Abstract
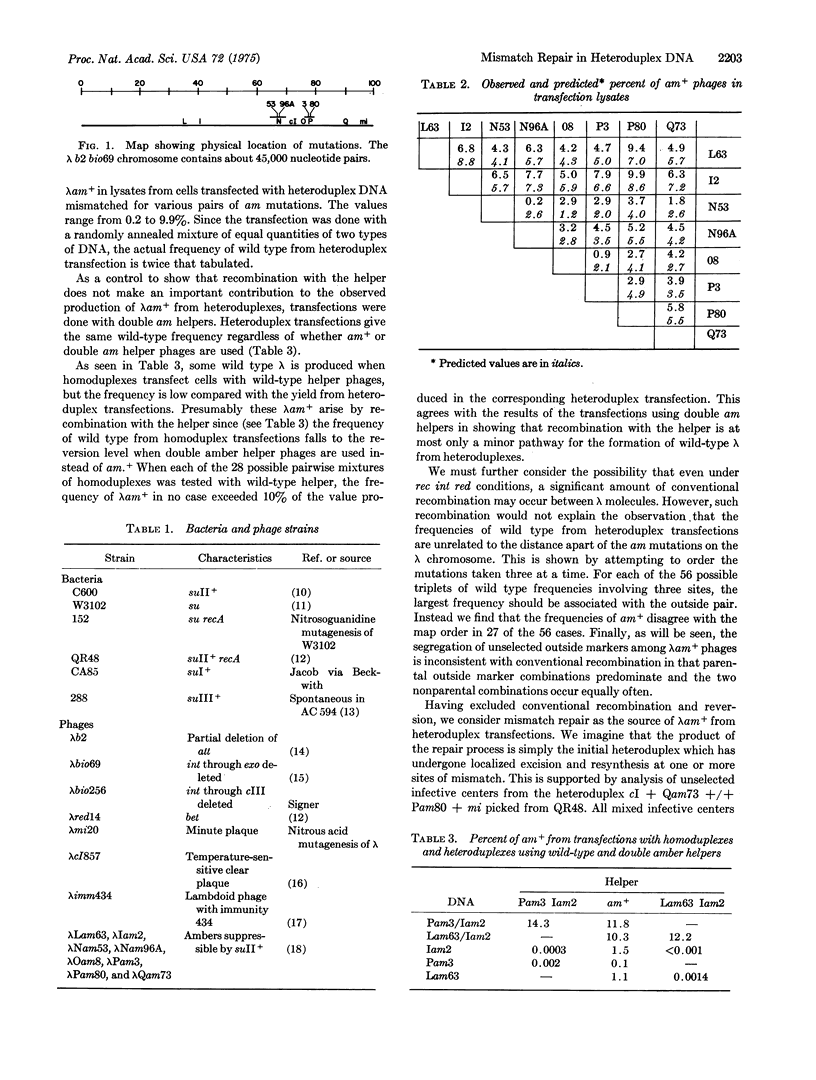
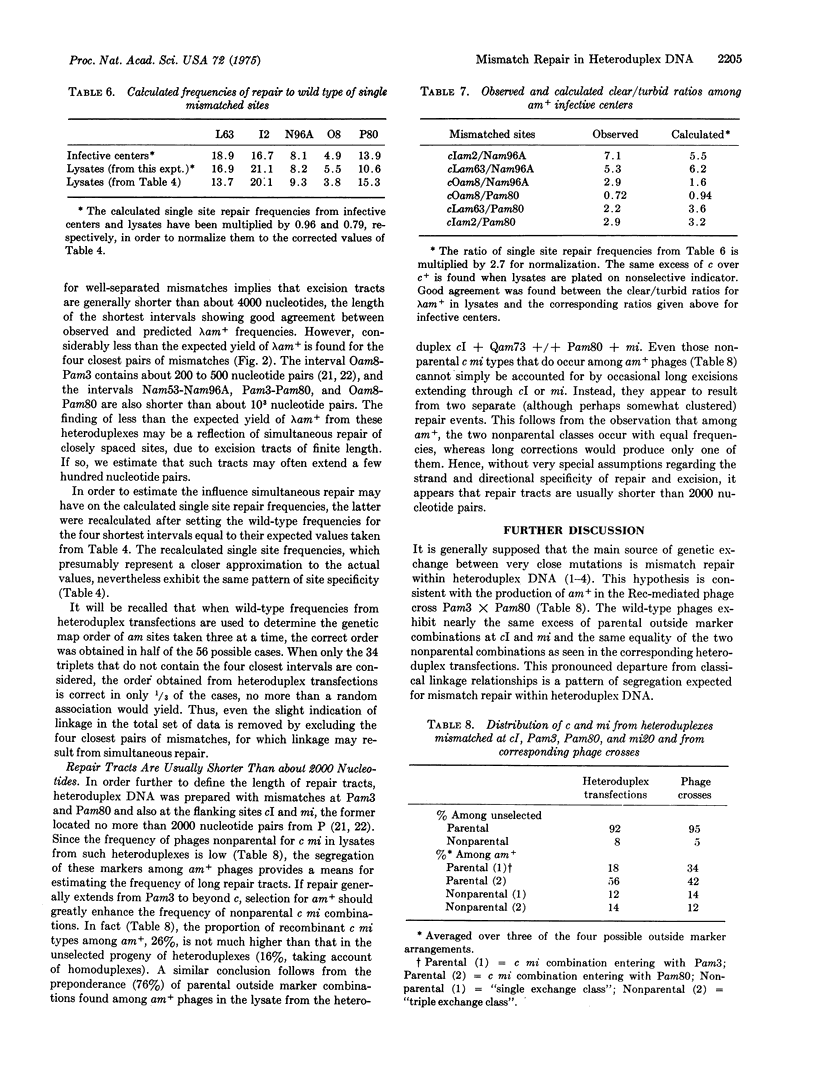
DNA with base pair mismatches was prepared by annealing mixtures of genetically marked DNA from bacteriophage lambda. This heteroduplex DNA was used to transfect bacteria under conditions minimizing recombination. Genetic analysis of the progeny phages indicates that: (i) Mismatch repair occurs, usually giving rise to a DNA molecule with one chain with the genotype arising from repair and one parental chain. (ii) The frequency of repair of a given mismatch to wild type depends on the marker, ranging from 3 to 20%. (iii) Excision tracts may extend several hundred nucleotides but are usually shorter than about 2000 nucleotides. (iv) In Rec-mediated bacteriophage crosses, recombination of markers closer than about 10-3 nucleotide pairs frequently occurs by mismatch repair within heteroduplex DNA. (V) The average amount of heteroduplex DNA formed in a Rec-mediated recombination event is a few thousand nucleotide pairs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amati P, Meselson M. Localized Negative Interference in Bacteriophage. Genetics. 1965 Mar;51(3):369–379. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.3.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas P. D., Jansz H. S. Asymmetric information transfer during phi X174 DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 14;63(3):557–568. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL A. Sensitive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1961 May;14:22–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL A. The different kinds of transducing particles in the lambda-gal system. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1958;23:83–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1958.023.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W., Hogness D. S. Gene orientation in bacteriophage lambda as determined from the genetic activities of heteroduplex DNA formed in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):661–678. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. The evolutionary advantage of recombination. Genetics. 1974 Oct;78(2):737–756. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.2.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. Molecular aspects of genetic exchange and gene conversion. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):273–287. