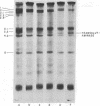
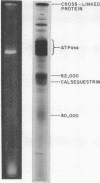
Abstract
Transglutaminase enzymes catalyze for the formation of epsilon(gamma-glutamyl)lysyl crosslinks, or the substitution of a variety of primary amines for the amide function of protein-bound glutaminyl residues. These enzymes should therefore be useful in crosslinking the proteins of membranes and in attaching a variety of chemical probes and labels to these proteins. This usefulness is demonstrated in experiments with the enzyme liver transglutaminase and the membranes with the enzyme liver transglutaminase and the membranes of mouse erythrocytes and of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brewer G. J., Singer S. J. On the disposition of the proteins of the membrane-containing bacteriophage PM2. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3580–3588. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connellan J. M., Chung S. I., Whetzel N. K., Bradley L. M., Folk J. E. Structural properties of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):1093–1098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton A., Adams M., Singer S. J. Bifunctional imidoesters as cross-linking reagents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):730–739. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Chung S. I. Molecular and catalytic properties of transglutaminases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;38:109–191. doi: 10.1002/9780470122839.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Cole P. W. Mechanism of action of guinea pig liver transglutaminase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme: identification of a functional cysteine essential for activity. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 10;241(23):5518–5525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Rule N. G., Ong H. H., Furlanetto R., Jacobsen A., Downey J., Oner N., Bruner-Lorand J. Amine specificity in transpeptidation. Inhibition of fibrin cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1968 Mar;7(3):1214–1223. doi: 10.1021/bi00843a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTONOSI A., FERETOS R. SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM. I. THE UPTAKE OF CA++ BY SARCOPLASMIC RETICULUM FRAGMENTS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:648–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Steers E., Jr Selective solubilization of a protein component of the red cell membrane. Science. 1968 Jan 12;159(3811):203–204. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3811.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum. IV. Solubilization of microsomal adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):71–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Morrison M. Exposed protein on the intact human erythrocyte. Biochemistry. 1971 May 11;10(10):1766–1771. doi: 10.1021/bi00786a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. Cross-linking the major proteins of the isolated erythrocyte membrane. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 14;66(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOFSY L., SINGER S. J. Effects of the amidination reaction on antibody activity and on the physical properties of some proteins. Biochemistry. 1963 Jan-Feb;2:104–116. doi: 10.1021/bi00901a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]