Abstract
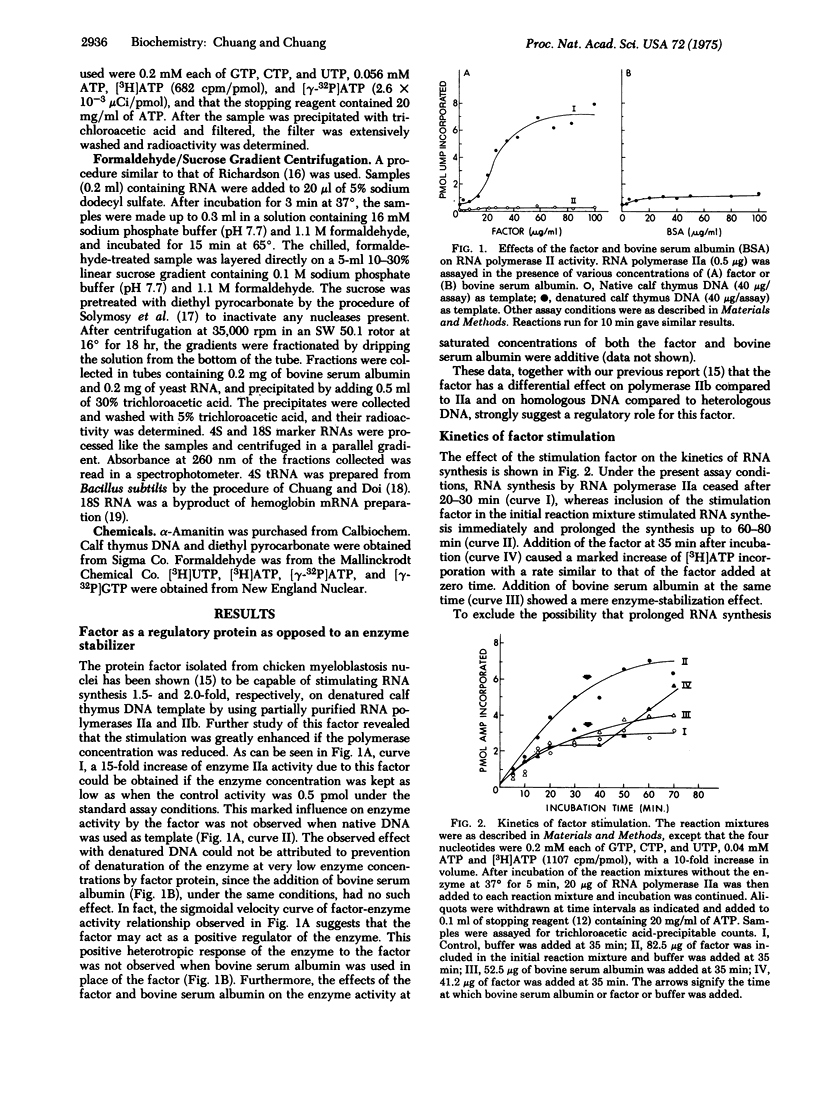
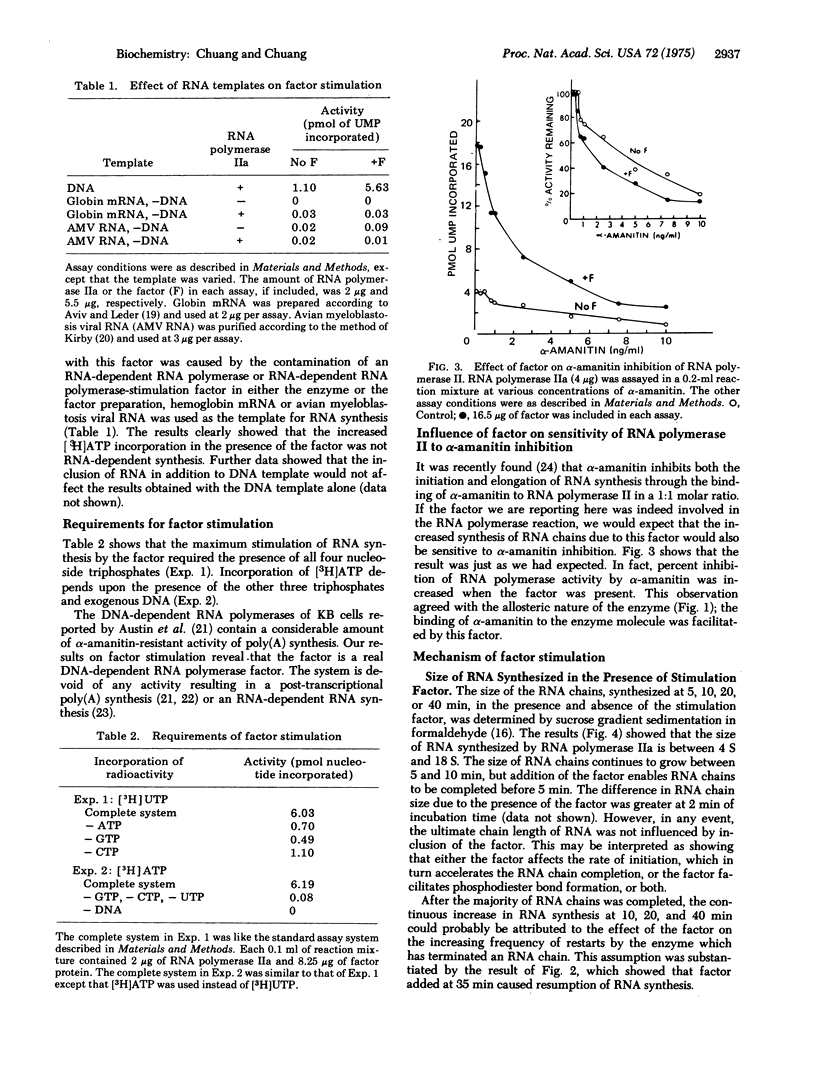
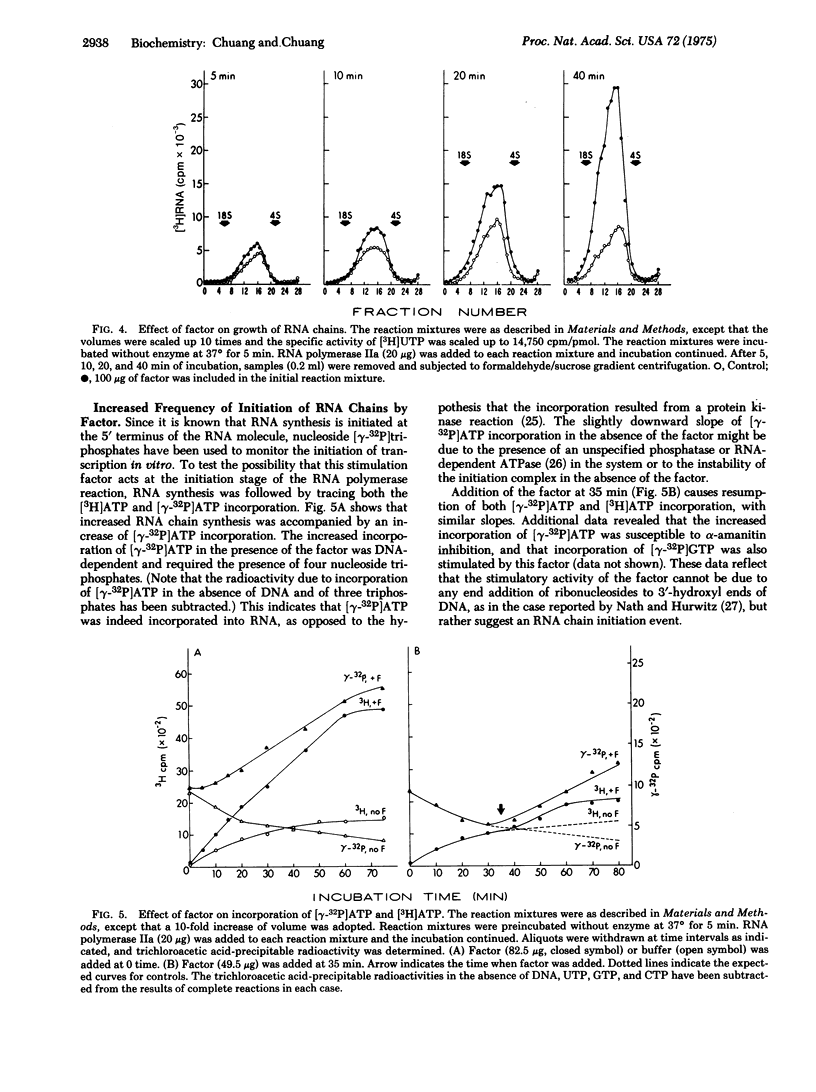
The mechanism of the effect of an RNA polymerase II (RNA nucleotidyltransferase II) stimulation factor isolated from the nuclei of chicken myeloblastosis cells was studied. The stimulation requires the presence of all four nucleoside triphosphates and depends upon an exogenous DNA template. In the absence of the factor, RNA synthesis ceases after 20-30 min, but in the presence of the factor, synthesis continues up to 60-80 min. Addition of the factor at 35 min after incubation causes resumption of RNA synthesis. The factor greatly stimulates the activity of RNA polymerase II at low enzyme concentrations. The RNA polymerase activity is more sensitive to alpha-amanitin inhibition when the factor is present. Experiments of [gamma-32P]ATP incorporation reveal that the factor provides for an increased frequency of initiation of RNA chains, both of the primary initiation events and re-initiation after previous ones were completed. A slightly higher rate of RNA chain growth was also observed with this factor but the ultimate size of RNA synthesized was not affected, as determined by formaldehyde/sucrose gradient centrifugation. These data suggest that the factor functions at the initiation stages of the RNA polymerase reaction.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin G. E., Bello L. J., Furth J. J. DNA dependent RNA polymerase of KB cells. I. Isolation of the enzymes and transcription of viral DNA, mammalian DNA and chromatin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 14;324(4):488–500. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90208-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebee T. J. Incorporation of (gamma32P)ATP by eukaryotic RNA polymerase A. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombik B. M., Baserga R. Increased RNA synthesis in nuclear monolayers of WI-38 cells stimulated to proliferate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. The selectivity of transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):721–775. