Abstract
A definitive assay for microbiological and biochemical research on the biodegradation of lignin was developed using radioactive synthetic lignins specifically labeled in the side chains, aromatic rings or in the methoxyl groups. The [14C]lignins were prepared by oxidative polymerization with peroxidase and H2O2 Of specifically labeled coniferyl alcohol (4-hydroxy-3-methyoxycinnamyl alcohol). The synthetic polymers were shown by spectroscopic and chemical methods to contain the same intermonomer linkages found in natural lignins. Incubation of the [14C]lignins with known lignin-degrading fungi and with a forest soil resulted in 14CO2 evolution.
Full text
PDF

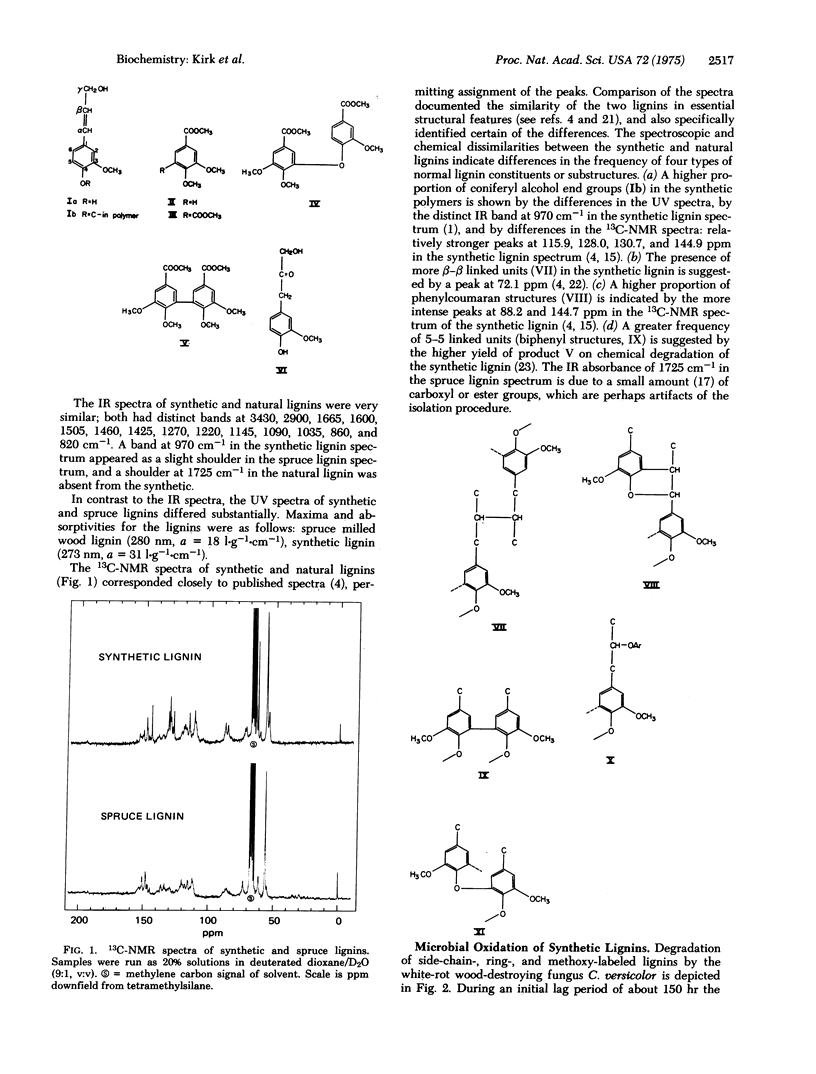
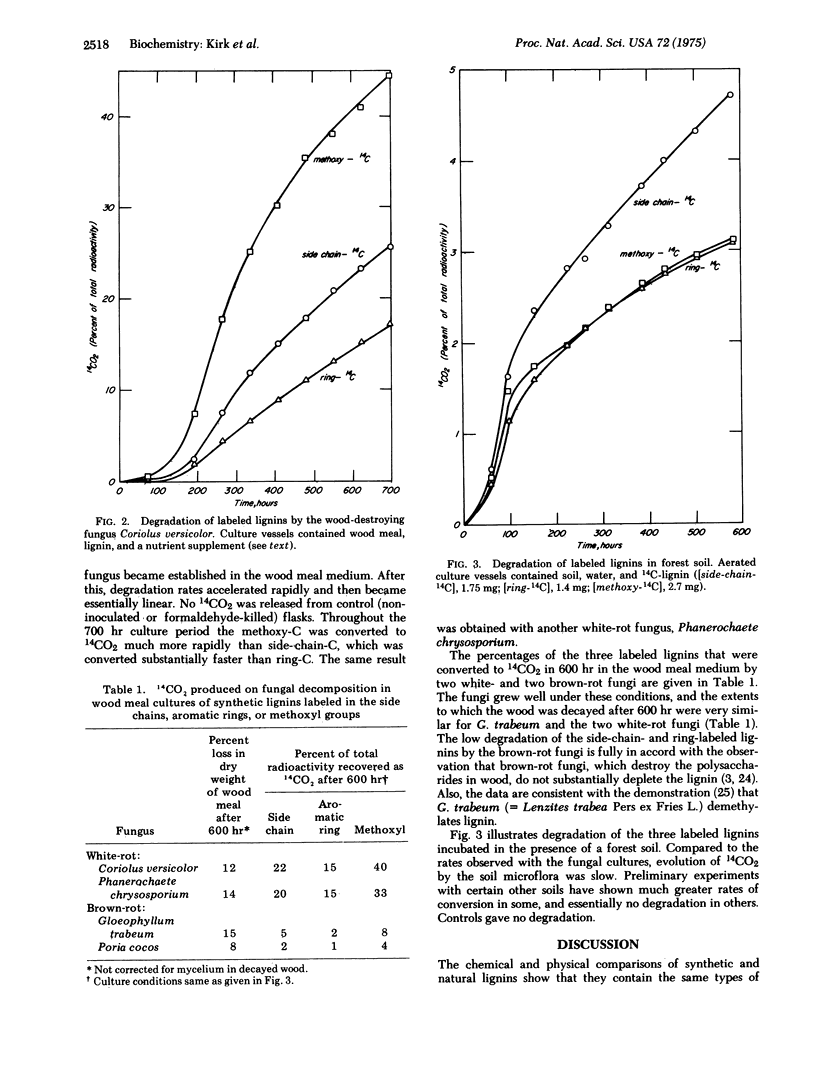

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Fine structure of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum: effect of growth temperature on morphology and ultrastructure. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):461–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.461-467.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


