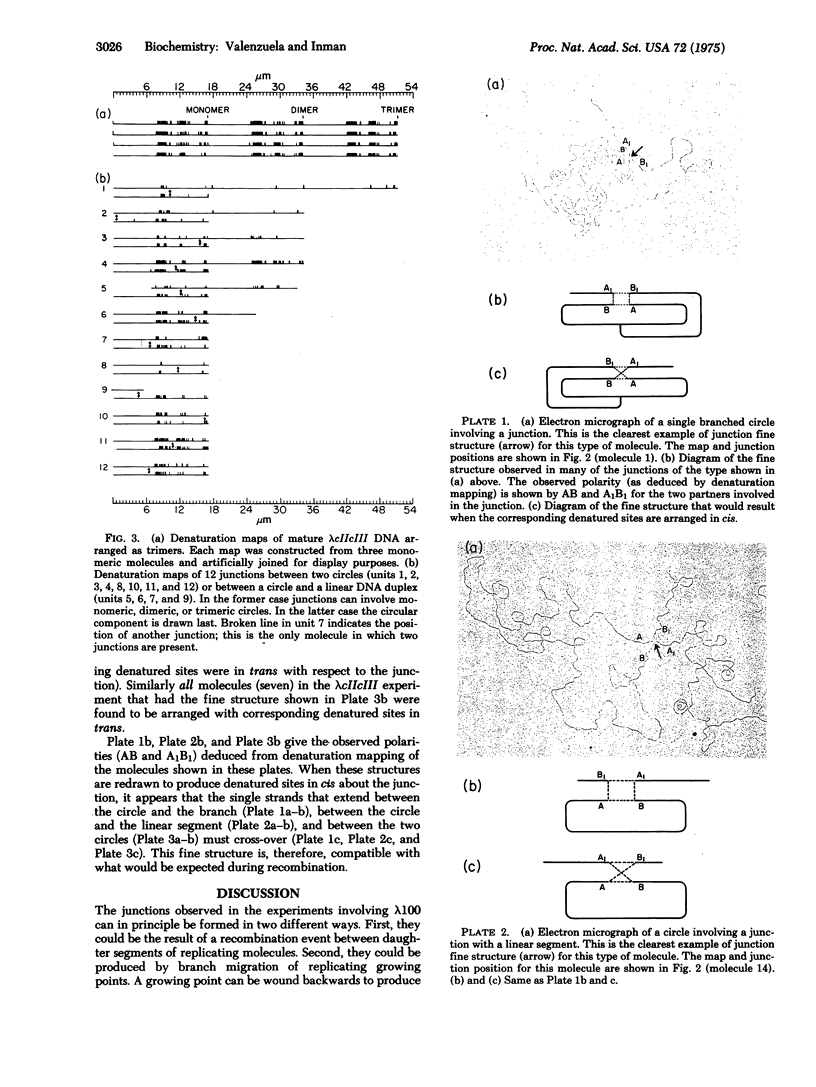
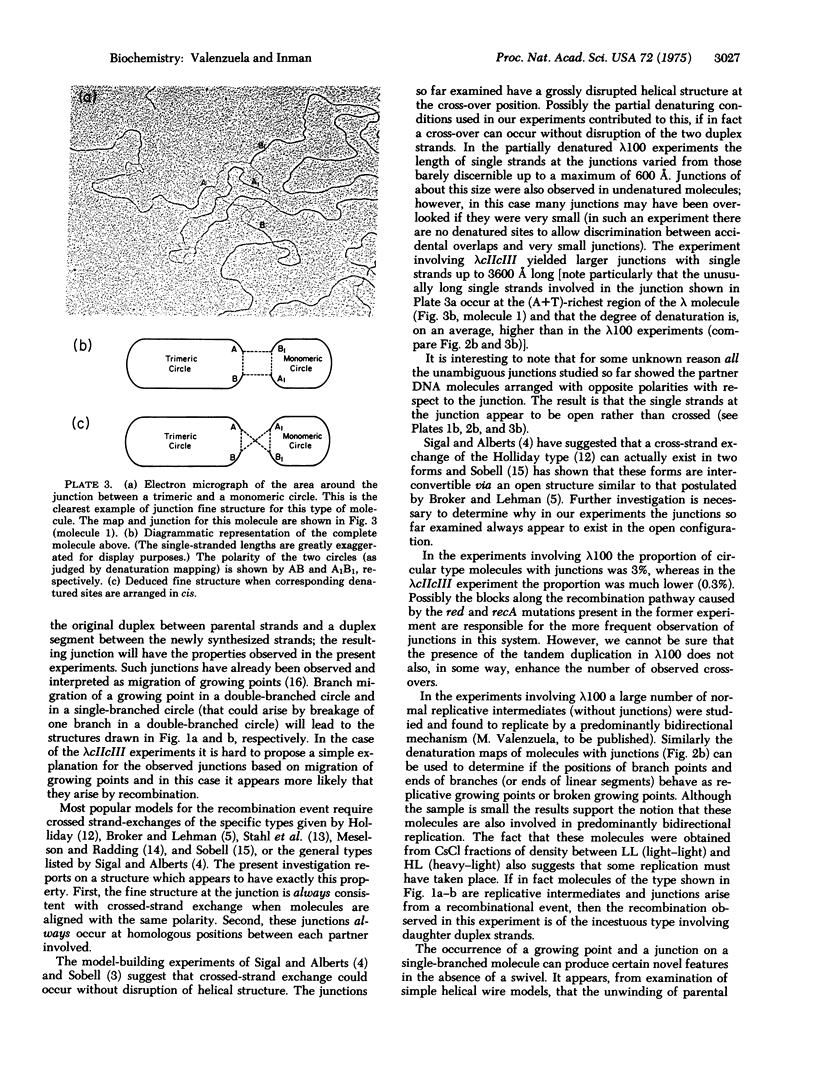
Abstract
At early times after infection of a recA derivative of Escherichia coli with lambdab221c126red270a42 phage, a low but significant proportion of intracellular lambda molecules show a novel junction. These junctions are also present, although in reduced numbers, in a lysate obtained at late times after infection of a recA+ host with lambdacIIcIII phage. Fine structure and denaturation mapping analyses showed that these junctions occur at homologous positions and that they are compatible with the occurrence of a cross-strand exchange between lambda DNA duplexes similar to the type proposed in most molecular models for genetic recombination. However, the results are also consistent with the structures expected if a replicating growing point undergoes branch migration.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broker T. R., Lehman I. R. Branched DNA molecules: intermediates in T4 recombination. J Mol Biol. 1971 Aug 28;60(1):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90453-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Inman R. B. Origin and direction of replication of bacteriophage 186 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1768–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W. Bacteriophage lambda derivatives carrying two copies of the cohesive end site. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):511–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W., Thomas J. O. Tandem genetic duplications in phage lambda. IV. The locations of spontaneously arising tandem duplications. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):147–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss R. D. Models of genetic recombination. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):445–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto L., Kasamatsu H., Pikó L., Vinograd J. Mitochondrial DNA replication in sea urchin oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Oct;63(1):146–159. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M. S., Radding C. M. A general model for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):358–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N., Alberts B. Genetic recombination: the nature of a crossed strand-exchange between two homologous DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):789–793. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. Molecular mechanism for genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2483–2487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobell H. M. Symmetry in protein-nucleic acid interaction and its genetic implications. Adv Genet. 1973;17:411–490. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60175-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