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang R. Y., Chuang L. F., Laszio J. Isolation and characterization of nuclear RNA polymerase II from chicken myeloblastosis cells. Cancer Res. 1975 Mar;35(3):687–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang R. Y., Doi R. H. Characterization of lysine transfer ribonucleic acid from vegetative cells and spores of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3476–3484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang R., Chuang L., Laszlo J. A new eukaryotic RNA polymerase factor: a factor from chicken myeloblastosis cells which stimulates transcription of denatured DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1231–1239. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90828-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet-Meilhac M., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. 11. Mechanism of the inhibition of RNA polymerases B by amatoxins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 27;353(2):160–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Philipson L., Wall R., Adesnik M. Polyadenylic acid sequences: role in conversion of nuclear RNA into messenger RNA. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):507–510. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Bonner J. Ascites tumor ribonucleic acid polymerases. Isolation, purification, and factor stimulation. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 31;12(16):3064–3071. doi: 10.1021/bi00740a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashinakagawa T., Onishi T., Muramatsu M. A factor stimulating the transcription by nucleolar RNA polymerase in the nucleolus of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 21;48(4):937–944. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90699-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., Dahmus M. E. Stimulation of eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerase by protein factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1383–1387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentfer D., Lezius A. G. Mouse-myeloma RNA polymerase B. Template specificities and the role of a transcription-stimulating factor. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct;30(2):278–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R. In vitro transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:409–446. