, Ekbom A. An Introduction to Epidemiology for Health Professionals. Springer Series on Epidemiology and Public Health. Vol. 1. New York: Springer; 2010. , Volume. [Google Scholar]
- Paik JH, Kollipara R, Chu G, Ji H, Xiao Y, Ding Z, Miao L, Tothova Z, Horner JW, Carrasco DR, Jiang S, Gilliland DG, Chin L, Wong WH, Castrillon DH, Depinho RA. FoxOs are lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell. 2007;128:309–323. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlikowska L, Hu D, Huntsman S, Sung A, Chu C, Chen J, Joyner AH, Schork NJ, Hsueh WC, Reiner AP, Psaty BM, Atzmon G, Barzilai N, Cummings SR, Browner WS, Kwok PY, Ziv E. Association of common genetic variation in the insulin/IGF1 signaling pathway with human longevity. Aging Cell. 2009;8:460–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng K, Li Y, Long L, Li D, Jia Q, Wang Y, Shen Q, Tang Y, Wen L, Kung HF, Peng Y. Knockdown of FoxO3a induces increased neuronal apoptosis during embryonic development in zebrafish. Neurosci. Lett. 2010;484:98–103. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.07.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pino E, Amamoto R, Zheng L, Cacquevel M, Sarria JC, Knott GW, Schneider BL. FOXO3 determines the accumulation of alpha-synuclein and controls the fate of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014;23:1435–1452. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MAR, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PIW, Daly MJ, Sham PC. PLINK: a toolset for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007;81:559–575. doi: 10.1086/519795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schips TG, Wietelmann A, Hohn K, Schimanski S, Walther P, Braun T, Wirth T, Maier HJ. FoxO3 induces reversible cardiac atrophy and autophagy in a transgenic mouse model. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011;91:587–597. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soerensen M, Dato S, Christensen K, McGue M, Stevnsner T, Bohr VA, Christiansen L. Replication of an association of variation in the FOXO3A gene with human longevity using both case-control and longitudinal data. Aging Cell. 2010;9:1010–1017. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soerensen M, Dato S, Tan Q, Thinggaard M, Kleindorp R, Beekman M, Jacobsen R, Suchiman HE, de Craen AJ, Westendorp RG, Schreiber S, Stevnsner T, Bohr VA, Slagboom PE, Nebel A, Vaupel JW, Christensen K, McGue M, Christiansen L. Human longevity and variation in GH/IGF-1/insulin signaling, DNA damage signaling and repair and pro/antioxidant pathway genes: cross sectional and longitudinal studies. Exp. Gerontol. 2012;47:379–387. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2012.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warr MR, Binnewies M, Flach J, Reynaud D, Garg T, Malhotra R, Debnath J, Passegue E. FOXO3A directs a protective autophagy program in haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2013;494:323–327. doi: 10.1038/nature11895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willcox BJ, Donlon TA, He Q, Chen R, Grove JS, Yano K, Masaki KH, Wilcox DC, Rodriguez B, Curb JD. FOXO3A genotype is strongly associated with human longevity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:13987–13992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801030105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng Y, Cheng L, Chen H, Cao H, Hauser ER, Liu Y, Xiao Z, Tan Q, Tian XL, Vaupel JW. Effects of FOXO genotypes on longevity: a biodemographic analysis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2010;65:1285–1299. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glq156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. Characteristics of the Discovery and Replication samples with respect to the phenotypes investigated.