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. D. Molecular basis for genetic recombination. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):247–257. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D., HOGNESS D. S. The transformation of Escherichia coli with deoxyribonucleic acid isolated from bacteriophage lambda-dg. J Mol Biol. 1960 Dec;2:392–415. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(60)80050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D., JACOB F. Recombination between related temperate bacteriophages and the genetic control of immunity and prophage localization. Virology. 1957 Dec;4(3):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manly K. F., Signer E. R., Radding C. M. Nonessential functions of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1969 Feb;37(2):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger M. Evidence for conversion of heteroduplex transforming DNAs to homoduplexes by recipient pneumococcal cells (DNA strand resolution-DNA repair-bacterial transformation-genetic recombination). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo V. E. On the physical structure of lambda recombinant DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 May 28;122(4):353–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00269436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN R., JACOB F. [On a thermosensitive repression system in the Escherichia coli lambda bacteriophage]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1962 Feb 19;254:1517–1519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E. R., Weil J. Recombination in bacteriophage lambda. I. Mutants deficient in general recombination. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz H. C., Trautner T. A. One way to do experiments on gene conversion? Transfection with heteroduplex SPP1 DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;109(1):84–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00334048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. L., Fox M. S. On the molecular basis of high negative interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1544–1548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse H. L. Symposium No. 5: Genetic exchange. Introduction by the Chairman. Advances in recombination research. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):237–245. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