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowery-Goldhammer C., Richardson J. P. An RNA-dependent nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase (ATPase) associated with rho termination factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2003–2007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller K., Bremer H. Heterogeneous initiation and termination of enzymically synthesized ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jul 14;43(1):89–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K., Hurwitz J. Covalent attachment of ribonucleotides at 3'-hydroxyl ends of deoxyribonucleic acid catalyzed by deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2605–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Rates of bacteriophage T4 RNA chain growth in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 14;49(1):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G. Multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in Xenopus laevis. Levels of activity during oocyte and embryonic development. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):249–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lawrence C., Thach R. E., Roeder R. G. Encephalomyocarditis virus infection of mouse plasmacytoma cells. II. Effect on host RNA synthesis and RNA polymerases. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.611-619.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solymosy F., Fedorcsák I., Gulyás A., Farkas G. L., Ehrenberg L. A new method based on the use of diethyl pyrocarbonate as a nuclease inhibitor for the extraction of undegraded nucleic acid from plant tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Sep 24;5(4):520–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman S., Pace N. R., Mills D. R., Levisohn R., Eikhom T. S., Taylor M. M., Peterson R. L., Bishop D. H. The mechanism of RNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:101–124. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Keller W. Mammalian deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases. I. Purification and properties of an -amanitin-sensitive ribonucleic acid polymerase and stimulatory factors from HeLa and KB cells. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3777–3788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu F. L., Feigelson P. Cortisone stimulation of nucleolar RNA polymerase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2177–2180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



