Abstract
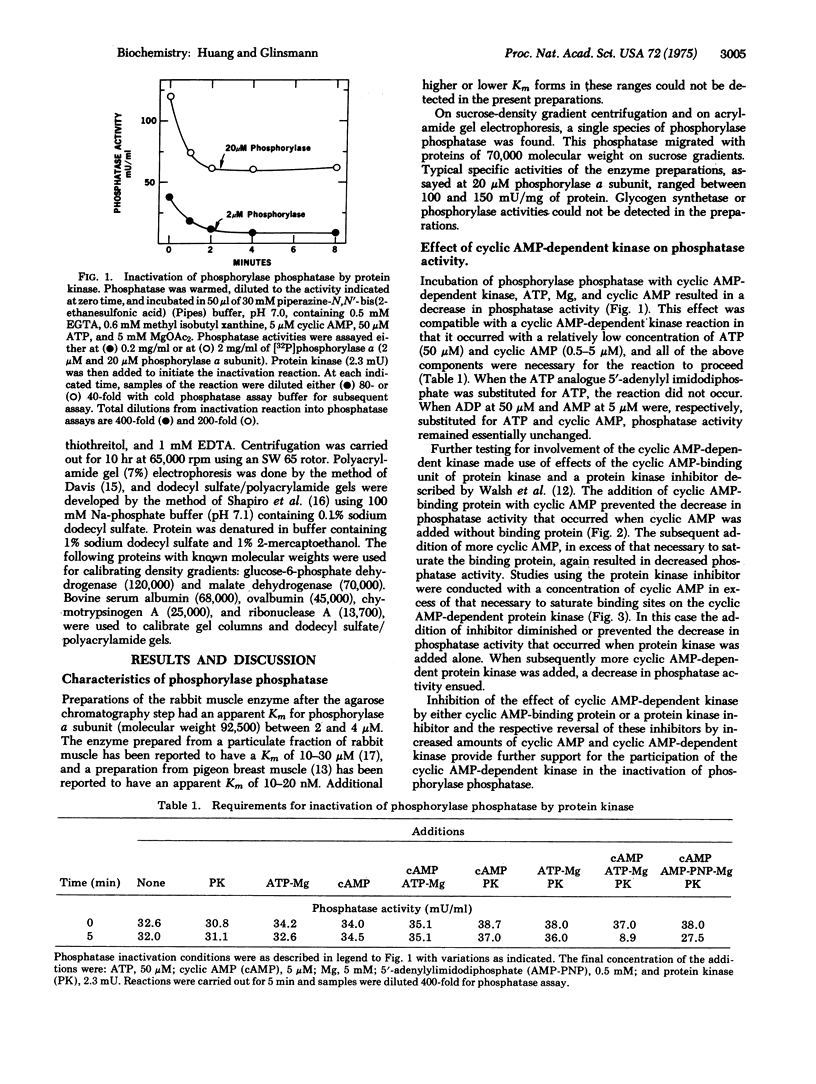
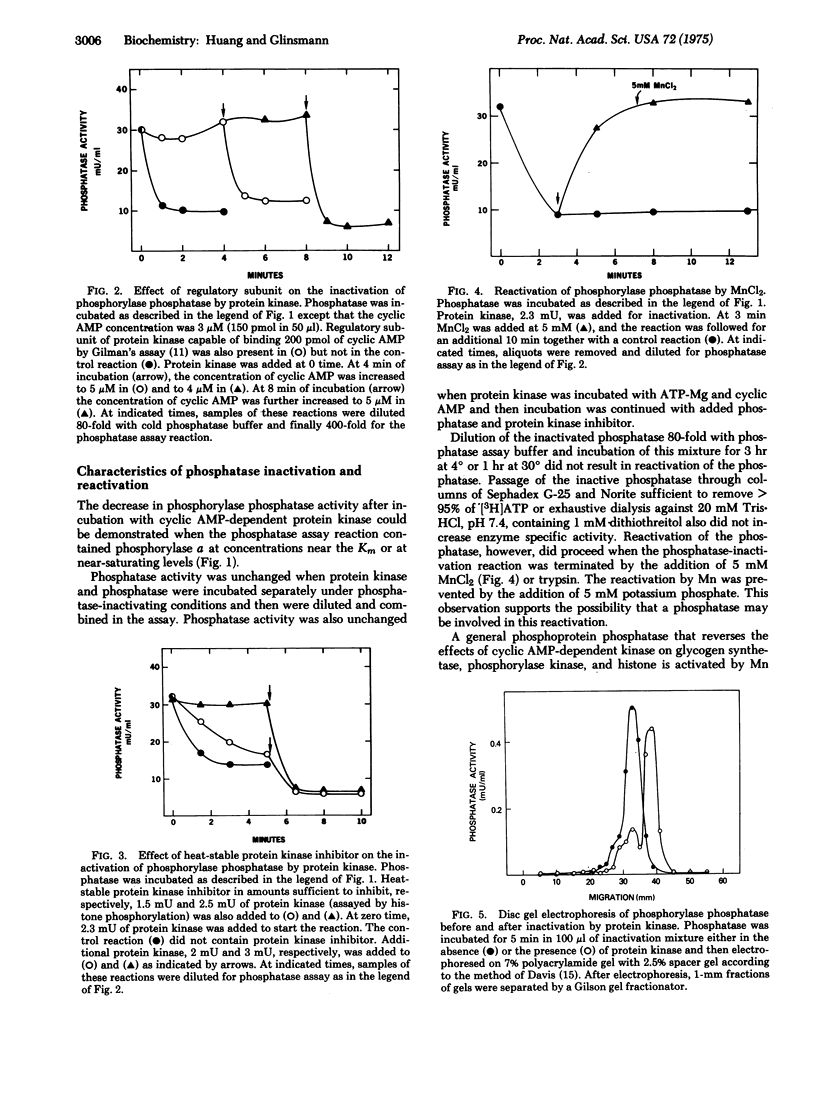
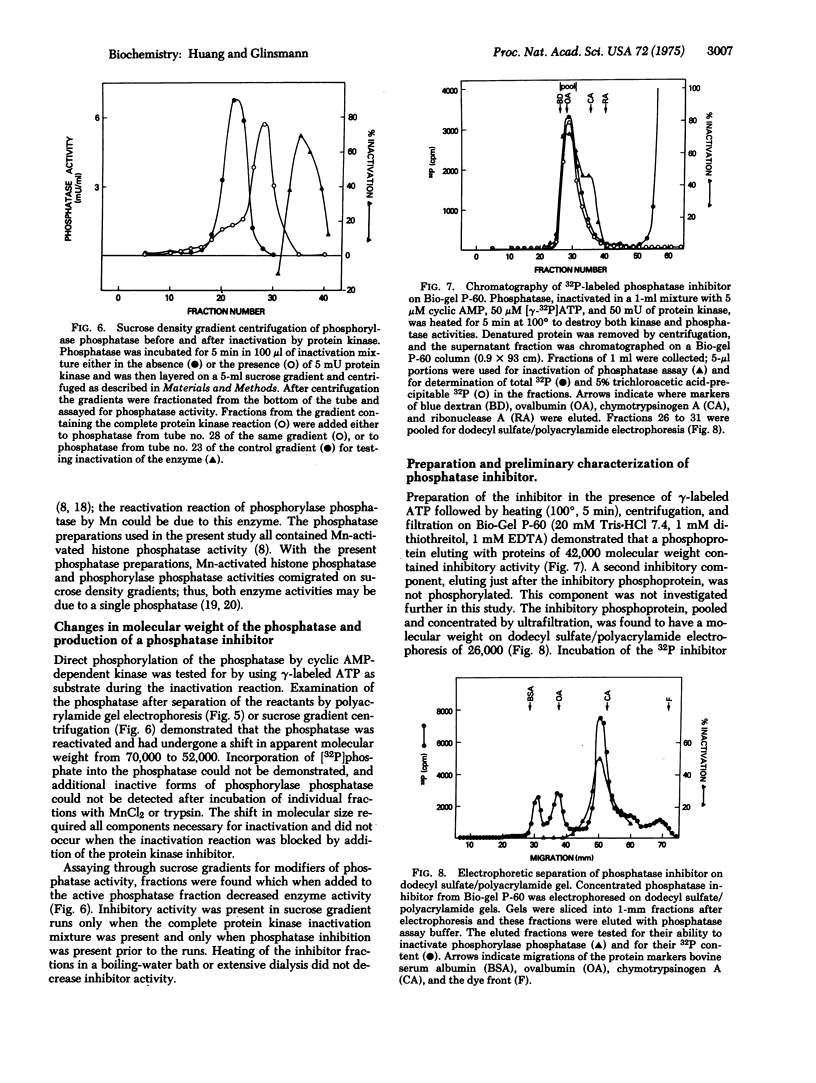
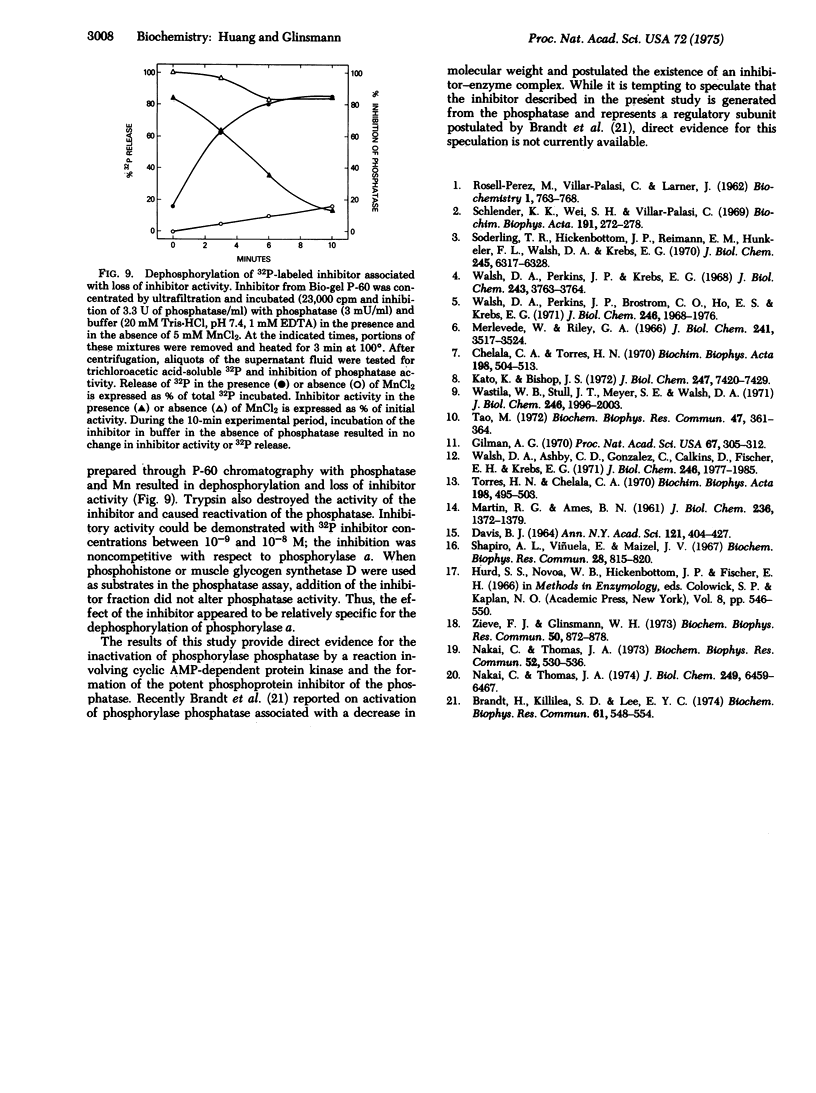
Partially purified rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.17; phosphoprotein phosphohydrolase) was inactivated when it was incubated with exogenous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.1.37; ATP:protein phosphotransferase), cyclic AMP, and ATP-Mg. Subsequent separation of the phosphatase by acrylamide gel electrophoresis or sucrose density centrifugation resulted in reactivation of the enzyme. The phosphatase decreased in molecular weight from approximately 70,000 to 52,000, and a phosphorylated inhibitor with molecular weight of 26,000 was found. Reactivation of phosphatase also occurred when it was incubated with MnCl2 or trypsin. The inhibitor was effective at less than 10(-8) M and was relatively heat stable. Its activity was destroyed by tryptic digestion and by dephosphorylation by a Mn-stimulated phosphatase. These observations support the possibility that phosphorylase phosphatase activity is controlled by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and a Mn-stimulated phosphatase by a reaction involving phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of a protein phosphatase inhibitor.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chelala C. A., Torres H. N. Regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase phosphatase activity. II. Interconversions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 18;198(3):504–513. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Bishop J. S. Glycogen synthetase-D phosphatase. I. Some new properties of the partially purified enzyme from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7420–7429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlevede W., Riley G. A. The activation and inactivation of phosphorylase phosphatase from bovine adrenal cortex. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3517–3524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai C., Thomas J. A. Properties of a phosphoprotein phosphatase from bovine heart with activity on glycogen synthase, phosphorylase, and histone. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 25;249(20):6459–6467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai C., Thomas J. A. Substrate specificity of glycogen synthase phosphatase from bovine heart: action on phosphorylase a and histone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):530–536. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90744-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSELL-PEREZ M., VILLAR-PALASI C., LARNER J. Studies on UDPG-glycogen transglucosylase. I. Preparation and differentiation of two activities of UDPG-glycogen transglucosylase from rat skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:763–768. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlender K. K., Wei S. H., Villar-Palasi C. UDP-glucose:glycogen alpha-4-glucosyltransferase I kinase activity of purified muscle protein kinase. Cyclic nucleotide specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 4;191(2):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90246-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R., Hickenbottom J. P., Reimann E. M., Hunkeler F. L., Walsh D. A., Krebs E. G. Inactivation of glycogen synthetase and activation of phosphorylase kinase by muscle adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 10;245(23):6317–6328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M. Rabbit red cell cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. I. Reversible subunit interaction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Apr 28;47(2):361–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90721-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres H. N., Chelala C. A. Regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase phosphatase activity. I. Kinetic properties of the active and inactive forms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 18;198(3):495–503. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Ashby C. D., Gonzalez C., Calkins D., Fischer E. H. Krebs EG: Purification and characterization of a protein inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1977–1985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Brosom C. O., Ho E. S., Kreb E. G. Catlysis of the phosphrylaseinase actition reaction. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1968–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh D. A., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. An adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependant protein kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3763–3765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wastila W. B., Stull J. T., Mayer S. E., Walsh D. A. Measurement of cyclic 3',5'-denosine monophosphate by the activation of skeletal muscle protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1996–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve F. J., Glinsmann W. H. Activation of glycogen synthetase and inactivation of phosphorylase kinase by the same phosphoprotein phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 5;50(3):872–878. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



