Abstract
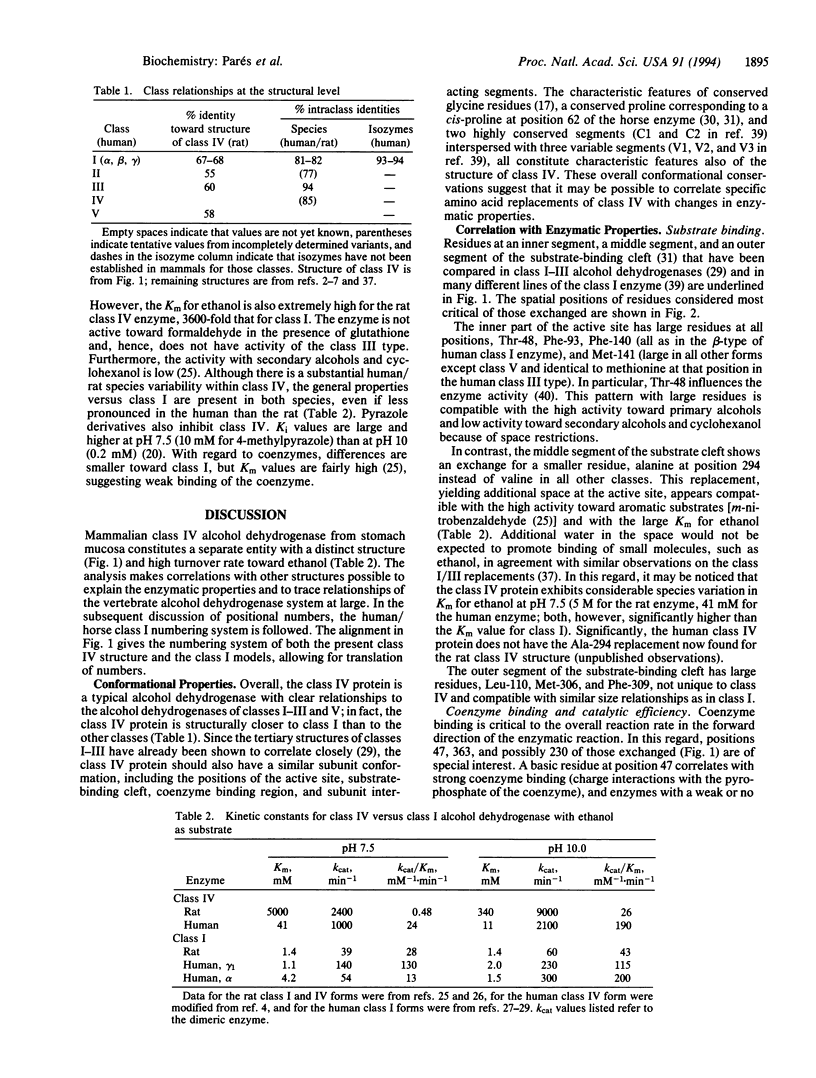
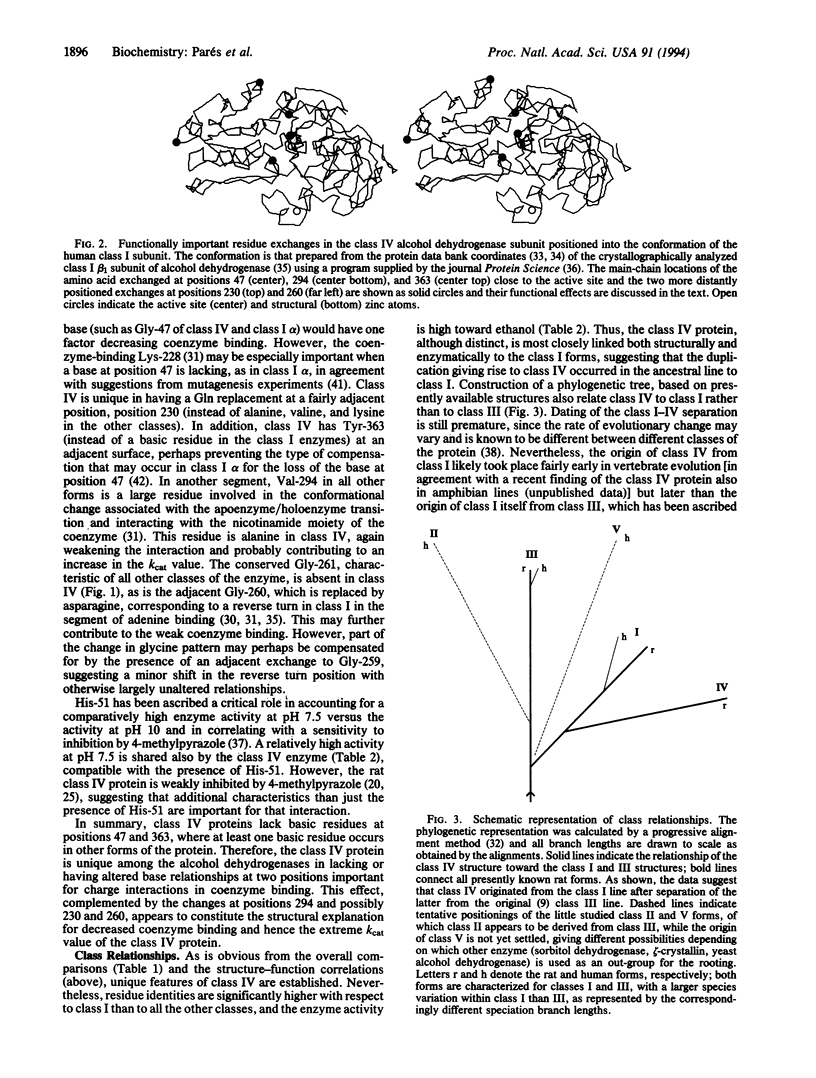
The structure of a mammalian class IV alcohol dehydrogenase has been determined by peptide analysis of the protein isolated from rat stomach. The structure indicates that the enzyme constitutes a separate alcohol dehydrogenase class, in agreement with the distinct enzymatic properties; the class IV enzyme is somewhat closer to class I (the "classical" liver alcohol dehydrogenase; approximately 68% residue identities) than to the other classes (II, III, and V; approximately 60% residue identities), suggesting that class IV might have originated through duplication of an early vertebrate class I gene. The activity of the class IV protein toward ethanol is even higher than that of the classical liver enzyme. Both Km and kcat values are high, the latter being the highest of any class characterized so far. Structurally, these properties are correlated with replacements at the active site, affecting both substrate and coenzyme binding. In particular, Ala-294 (instead of valine) results in increased space in the middle section of the substrate cleft, Gly-47 (instead of a basic residue) results in decreased charge interactions with the coenzyme pyrophosphate, and Tyr-363 (instead of a basic residue) may also affect coenzyme binding. In combination, these exchanges are compatible with a promotion of the off dissociation and an increased turnover rate. In contrast, residues at the inner part of the substrate cleft are bulky, accounting for low activity toward secondary alcohols and cyclohexanol. Exchanges at positions 259-261 involve minor shifts in glycine residues at a reverse turn in the coenzyme-binding fold. Clearly, class IV is distinct in structure, ethanol turnover, stomach expression, and possible emergence from class I.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boleda M. D., Julià P., Moreno A., Parés X. Role of extrahepatic alcohol dehydrogenase in rat ethanol metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Oct;274(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90416-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boleda M. D., Saubi N., Farrés J., Parés X. Physiological substrates for rat alcohol dehydrogenase classes: aldehydes of lipid peroxidation, omega-hydroxyfatty acids, and retinoids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Nov 15;307(1):85–90. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrás T., Persson B., Jörnvall H. Eye lens zeta-crystallin relationships to the family of "long-chain" alcohol/polyol dehydrogenases. Protein trimming and conservation of stable parts. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6133–6139. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosron W. F., Magnes L. J., Li T. K. Kinetic and electrophoretic properties of native and recombined isoenzymes of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1852–1857. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett K. G., Felder M. R. Genetic regulation of liver alcohol dehydrogenase in Peromyscus. Biochem Genet. 1978 Jun;16(5-6):443–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00484210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cederlund E., Peralba J. M., Parés X., Jörnvall H. Amphibian alcohol dehydrogenase, the major frog liver enzyme. Relationships to other forms and assessment of an early gene duplication separating vertebrate class I and class III alcohol dehydrogenases. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 19;30(11):2811–2816. doi: 10.1021/bi00225a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. S., Yoshida A. Enzymatic properties of the protein encoded by newly cloned human alcohol dehydrogenase ADH6 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):743–747. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91253-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson O., Jörnvall H. "Enzymogenesis": classical liver alcohol dehydrogenase origin from the glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9247–9251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Müller-Wille P., Horjales E., Futer O., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L., Hög J. O., Kaiser R., Jörnvall H. Comparison of three classes of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Emphasis on different substrate binding pockets. