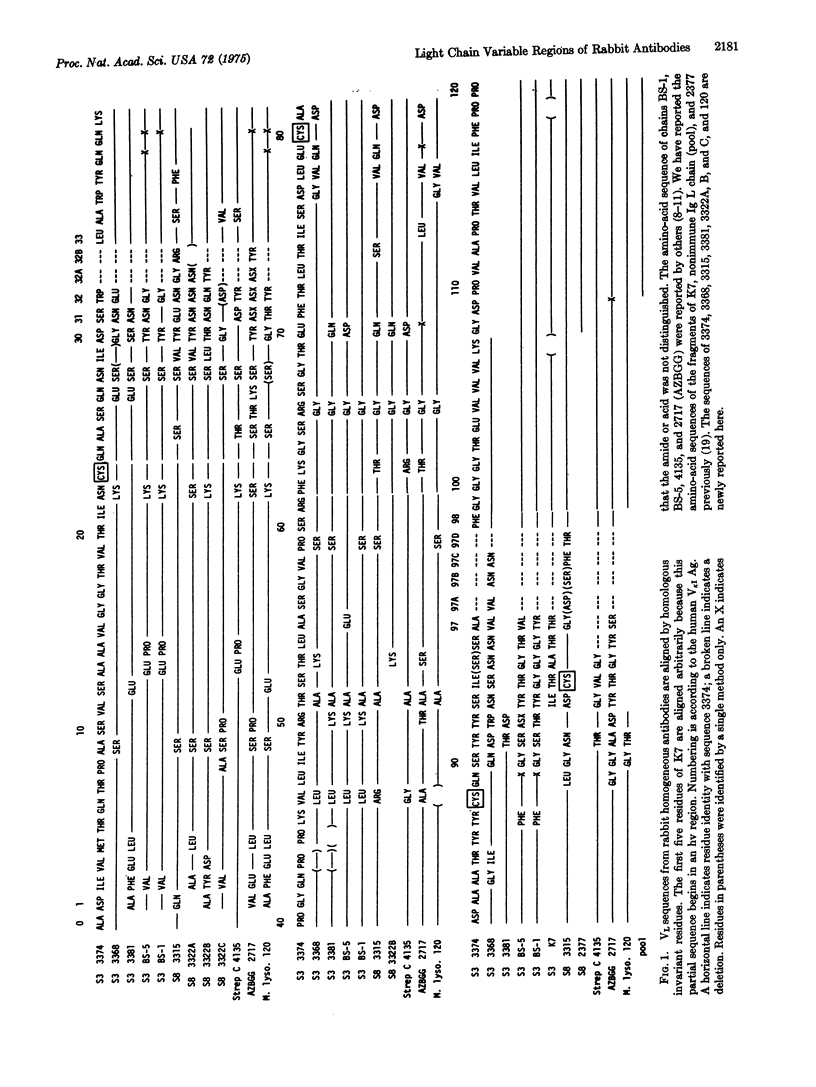
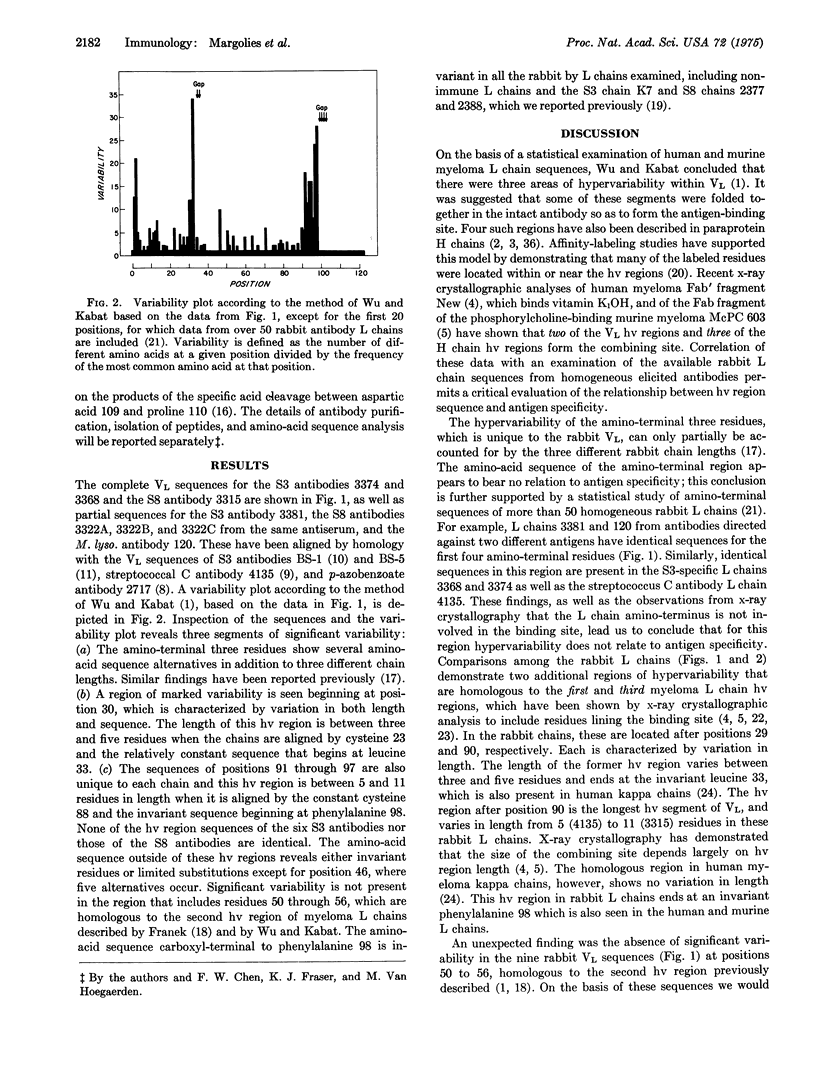
Abstract
We report the complete variable region sequences of three homogeneous rabbit antibody light chains and the partial sequences of five others. Wehn these are compared to other published rabbit light chain sequences, two regions of markedly increased variability are revealed, which are homologous in position to the first and third hypervariable regions of murine and human myeloma light chains. In addition, there is increased variability among the first three residues at the aminoterminal end. A hypervariable region homologous to that identified at positions 50 to 56 in myeloma light chains is not present in these rabbit antibody light chains. The available three-dimensional models of Fab fragments based on x-ray crystallography indicate that neither the amino-terminal portion of the light chain nor the region homologous to positions 50 to 56 forms a part of the combining site. Comparison of the hypervariable regions among six light chains from antibodies to Type III pneumococcal polysaccharide and among four from antibodies to Type VIII pneumococcal polysaccharide suggests that a large number of different sequences may be found in antibodies specific for these relatively simple antigens. Certain residues outside of the hypervariable regions are invariant in the rabbit light chains and correspond to residues that are required for proper chain folding in human and murine myeloma light chains, indicating that the general conformation of myeloma light chains is the same as that of light chains of elicited antibodies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Roholt O. A., Chersi A., Radzimski G., Pressman D. Amino acid sequence of the light chain derived from a rabbit anti-p-azobenzoate antibody of restricted heterogeneity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 21;53(4):1122–1129. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90581-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baczko K., Braun D. G., Hess M., Hilschmann N. Die Primärstruktur einer monoklonalen Immunglobulin L-Kette der Subgruppe IV vom lambda-Typ (Bence-Jones-Protein Bau): Untergruppen innerhalb der Subgruppen. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1970 Jun;351(6):763–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstad P., Farnsworth V., Weigert M., Cohn M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin heavy chains are coded by multiple germ line variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4096–4100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstad P., Rudikoff S., Potter M., Cohn M., Konigsberg W., Hood L. Immunoglobulin structure: amino terminal sequences of mouse myeloma proteins that bind phosphorylcholine. Science. 1974 Mar 8;183(4128):962–966. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4128.962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald B. M. An immunoglobulin light chain of subgroup III-1 of lambda type with a free sulfhydryl group. Can J Biochem. 1971 Aug;49(8):900–902. doi: 10.1139/o71-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Structure of antibodies with shared idiotypy: the complete sequence of the heavy chain variable regions of two immunoglobulin M anti-gamma globulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4032–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Kehoe J. M. Variable region sequences of five human immunoglobulin heavy chains of the VH3 subgroup: definitive identification of four heavy chain hypervariable regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):845–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebra J. J., Koo P. H., Ray A. Specificity of antibodies: primary structural basis of hapten binding. Science. 1974 Oct 18;186(4160):263–265. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4160.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F. W., Strosberg A. D., Haber E. Evolution of the immune response to type 3 and 8 pneumococcal polysaccharides. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):98–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. C., Kindt T. J., Krause R. M. Amino-acid sequence of an allotype b4 light chain from a rabbit antibody to streptococcal carbohydrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):1995–1998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng W. C., Fraser K. J., Haber E. Fractionation of antibodies to the pneumococcal polysaccharides by affinity chromatography. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1677–1689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epp O., Colman P., Fehlhammer H., Bode W., Schiffer M., Huber R., Palm W. Crystal and molecular structure of a dimer composed of the variable portions of the Bence-Jones protein REI. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):513–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser K. J., Pulsen K., Haber E. Specific cleavage between variable and constant domains of rabbit antibody light chains by dilute acid hydrolysis. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4974–4977. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gally J. A., Edelman G. M. The genetic control of immunoglobulin synthesis. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:1–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber E. Antibodies of restricted heterogeneity for structural study. Fed Proc. 1970 Jan-Feb;29(1):66–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holowka D. A., Strosberg A. D., Kimball J. W., Haber E., Cathou R. E. Changes in intrinsic circular dichroism of several homogeneous anti-type 3 pneumococcal antibodies on binding of a small hapten. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3399–3403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C. Amino acid sequence of the N-terminal 139 residues of light chain derived from a homogeneous rabbit antibody. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj1410001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the variable regions of light chains derived from two homogeneous rabbit anti-pneumococcal antibodies. Biochem J. 1974 Jul;141(1):15–25. doi: 10.1042/bj1410015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat E. A., Wu T. T. Attempts to locate complementarity-determining residues in the variable positions of light and heavy chains. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Dec 31;190:382–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe J. M., Capra J. D. Localization of two additional hypervariable regions in immunoglobulin heavy chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2019–2021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause R. M. Experimental approaches to homogenous antibody populations. Factors controlling the occurrence of antibodies with uniform properties. Fed Proc. 1970 Jan-Feb;29(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Clegg J. B., Jarvis J. M. Immunoglobulin lambda-chains. The complete amino acid sequence of a Bence-Jones protein. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):631–652. doi: 10.1042/bj1100631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J., Amzel L. M., Chen B. L., Phizackerley R. P., Saul F. The three-dimensional structure of the fab' fragment of a human myeloma immunoglobulin at 2.0-angstrom resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3440–3444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Girling R. L., Ely K. R., Edmundson A. B. Structure of a lambda-type Bence-Jones protein at 3.5-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4620–4631. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T., Sledge C., Capra J. D., Woods R., Clem W., Hood L. A sequence restriction in the variable region of immunoglobulin light chains from sharks, birds, and mammals. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):633–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strosberg A. D., Fraser K. J., Margolies M. N., Haber E. Amino acid sequence of rabbit pneumococcal antibody. I. Light-chain cysteine-containing peptides. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4978–4985. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. R., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Thin-layer chromatography of sub-nanomole amounts of phenylthiohydantoin (PTH) amino acids on polyamide sheets. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):624–628. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hoegaerden M., Janssens R., Kanarek L. Homogeneous anti-Micrococcus lysodeicticus rabbit antibodies. Arch Int Physiol Biochim. 1973 Feb;81(1):210–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