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Oct 24;193(2):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Nordström B., Zeppezauer E., Söderlund G., Ohlsson I., Boiwe T., Söderberg B. O., Tapia O., Brändén C. I., Akeson A. Three-dimensional structure of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2-4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):27–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Samama J. P., Jones T. A. Crystallographic investigations of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide binding to horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):5982–5996. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström G., Cronholm T., Norsten-Hög C., Ingelman-Sundberg M. Dehydrogenase-dependent metabolism of alcohols in gastric mucosa of deer mice lacking hepatic alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993 May 25;45(10):1989–1994. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(93)90008-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng D. F., Doolittle R. F. Progressive alignment and phylogenetic tree construction of protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:375–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frezza M., di Padova C., Pozzato G., Terpin M., Baraona E., Lieber C. S. High blood alcohol levels in women. The role of decreased gastric alcohol dehydrogenase activity and first-pass metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 11;322(2):95–99. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001113220205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmqvist L., Ericsson M., Shafqat J., Carlquist M., Siddiqi A. R., Hög J. O., Jörnvall H. Reptilian alcohol dehydrogenase. Heterogeneity relevant to class multiplicity of the mammalian enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 24;298(2-3):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80080-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley T. D., Bosron W. F., Hamilton J. A., Amzel L. M. Structure of human beta 1 beta 1 alcohol dehydrogenase: catalytic effects of non-active-site substitutions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8149–8153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög J. O., Eklund H., Jörnvall H. A single-residue exchange gives human recombinant beta beta alcohol dehydrogenase gamma gamma isozyme properties. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 15;205(2):519–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Sunagawa M., Mori A., Imai C., Fukuda M., Takagi M., Yano K. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the 72-kilodalton dehydrogenase subunit of alcohol dehydrogenase from Acetobacter aceti. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3115–3122. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3115-3122.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito D., Lieber C. S. Ethanol metabolism in deermice: role of extrahepatic alcohol dehydrogenase. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1993 Aug;17(4):919–925. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1993.tb00864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julià P., Farrés J., Parés X. Characterization of three isoenzymes of rat alcohol dehydrogenase. Tissue distribution and physical and enzymatic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 2;162(1):179–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julià P., Pareś X., Jörnvall H. Rat liver alcohol dehydrogenase of class III. Primary structure, functional consequences and relationships to other alcohol dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 15;172(1):73–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Hög J. O., von Bahr-Lindström H., Vallee B. L. Mammalian alcohol dehydrogenases of separate classes: intermediates between different enzymes and intraclass isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2580–2584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Persson B., Jörnvall H. Variability patterns of dehydrogenases versus peptide hormones and proteases/antiproteases. FEBS Lett. 1993 Nov 29;335(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80441-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Persson M., Jeffery J. Alcohol and polyol dehydrogenases are both divided into two protein types, and structural properties cross-relate the different enzyme activities within each type. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4226–4230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivusalo M., Baumann M., Uotila L. Evidence for the identity of glutathione-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase and class III alcohol dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1989 Oct 23;257(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81797-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. R., Dennis M. S., Forsythe I. J., Liu C. C., Green D. W., Kratzer D. A., Plapp B. V. Alpha-isoenzyme of alcohol dehydrogenase from monkey liver. Cloning, expression, mechanism, coenzyme, and substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12592–12599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno A., Parés X. Purification and characterization of a new alcohol dehydrogenase from human stomach. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1128–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parés X., Cederlund E., Moreno A., Saubi N., Hög J. O., Jörnvall H. Class IV alcohol dehydrogenase (the gastric enzyme). Structural analysis of human sigma sigma-ADH reveals class IV to be variable and confirms the presence of a fifth mammalian alcohol dehydrogenase class. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 25;303(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80479-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parés X., Moreno A., Cederlund E., Hög J. O., Jörnvall J. Class IV mammalian alcohol dehydrogenase. Structural data of the rat stomach enzyme reveal a new class well separated from those already characterized. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80822-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B., Bergman T., Keung W. M., Waldenström U., Holmquist B., Vallee B. L., Jörnvall H. Basic features of class-I alcohol dehydrogenase: variable and constant segments coordinated by inter-class and intra-class variability. Conclusions from characterization of the alligator enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 15;216(1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson D. C., Richardson J. S. The kinemage: a tool for scientific communication. Protein Sci. 1992 Jan;1(1):3–9. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scopes R. K. An iron-activated alcohol dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 13;156(2):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80517-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone C. L., Hurley T. D., Amzel L. M., Dunn M. F., Bosron W. F. Kinetics of a glycine for Arg-47 human alcohol dehydrogenase mutant can be explained by Lys-228 recruitment into the pyrophosphate binding site. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;328:429–437. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2904-0_45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone C. L., Thomasson H. R., Bosron W. F., Li T. K. Purification and partial amino acid sequence of a high-activity human stomach alcohol dehydrogenase. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1993 Aug;17(4):911–918. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1993.tb00863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L., Bazzone T. J. Isozymes of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1983;8:219–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner F. W., Burger A. R., Vallee B. L. Kinetic properties of human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: oxidation of alcohols by class I isoenzymes. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1857–1863. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Paquin C. E. Homology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ADH4 to an iron-activated alcohol dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):374–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00329668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasunami M., Chen C. S., Yoshida A. A human alcohol dehydrogenase gene (ADH6) encoding an additional class of isozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7610–7614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin S. J., Vagelopoulos N., Wang S. L., Jörnvall H. Structural features of stomach aldehyde dehydrogenase distinguish dimeric aldehyde dehydrogenase as a 'variable' enzyme. 'Variable' and 'constant' enzymes within the alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase families. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 20;283(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80559-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ophem P. W., Van Beeumen J., Duine J. A. NAD-linked, factor-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase or trimeric, zinc-containing, long-chain alcohol dehydrogenase from Amycolatopsis methanolica. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



